![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define an autoregression |
An autoregression is where both the dependent and the independent variables are from the same stochastic process |
|
|
By repeating a substitution of lagged variables in an AR(1) what is the outcome? |
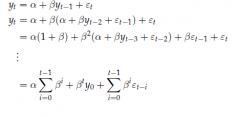
|
|
|
What are the unconditional means and variance of an AR process |

|
|
|
Describe Autocovariance and derive it |

|
|
|
Derive Autocorrelation and explain it's meaning |

Therefore Autocorrelation is a decaying process. The smaller the persistence parameter the faster it decays |
|
|
Derive R^2 and adj R^2 |
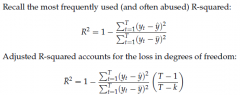
|
|
|
What are the two substitutes instead of R^2 to measure goodness of fit? |
|
|
|
Derive both AIC and SIC |
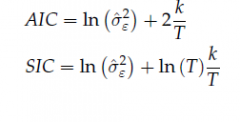
|
|
|
What are the key points about information criterion |
|
|
|
What is the optimal lag length |
STEPS
|
|
|
Explain Integration in a TSD sense |
A weakly dependent process is said to be integrated of order 0. Any or I(p) can be made to be weakly dependent and covariant stationary as an extension, by differencing p times. Otherwise put as having p unit roots. In economics integrated process of order 0,1 and 2 are most common. |
|
|
Explain the unit root testing process. Both in terms of the persistence parameter and the differenced persisten parameter. |
Unit root testing tests for random walk. As previously discussed, unit root makes inferencing impossible. The testing is based on the null that unit root exists i.e b = 1. and the alternative is unit root doesn't exist i.e b < 1. This is a one sided test because should b>1 it is determined an explosive process and we find the same issues as before. Another form of this test requires first order differencing. The null is then changed from unit root to 0. This is mostly done for convenience, i.e gamma = 0 and the alternative is the one sided gamma < 0. However under the null the model becomes integrated of order 1 meaning the usually t statistics are no longer applicable. |
|
|
Explain Dickey Fuller distribution |
The asymptotic distribution of the t statistic under unit root test's null is called the Dickey Fuller distribution. |
|
|
Describe simply what a Dickey Fuller test is |
Firstly, conducting a regular testing process to procure a tstatistic. Then using a Dickey Fuller distribution to tabulate the correct critical values. conduct the rejction as you would any other one sided t-distribution. |
|
|
Name one major risk of a model being perceived to have unit root - a stochastic trend. |
Although a trend may appear stochastic, deterministic trend may still exist. As such it can be dealt with as any other deterministic trend, by incorporating a trend variable. However this leads to its own distribution as well Dickey Fuller - case 2 |
|
|
What is the Augmented Dickey Fuller test? |
The Dickey Fuller test is based on the assumption that error is white noise - mean 0 and constant variance, furthermore that it is uncorrelated with all past error terms. In order to account for this run the DF test on an augmented AR(p) model. Distributions are not affected and thus regular properties may be used. |

