![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How is D-Dimer used in the diagnostic algorhythm for PE?
|
The utility of D-Dimer is that LOW pretest probability + LOW D-dimer = NO PE.
PE Algorhythm: Determine Wells Score: • <= 4 equals low prob • > 4 equals high prob • Low prob + Neg D-dimer = no PE • Low prob + high D-dimer --> CT chest • High probability Wells --> CT Chest • Neg chest CT = no PE • Pos chest CT = PE Note: there is no role for D-dimer testing in pts with high probability PE. Go straight to CT! |
|
|
What are the indication for a Greenfield Filter in pts w/ DVT?
|
Proximal LE DVT +:
• Contraindication to drug tx • Urgent surgery rqd that precludes anti-coagulation • Medical tx failure |
|
|
What is a 'silent' aortic dissection?
Presentation? |
A painless presentation of thoracic aortic dissection
Pt presents w/ only ischemic or neurologic sx that may appear to be a CVA, MI, or peripheral vascular issue. Be aware of this presentation! Thrombolytics (for suspected AMI, etc) would be DEVASTATING. |
|
|
What is the INITIAL treatment of thoracic aortic dissection?
|
MEDICAL tx to control the forces of propagation: BP, HR, rate of rise of aortic pulse pressure.
ß-Blockers (IV) -- titrate to HR 60-80 (esmolol is short acting and easily titratable as a drip) Nipride -- titrate to SP 100 - 120 Note: An alternative to ß-Bl and nipride is to use IV LABETALOL as a single agent. Note: If suspicion is high for TAD, begin tx immediately; do not wait for confirmatory study results! |
|
|
What is the management of thoracic aortic dissection based on location?
|
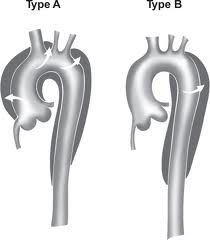
Type A -- immediate surgery
Type B -- medical management unless complications are present |
|
|
What is the most common cause of death in PE pts (other than massive embolization)?
|
Progressive right ventricular failure
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of subclavian and axillary vein DVT?
Next most common cause? What is the risk of PE from an upper extremity DVT? |
Most common:
• SUBCLAVIAN CATHETER Also: • EFFORT thrombosis (ie, strenous activity in a young person) Risk of PE -- 15% |
|
|
What is the most common symptom seen in pulmonary embolism?
What is the most EKG abnormality? |
Most common sx -- DYSPNEA
Most common EKG abnormality -- SINUS TACHYCARDIA |
|
|
What is the relative incidence of AAA vs TAD?
|
TAD > AAA by 2:1
|
|
|
What is the relative prevalence of ascending vs descending TADs?
|
60% of TADs are DESCENDING
|
|
|
What is the role of aggressive lowering of BP in a hypertensive pt with RUPTURED AAA?
|
There is NO EVIDENCE that aggressive lowering of BP is helpful, and it may predispose to unnecessary HoTN
|
|
|
What is the thrombolytic agent of choice in the tx of PE? Why?
|
TPA
Preferred b/c: • Significant improvement in hemodynamic parameters in < 2 hrs • Lower risk of bleeding b/c it is given over 2 hrs Note: Streptokinase is also approved for the tx of PE |
|
|
What is the treatment protocol for hypertensive emergency + aortic dissection?
|
Drugs of choice:
• IV ß-blocker (esmolol, propranolol) + • IV Nipride Give ß-blocker first to minimize reflex tachycardia associated w/ Nipride Other agents: • Labetolol IV |
|
|
What is the treatment protocol of ISOLATED CALF DVT?
|
Tx is controversial even though isolated calf thrombi do propagate and embolize.
If an isolated calf DVT is detected, the pt should be anticoagulated and, if the tibial veins are involved, tx'd as a proximal DVT. |
|
|
What is the untreated mortality rate of thoracic aortic dissection?
|
33% w/in 24 hrs
50% w/in 48 hrs >75% w/in 2 wks 90% w/in 1-3 mos |
|
|
What is Virchow's triad?
What is its significance? |
1) Statis (venous)
2) Hypercoagulability 3) Endothelial damage 'SHE' Virchow's triad are risk factors for DVT/ PE |
|
|
What non-aortic aneurism is often seen concommitantly with AAA?
|
POPLITEAL artery aneurism
Popliteal artery aneurisms are the most common non-aortic aneurism |
|
|
What percent of elderly adults have an AAA?
What percent are palpable? |
Prevalence -- 2% of elderly
Palpable -- 77-90% |
|
|
What percent of Marfan's patients develop thoracic aortic dissection?
|
50% (although only 10% of all dissections are due to Marfan's)
|
|
|
What percent of TAD pts are under the age of 50?
Why? |
20%
Why: • MARFANS • Pregnancy • Turner's |
|
|
In pts with thoracic aortic dissection, what is the mechanism of disparate BP readings in left and right upper extremities?
How often is this seen in aortic dissection? |
Mechanism -- Unilateral extension of the dissection into the subclavian artery.
Occurs in a MINORITY of cases of TAD. |
|
|
In which medical conditions other than thrombosis can the D-Dimer test be positive?
|
• AMI
• CVA • Trauma • Post-op • Elderly • Pregnancy |
|
|
Other than chest pain, what organ-based sxs do pts with thoracic aortic dissection present with?
|
Neuro:
• CVA-like sx • Visual changes • Syncope • Acute paraplegia Vascular: • Cold, PULSELESS extremity • AMI (if coronary ostia involved) GI -- MESENTERIC ISCHEMIA GU: • Flank pain • Hematuria |
|
|
State the 2 major thoracic aortic dissection classification systems
|
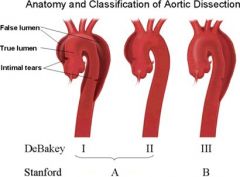
• Debakey Type I (MOST COMMON) -- Ascending and descending aorta
• Debakey Type II -- Ascending only • Debakey Type IIIA -- Descending only (entirely above diaphragm) • Debakey Type IIIB -- Descending only (dissection traverses diaphragm) • Stanford Type A -- Ascending only (Debakey I and II) Stanford Type B -- Decending only (Debakey Type III) |
|
|
State the risk factors for AAA
|
• Advanced age
• Male • FHx • Smoker • HTN • CAD • PVD • Hypercholesterolemia |
|
|
State the specific complications associated with:
• TPA • SK • APSAC What complication is common to all thrombolytics? |
TPA: cerebral hemorrhage
SK: HoTN, allergic phenomena APSAC: HoTN, allergic phenomena Reperfusion dysrhythmias are common to all thrombolytics (incidence > 50%) |
|
|
What anatomical landmark is used to distinguish ascending from descending dissecting TADs?
|
Distal to the LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY = desecending
|
|
|
What are the clinical findings of thoracic aortic dissection?
• BP • Skin • Pulses • Murmur |
BP:
• Ascending aorta: Nl or decreased • Descending: Increased • 20 mm difference in arms Cool, clammy skin despite elevated BP Unequal or absent pulses (hallmark of dissection) Aortic insufficiency murmur (w/ Type A) Cardiac tamponade (Type A) |
|
|
What are the current indications for thrombolytics in the setting of PE? What med should be given immediately following administration of thrombolytics?
|
• Hemodynamic instability w/ confirmed PE
• Hemodynamic instability in pts w/ strong clinical suspicion of PE, and RV dysfxn by echo • Stable pts with RV DYSFXN and confirmed PE Give full dose HEPARIN immediately following thrombolytics. |
|
|
What are the CXR radiographic signs of PE?
|
Hampton's Hump -- a triangular pleural-based density with a rounded apex that points toward the hilum
Westermark's Sign -- Dilation of the pulmonary vessels proximal to the embolus, with oligemia distally Elevated hemidiaphragm |
|
|
What are the EKG findings in PE?
|
Evidence of Right heart strain:
• P pulmonale (peaked P in lead II) • LAD or RAD • S1Q3T3 • Afib • RBBB |
|
|
What are the indications for thrombolytics in pts with DVT?
|
UNCLEAR!
Thrombolytics are usually reserved for: • < 60 yo w/ massive or limb-threatening iliofemoral thrombosis • Upper extremity DVT w/ sx for < 1 wk and low risk of bleeding |
|
|
What are the physical exam findings in AAA?
|
Pulsative mass in epigastric area (seen in 77% of pts w/ ruptured AAA)
Abdominal or femoral BRUITS Distal extremity ischemia |
|
|
What are the risk factors for thoracic aortic dissection?
|
• HTN (most common)
• Cocaine/ Methamphetamine use (causes HTN ) • Connective tissue dz (Marfans, Ehlers-Danlos, SLE, Giant cell arteritis) • AORTIC VALVE STENOSIS (congenital bicuspid aortic valve) • Pregnancy (3rd trimester) • Turner's syndrome • Tobacco |
|
|
What are the sx of rupturing AAA?
|
Classic sx:
• SUDDEN onset of severe abd/ back/ flank pain • +/- Syncopy (from hemorrhage) Flank Pain: • Usually LEFT side • W/ hematuria Abd Pain: • LLQ w/ heme + stool Ecchymoses, 2° to bleeding: • On abd wall, flank, scrotum, perineum Femoral Neuropathy: • From femoral nerve compression due to hematoma |
|
|
What are the Well's Criteria for PE?
|
• Suspected PE
• Alternative dx less likely than PE • Pulse > 100 • H/o hemoptysis • H/o malignancy • H/o previous DVT/PE • Immobilization or surgery w/in 4 wks |
|
|
What condition should be immediately suspected in a pt with syncope in the face of thoracic aortic dissection?
|
Pericardial effusion/ tamponade
|
|
|
What defines aortic aneurisms as TRUE aneurisms?
What is the location of the vast majority of AAAs? |
A true aneurism -- involves all 3 layers of the arterial wall
97% of aneurisms are INFRARENAL |
|
|
What drugs are used to manage shock in the hypotensive PE pt? What is the role of volume loading?
|
ISOPROTERENOL:
• is a pure ß-agonist and is preferred over dopamine b/c it is a more effective dilator of pulmonary arterioles. • Improves RV contractility • Decreases RV outflow resistance NOREPINEPHRINE: • May be required in the event that Isoproterenol does not increase cardiac output enough to compensate for the decreased PVR --> HoTN worsens PE pts die of RV failure. Volume loading can worsen RV fxn and is usually not very helpful. |
|
|
Describe the EKG findings of thoracic aortic dissection
|
Up to 40% of pts with thoracic aortic dissection have EKG findings c/w AMI/ ischemia
INFERIOR wall pattern is the most common since this involves the RIGHT coronary artery MI pts w/ clinical findings suggestive of thoracic aortic dissection should have a CT or TEE to r/o TAD. |
|
|
What is the 'classic triad' of sx in the presentation of PE?
|
• Dyspnea
• Pleuritic chest pain • Hemoptysis |
|
|
What is the diagnostic algorhythm for the dx of PE in pregnant pts?
|
Test #1: LE DVT u/s
• If positive, tx for PE • If negative, get V/Q Note: D-Dimer test is elevated in pregnant pts and is therefore an unreliable test in this pt population! |
|
|
Describe the pain of thoracic aortic dissection. Match the pain location to the dissection site.
|
Pain:
• Abrupt onset • Maximal from onset • Tearing or ripping quality • Pain migrates as dissection propagates Ascending Dissection: • Ant CP radiating to neck/ jaw/ arm Descending Dissection: • Interscapular back pain radiating into abdomen or lumbar area |
|
|
Describe the pathophysiology of thoracic artery dissection.
What factors control its propagation? |
Pathophysiology:
• Intimal tear --> blood leaks into the media --> cleaves it longitudinally from the adventitia Propagation dependent upon: • Blood pressure • Steepness of the pulse wave (rate of change in pressure/time) |
|
|
What is Phlegmasia alba dolens?
|
Massive iliofemoral thrombosis associated with ARTERIAL SPASM
• Leg is swollen but NOT tense • Skin is doughy and white PAD occurs in conjunction with phlegmasia cerulea dolens. Once the arterial spasm resolves, the leg reverts to the baseline cyanotic PCD. |
|
|
What is Phlegmasia cerulea dolens?
Exam findings? |
An ISCHEMIC form of VENOUS occlusion due to massive ILIOFEMORAL thrombosis
• The leg is TENSE, swollen, painful and CYANOTIC • PETICHIAE and BULLAE may be present • Occasionally results in venous gangrene |
|
|
What is the maximum blood pressure threshhold for tx with tPA?
|
< 185/110
|
|
|
Which type of aortic dissection is more common:
thoracic or abdominal? |
Thoracic (2 - 3x more common)
|
|
|
What are the 6 immediately life-threatening diagnoses that must by ruled out in chest pain patients?
|
• ACS
• Tension pneumo • Thoracic aortic dissection • Tamponade • PE • Esophageal rupture |
|
|
What is the formula for determining the normal A-a gradient value corrected for age?
|
Nl A-a gradient = Age/4 + 4
|

