![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Atmospheric Stability?
|
The atmosphere's resistance to vertical motion.
|
|
|
What is Adiabatic Heating?
|
As an air mas descends, it heats, compresses, and pressure increases.
|
|
|
What is Adiabatic Cooling?
|
As an air mass ascends, it cools, expands, and pressure decreases.
|
|
|
What is the Adiabatic Lapse Rate for dry air?
|
3°C (5.4°F) per 1,000 feet.
|
|
|
What is the Adiabatic Lapse Rate for moist air?
|
The moist lapse rate varies from 1.1°C to 2.8°C (2°F to 5°F) per 1,000 feet.
|
|
|
What is a Temperature Inversion? What are it's characteristics?
|
A temperature inversion is any time temperature increases with altitude. Inversions are characterized by a layer of stable air and poor visibility.
|
|
|
What is the Dewpoint Lapse Rate?
|
1°F per 1,000 feet.
|
|
|
What is the formula for estimating Cloud Bases?
|
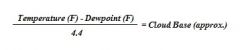
|
|
|
When does Dew form?
|
When objects cool to a temperature below the dewpoint of the surrounding air.
|
|
|
When does Frost form?
|
When objects cool to a temperature below the dewpoint of the surrounding air and the dewpoint is below freezing.
|
|
|
How do clouds form?
|
As air cools to its saturation point, water vapor condenses on condensation nuclei forming clouds or, when close to the surface, fog.
|
|
|
What are the types of Low Clouds?
|
Stratus, Stratocumulus, Nimbostratus.
|
|
|
Describe Stratus Clouds, and how they form
|
Stratus clouds are layered, form in stable air, have a gray, uniform appearance, and cover a wide area. Stratus clouds have little or no turbulence, and pose an icing risk if temperatures are at or near freezing.
Stratus clouds form when moist, stable air is lifted up sloping terrain, or when warm rain evaporates as if falls through cool airl. |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of Nimbostratus Clouds
|
Nibostratus clouds are gray or black, can be several thousands of feet thick, contain large quantities of moisture, and produce widespread areas of rain or snow. If temperatures are at or near freezing they can cause heavy aircraft icing.
|
|
|
Describe Stratocumulus Clouds. How are they formed?
|
Stratocumulus clouds are white, puffy clouds that form when stable air is lifted.
They are formed when cumulus clouds spread out, or when a stratus layer breaks up. |
|
|
What altitude are low clouds found?
|
From the ground to 6,500 AGL.
|
|
|
What is Fog?
|
Fog is a low cloud which has its base within 50 feet of the of the ground.
|
|
|
What is Ground Fog?
|
Fog that is less than 20 feet deep.
|
|
|
What is Radiation Fog?
|
Radiation fog forms over low-lying, fairly flat surfaces on clear, calm, humid nights. As the surface cools by radiation, the adjacent air also cools to the dewpoint. Radiation fog is characterized by stable air associated with a high pressure system.
|
|
|
What is Advection Fog?
|
Advection fog is caused when a low layer of warm, moist air moves over a cooler surface.
|
|
|
What is Upslope Fog?
|
Upslope fog forms when moist, stable air is forced up a sloping land mass.
|
|
|
What is Steam Fog?
|
Steam fog, also known as sea smoke, occurs as cold, dry air moves over comparatively warmer water. When the warmer water evaporates, it rises upwards and condenses resembling smoke. This water vapor can pose an icing hazard to aircraft. Icing and low-level turbulence are associated with steam fog.
|
|
|
What are the types of Middle Clouds?
|
Altostratus and Altocumulus.
|
|
|
At what altitude are middle clouds found?
|
Middle clouds are found from 6,500 to 20,000 AGL.
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Altostratus Clouds?
|
Altostratus clouds are flat, dense clouds that cover a wide area and have a uniform gray or gray-white color. Although they produce minimal turbulence, they can produce moderate aircraft icing.
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Altocumulus Clouds?
|
Altocumulus clouds are gray or white, patchy clouds of uniform appearance. They usually extend over a wide area.
|
|
|
What are the types of High Clouds?
|
Cirrus, Cirrostratus, and Cirrocumulus.
|
|
|
At what altitude are high clouds found?
|
High clouds have bases that begin above 20,000 feet AGL.
|
|
|
Describe the characteristics of Cirrus Clouds
|
Cirrus clouds form in stable air at high altitudes (30,000+ feet AGL), have a thin, whisp appearance, and are white or light gray in color. Cirrus clouds often exist in patches or narrow bands.
|
|
|
Describe the characteristics of Cirrostratus Clouds
|
Cirrostratus clouds are thin, white clouds that often form in long bands or sheets against a deep blue sky. They may be several thousands of feet thick, though moisture content is low.
|
|
|
Describe the characteristics of Cirrocumulus Clouds
|
Cirrocumulus clouds are white and patchy, and have a cotton-like appearance. Cirrocumulus clouds are formed by convective currents at high altitudes and, as such, can produce light turbulence.
|
|
|
What are the types of clouds with vertical development?
|
Cumulus, towering cumulus, and cumulonimbus clouds.
|
|
|
Describe the characteristics of Cumulus Clouds
|
Cumulus clouds form in convective currents caused by the heating of the Earth's surface. They usually have flat bottoms with dome-shaped tops.
|
|
|
What are fair weather cumulus clouds? What flight conditions can be expected from these clouds?
|
Widely spaced cumulus clouds are called fair weather cumulus clouds. Turbulence can be expected, though with little icing and precipitation.
|
|
|
Describe the characteristics of Towering Cumulus Clouds
|
Towering cumulus clouds look like large mounds of cotton with billowing cauliflower tops. They may have a brilliant white top with a gray bottom. These clouds indicate a fairly deep area of unstable air, and contain moderate to heavy turbulence with icing. These often develop into thunderstorms.
|
|
|
Describe the characteristics of Cumulonimbus Clouds
|
Commonly called thunderstorms or anvil clouds, these clouds form in very unstable air. They are gray-white to black in color, and contain large amounts of moisture.
|

