![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
• Explain the roles of antibodies in immunity
[LO] |
1. Binding - binding and identifying Ag and foreign substances
2. recruitment and activation of effector molecules to eliminate antibody bathed material |
|
|
Name each of the antibody classes and their role in immunity [LO]
|
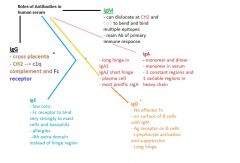
|
|
|
Draw a diagram of each of the antibody classes and be able to
identify: • The heavy and light chains • Domains • Hinge region • Presence of J chain [LO] |
![[LO]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/55/97/93/2559793_m.jpg)
[LO]
|
|
|
Know the relative concentrations of the Ig classes in serum and secretions [LO]
|
![[LO]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/56/18/24/2561824_m.jpg)
[LO]
|
|
|
Explain how antibodies attach to antigens and Fc receptors [LO]
|
[LO]
IgG antibodies are Y-shaped protein structures made up of different regions. The two arms of the Y are known as Fab regions, where Fab stands for fragment, antigen-binding. Fc is the tail region, with Fc standing for fraction, crystallizable. Fab regions attach to antigens while the Fc region binds to Fc receptors on the surface of a cell. |
|
|
What role do antibodies and Fc receptors play in immunity? [LO]
|
Binding of antibody via Fc receptors activates other cells to
up- or down-regulate immune response |
|
|
What is the approximate weight of an Ab?
|
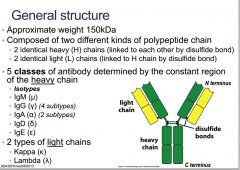
150kDa
|
|
|
What are the two different kinds of polypeptide chain that create an Ab?
|
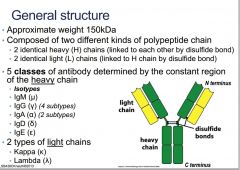
heavy and light chains
|
|
|
What bond unites the heavy chains?
|
disulfide bonds
|
|
|
What are the light chains bonded to?
|
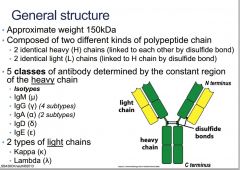
identicle L chains are linked to the H chain by the disulfide bond
|
|
|
What are the 5 classes of antibody determined by the constant region of the heavy chain?
|

|
|
|
What are the two types of light chain?
|

|
|
|
Draw and identify the antigen binding site on an igG
|

|
|
|
Locate the disufide bonds on your diagram of an IgG
|

|
|
|
What is the Fab site?
|
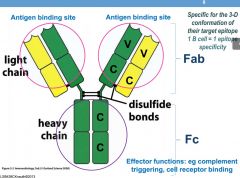
Antigen binding site
|
|
|
What is an Fc site?
|
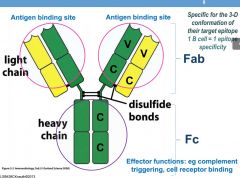
effector functions - complement triggering, cell receptor binding
|
|
|
Describe light chain configuration
|

|
|
|
Describe heavy chain configurations
|
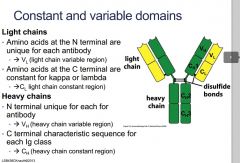
|
|
|
Describe AbAg binding in the Fab section
|

16 aa contact 16aa in Ag
|
|
|
Describe the hinge function and morphology
|

|
|
|
Describe the domain functions of CL
|

|
|
|
Describe the domain fn of CH1
|

|
|
|
Describe the domain function of CH2
|

|
|
|
Describe the domain function of Ch3
|

|
|
|
Describe hypervariable regions
|

|
|
|
What are the amino acid positions of hypervariable regions?
|

|
|
|
What are CDRs
|
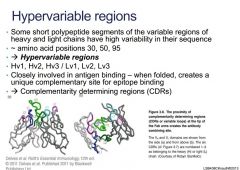
Complementarity determining regions
|
|
|
How long is the light chain in IgG?
|
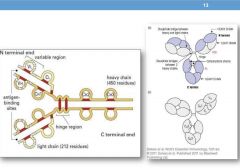
212
|
|
|
How long is the heavy chain in IgG?
|
450
|
|
|
describe how one can attain pepsin and other fragments
|

|
|
|
What is the valency of IgG?
|
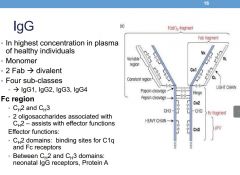
divalent -> 2
|
|
|
How many subclasses exist for IgG?
|
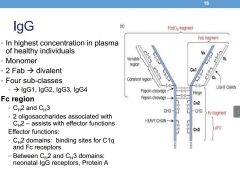
1,2,3,4
|
|
|
Describe the Fc region of an IgG
|

|
|
|
What can IgG4 do that other IgG subclasses cannot
|
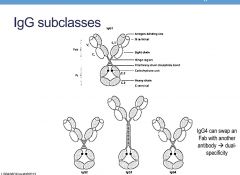
|
|
|
Describe IgM
|

|
|
|
Which Ig is a pentameter?
|

|
|
|
Describe IgM heavy chains
|

|
|
|
dEscribe location and bonding of J chain
|

|
|
|
Describe formational capabilities of IgM molecule
|

|
|
|
Which Ig can bind complement
|

|
|
|
What is the main Ab of primary immune response?
|
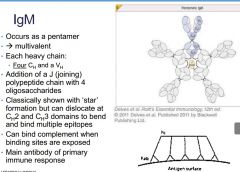
|
|
|
Describe IgA molecule with diagram
|

|
|
|
What are the relative concentrations of each of the Ig classes in serum?
|

|

