![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is this Description of Below:
An international computer network providing e-mail and information from computers in educational institutions, government agencies, and industry, accessible to the general public via modem links |
The Internet
|
|
|
What is this Description of Below:
Shared Resources – Servers Always connected to the Internet Listens for requests and responds with required data Web Servers Email Servers |
Interconnected Clients and Servers
|
|
|
What is this Description of Below:
Web Browsers Email Client Connect to the Internet as required Make requests and receive response data Display information |
End Users – Clients (Via PC, Mobile phone, etc.
|
|
|
Usually confined to a single building or group of buildings
|
LAN – Local Area Network
|
|
|
Usually uses some form of public or commercial communications network to connect computers is widely dispersed geographical areas.
|
WAN – Wide Area Network
|
|
|
A private network contained within an organization or business used to share information and resources among co-workers
|
Intranet
|
|
|
A private network that securely shares part of an organization’s information or operations with external partners
|
Extranet
|
|
|
Network Infrastructure
|
Built on standard protocols – TCP/IP
|
|
|
What is this Description of Below:
e.g. the World Wide Web Web servers host content Web clients (browsers) access content Standard delivery – HTTP Standard content – HTML, CSS, etc. |
Applications – e.g. the World Wide Web
|
|
|
Beginnings:
A network to interconnect computers at universities and research facilities Fault tolerence Messages can travel via different routes If one route down, then use a different one. Made possible by TCP/IP protocol |
Beginnings:
A network to interconnect computers at universities and research facilities Fault tolerence Messages can travel via different routes If one route down, then use a different one. Made possible by TCP/IP protocol |
|
|
Developed by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) as the ARPAnet
|
Four computers(!) connected by the end of 1969
1989 - 100,000 connected hosts 1992 – First commercial use - 1,000,000 hosts 2006 – 439 million host computers 2013 - 2,406 million Internet users |
|
|
What is this Description of Below:
Text Based News, Gopher, FTP, SMTP (Email) Not easy to use or find information |
Internet Pre WWW
|
|
|
What is this Description of Below:
Enable document linking and sharing between research scientists Based A system of “Hyperlinked” documents Common standards – HTTP (HypertText Transfer Protocol) HTML HyperText Markup Language) |
CERN 1991: Tim Berners Lee envisioned the WWW
|
|
|
What is this Description of Below:
Mosaic Developed at the National Centre for Super Computing Applications (NCSA) at the University of Illinois, USA Another browser, Netscape Navigator, also had its origins here |
1993 – First graphical Web Browser
|
|
|
The web browser was significant Leap why ?
|
The web browser provided the first graphical interface to the Internet (the WWW)
Commercial development along with the HTTP standard resulted in huge growth of the WWW |
|
|
What is ICAN?
|
Internet Corporation for Assigned Numbers and Names (ICANN)
|
|
|
Who is IANA and what do they coorordinate?
|
Co-ordinate:
Internet Domain Naming (IANA - Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) IP Address Numbers Protocol Parameters and Port Numbers |
|
|
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) who are they ?
|
Produces Specifications (called recommendations) for standardised development of the WWW
Web architecture User interface Technology and society Web Accessability Initiative (WAI) Recommendations are guidelines (rather than rules) Produced by working groups with inut from major corporations. REMEMBER These guidelines are not always followed… Browser incompatibilities Difficult for developers |
|
|
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
|
Develop new Internet Standard Specifications (Protocols)
|
|
|
Internet Architecture Board (IAB)
|
Defines the overall architecture of the Internet
Publication of Request for Comments (RFC) documents Formal IETF document, open for review http://www.ietf.org/rfc.html Final Version of RFC becomes the standard |
|
|
What is this Description of Below:
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol Internet Protocol |
Underlying Network
|
|
|
What is this Description of Below:
Path Selection Used to determine network route from host to host Forward packets to the next ‘router’ until destination is reached Addressing provides unique Internet address to each host in a network E.g. 193.1.127.22 In example Green is Network ID and Red is Host ID Analogous to a Telephone number 00 353 1 404 2000 |
IP (Internet Protocol)
|
|
|
What is this Description of Below:
Breaks messages into ‘packets’ Ensures reliable communication Ports Identify Sending and receiving applications Common applications are assigned ports, e.g: HTTP – Port 80 FTP – Port 21 (and 20) SMTP – Port 25 Analogous to telephone extensions 00-353-1-404 2354 |
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
|
|
|
What is this Description of Below, and learn the steps:
Common Examples HTTP – Hypertext Transfer Protocol FTP – File Transfer Protocol DNS – Domain Name System SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Define rules for communication and message formats between applications running on the Internet How a web page is requested, located, and delivered.. Request from browser Server processes request and sends reply Browser receives reply and displays it to user What media formats are understood |
Application Layer Protocols
|
|
|
What is this Description of Below:
Typing the IP address and TCP port in a web browser address bar works but has some drawbacks |
URLs and Domain Names
|
|
|
The ‘web address’ (or URL) in the previous example is not very user friendly
IP addresses are not always easy to remember Especially IPv6 addresses! 3ffe:ffff:101::230:6eff:fe04:d9ff Solution: ?? |

Solution: Use user friendly URL
Uniform Resource Locator (originally Universal Resource Locator) Represent the address of a www resource (html doc, image, etc.) |
|
|
DNS STANDS FOR??
|
DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM
|
|
|
What DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM USED FOR?
|
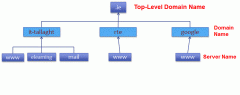
Provide user friendly naming system for organisations and other entities on the Internet
A domain names represents an IP addresses IP address may change but domain name should still work Provide logical hierarchical structure |
|
|
Fully Qualified Domain Name:
|
Fully Qualified Domain Name: www.it-tallaght.ie
ie – TLD it-tallaght – Domain Name www – Server Name |
|
|
TLD examples Name some
|
TLD examples (Full list: http://www.iana.org/domains/root/db/ )
Generic (Administered by ICANN) .com – commercial .net – Internet service and communications providers .org – Nonprofit .biz – Businesses |
|
|
Country specific some examples
|
Country specific (.ie administered by IEDR – IE Domain Registry)
.ie .fr .de .uk |
|
|
DNS resolves a fully qualified domain name to?
|
DNS resolves a fully qualified domain name to its assigned IP address
|
|
|
Markup languages are used to add ????
|
Markup languages are used to add formatting and layout to text documents
|
|
|
Markup languages is A system of ??
|
Markup languages is A system of codes or ‘tags’ is used to specify how text should be formatted.
|
|
|
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)
A set of codes/ tags used to format text in web pages A web browser does what??? |
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)
A set of codes/ tags used to format text in web pages A web browser parses an HTML file, displaying the web page and associated files. |
|
|
XML WHAT IS IT?
|
Extensible Markup Language (XML)
Used by developers to create new tags to describe any information Create common information formats and share on the Web Separate data and presentation Meaning of XML tags defined in a separate schema or Document Type Definition (DTD) |
|
|
Extensible HTML (XHTML)
|
Extensible HTML (XHTML)
Developed by the W3C, XHTML redefines HTML 4.01 using XML The elements and attributes of HTML 4.01 The syntax of XML Ability to extend the language by adding new tags Increased platform interoperability – especially for mobile devices |
|
|
Standard Generalised Markup Languafe (SGML)
|
Standard Generalised Markup Languafe (SGML)
A standard used to define markup languages E.g. the set of tags for HTML Defined in a DTD |

