![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CSR in USA (development) |
1920s - Corporate Indiv Corporate Practices 1920s? - Political Tax incentives, cultural norms 1953; 1960s - Academic Responsibilities of Businessman
In many ways, the home of CSR |
|
|
CSR in Europe (Development) |
1996 - Corporate Launch of 'CSR Europe' 2001 - Political Green Paper CSR by EU Commission 2002 - Academic European Academy of Business Society |
|
|
Two institutional Approaches |
1. Historically Embedded 2. New ways of doing mngmt across borders
|
|
|
Two Types of Institutions |
1. Body/Legislature/Court (Politics/lawyers) 2. Patterned Behaviour (idea or expectation about behaviour) -- an org would help to shape this, but you don't need it. It could be socially/economically driven
The "bodies" are more important in Europe |
|
|
CSR in America |
-Self perception, more likely to report -Mainly outside business processes -Skepticism about govt -broad philanthropy -USA has to create its own welfare economy -CSR is "part of core values"
--wider shareholder spread and activism |
|
|
CSR in UK |
Combined education/quality of life/arts + environmental issues with production processes
-CSR is "performance driven" - has had a comparatively large public sector & welfare state
-- wider shareholder spread and activism |
|
|
US tax incentives for: |
Business/general philanthropy foundations employee health; retirement; sickness insurance |
|
|
CSR implicit and explicit graph |
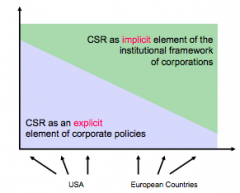
|
|
|
Explicit CSR |
(Matten and Moon) -Corporations assume responsibility in society -Voluntary corp. policies/programs/strategies -Motivated by: perceived expectations of all stakeholders of corporation |
|
|
Implicit CSR |
(Matten and Moon) -Formal institutions assume responsibility -Values/norms/rules which result in req'mts for corporations -Motivated by: societal consensus on legitimate expectations toward role/contribution of all major groups in society |
|
|
CSR as a dual construct |
**all companies have a bit of implicit and explicit**
explicit --> implicit implicit --> explicit (when companies want to reach new standards) |
|
|
NBS approach to implicit CSR |
say what?
|
|
|
Implicit CSR and European National Business Systems |
-Stronger role of state -minor role of capital markets -highly regulated markets for labour -powerful position of trade unions
|
|
|
Explicit CSR and Neo-Institutionalism |
business institutions = "organizational fields" -- other people in industry influence --> independent of nationality
--> explains diffusion of management concepts beyond national or industrial borders |
|
|
3 ways to legitimize management practices
|
1. Coercive Isomorphisms 2. Mimetic Processes 3. Normative Pressures
--> These are the three reasons for more explicit CSR (above national level) |
|
|
Coercive Isomorphisms |
External rules/laws/demands/expectations/norms
- to be respected to avoid sanctions or loss of trust |
|
|
Mimetic Processes |
Complex technologies, goal ambiguities cause managers to just implement "best practices"
--> don't want to be singled out as irresponsible |
|
|
Normative Pressures |
Professionalization of mngmt by increasing certification for global networks, esp. in context of profess/educ/industry associations
--> what's good, what ought to happen |
|
|
Explicit CSR in Europe - CIs |
-Standardization of the EU -Industrial Metastandards -Global NGOs sanction corporations -Role of global investors -Cutback of welfare state -Corporations in privatized public sector
|
|
|
Explicit CSR in Europe - MPs |
-Adoption of American management processes by European companies -Leading role of American MNCs in CSR in Europe (Codes of conduct, social accounting, philanthropy) |
|
|
Explicit CSR in Europe - NPs |
-increase of CSR in mngmt education -Emergence of CSR proff networks and industry associations -CSR as civil society focus |
|
|
Features of European explicit CSR |
-role of regulating/govt bodies -multi-stakeholder approach -Corp involvement in regulatory process -dominant role of ecological issues -marginal philanthropy -mainly secular approach |
|
|
Implications of the framework |
1. Descriptive - your CSR may not be effective in a different context (institutional/national) 2. Instrumental - CSR has to be adopted to specific institutional/national environment 3. Normative - revisiting core assumptions of anglo-amer csr debate
Explicit CSR as preferable way to allocate social resources |
|
|
What can explicit CSR address? |
The limits to the "rules" -rules create complacency to 'check' the boxes, rather than effectively addressing CSR
|
|
|
Why was CSR not discussed in before? |
- did not use the label of CSR - practised -- often reluctantly -- as part of membership of the wider institutional framework of business/society |
|
|
Why has CSR become an explicit issue? |
-Globalization confronts Eur. MNCs with contexts which institutionalize CSR differently from their home country
-Changes in the 'organizational field' of companies popularize CSR as management idea |
|
|
blank |
blank |

