![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is weed competition?
|
how long weeds and crop can grow together before there is damage
|
|
|
What is interference?
|
competition + other factors that impair the crop
|
|
|
What are the increasing factors that determine the amount of competition?
|
light, water, nutrients, space
|
|
|
8-10 weeks
|
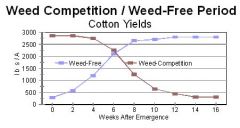
How long does this crop need to be weed-free to have max yield?
|
|
|
There is a big loss in yield
|
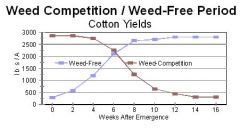
What happens if you wait 6 weeks to spray herbicide?
|
|
|
between weeks 2-4
|
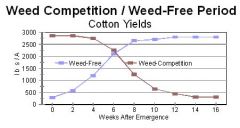
When is the crop the most sensitive?
|
|
|
field corn b/c it only needs to be weed-free for 4 weeks to have no effect on yield
|
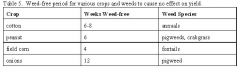
What crop is the most competitive and why?
|
|
|
The longer a weed is in competition, the larger % yield reduction
|
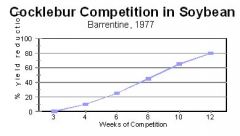
Interpret this table.
|
|
|
yield decreases the longer a weed in the field
|
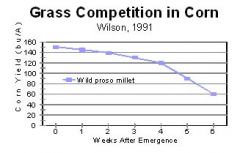
Interpret this table.
|
|
|
What factors affect weed/crop interference?
|
Time of weed/crop emergence
Growth form Weed Density |
|
|
How does the time of weed/crop emergence affect interference?
|
1) the plant that emerges first gains the advantage
2) affected competition is greatest when plants are young 3) late season weeds has a quality and nutrient (P & K) issue |
|
|
How does growth form affect interference?
|
Root- tap vs fibrous
Height- prostrate vs tall Leaf area Branching |
|
|
Which is more competitive- tall plants that grow fast or prostrate and spindly?
|
fast growing tall plants
|
|
|
Yield decreases as weed density increases
|
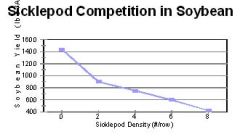
Explain how weed density affects the crop.
|
|
|
May not need to spray if there isn't many weeds in the field and not much yield loss
|
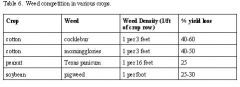
Explain why this information may be important to a grower.
|
|
|
What is the physiological basis of competition above ground? What can increase this competition?
|
weeds that take the most light away will be more competitive
Factors: bigger leaf area, lie flat, vining habit, lower light compensation point |
|
|
What is the physiological basis of competition below ground? What can increase this competition?
|
Early and rapid root penetration
Factors: high root density, distribution of roots (fibrous vs. tap), nutrients- N, P, K |
|
|
When is water an issue during competition?
|
when it is under irrigation and limiting during fruit/seed development
|
|
|
What ways can manipulating the crop gain competitiveness?
|
1) Row spacing- narrow rows allow for quicker canopy of crop
2) Fertilizer placement- in the row 3) Drip irrigation 4) Breeding |
|
|
What are some mechanisms of interference?
|
1) Crop quality
2) Harvest losses 3) Interference with other pest control methods, spray deposition 4) Hand harvesting 5) Staining on cotton |
|
|
What is allelopathy?
|
chemical interference of one plant with another, produces toxin that deters germination or growth of neighboring plant
|
|
|
What is allelopathy influenced by?
|
Growth of allelopathic plant
Growth of affected plant Breakdown rate of residue containing toxin |
|
|
What can allelopathy occur from?
|
Volatilization
Leaching of residues Exudation Decomposition of plant residues |
|
|
What is the effect of black walnut on bermudagrass?
|
kept it from growing in it drip due to its allelopathic effect
|
|
|
What is parasitism?
|
one plant physically interferring with growth and development of another plant; physical attachment
|
|
|
Give some examples of parasitic weeds?
|
dodder, mistletoe, witchweed
|
|
|
What are some characteristics of parasitic plants?
|
occurs in flowering plants
receives all or partial requirements from host fully photosynthetic or non-photosynthetic attaches via haustoria special adaptations such as sticky seeds, exploding seed pods, host excreted stimulant |

