![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 5 types of air masses? |
- Arctic Continental (Ca) - Extremely cold / dry - Polar Continental (Cp) - Very cold / dry - Polar Maritime (Mp) - Cold / wet - Tropical Continental (Ct) - Very hot / dry - Tropical Maritime (Mt) - Hot / wet |
|
|
What air mass will have the most energy? |
Maritime Tropical will have the most energy because of the available moisture and high temperatures. |
|
|
What are the 7 global temperature controls? |
- Latitude - Seasons - Continentality - Albedo - Available Moisture - Urban Heat Island - Elevation |
|
|
What are the 5 global precipitation controls? |
- Orographic Uplift / Rainshadow - Convection - Tropical Cyclones - Mid Latitude Cyclones - Convergence |
|
|
What is a Mid Latitude Cyclone? |
- It involves two air masses (Warm and Cold) - These air masses don't want to mix, this is where a front is born. |
|
|
What is a front? |
A front happens when two different air masses separate. One is generally warmer and higher in moisture content, the other is colder. |
|
|
What is a dry line? |
A dry line is a front that develops when two different air masses have equal temperatures, but differing levels of humidity (densities). |
|
|
What are the 4 types of fronts? |
- Warm front - Cold front - Occluded front - Stationary front |
|
|
What is divergence aloft? |
Divergence aloft, caused by decreasing
|
|
|
What is convergence aloft? |
Convergence aloft, caused by increasing
Think Ice Skater |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a warm front? |
- Divergence aloft - Gradual uplift of air as front approaches - Light rain for long duration - Often more rain than a cold front - T-storms and tornadoes if conditionally unstable. |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a cold front? |
- Steep Lapse Rate - Forces air to rise rapidly - Thunderstorms are common - Often form a squall line - Heavy rain for short duration - Can form Supercells and Tornado Outbreaks |
|
|
What are the characteristics of an occluded front? |
- Cold front overtakes the warm front - Warm, wet lifting air produces - Heavy precipitation ( Long duration ) - Concentrates at a knot ( Low pressure center ) - Low pressure center ( Highest Energy ) |
|
|
How is an occluded front formed? |
- Begins as two distinct fronts (Cold and Warm) - Cold catches the warm and lifts it off the ground - This forms the occluded front - Energy is released from the warm air - Storm dissipates |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a stationary front? |
- Variable rain, long duration - Front separates warm and cold air - Storms move along the front can product flooding rains. |
|
|
How is a low pressure formed? |
A low pressure is formed when one of two air masses initiates vorticity around the area of lowest pressure. |
|
|
What is vorticity? |
Vorticity = Spin. The faster the spin the more energy is involved = higher wind speeds. |
|
|
What factors impact vorticity? |
- Temperature gradient between air masses - Moisture gradient between air masses - warm moist vs cold dry air mass = powerful storm. |
|
|
What are the characteristics of vorticity? |
- The greater the energy difference between two air masses, the faster they will "breakout" past each other "higher winds". - Faster the movement, faster the vorticity - Greater vorticity = lower pressure - Lower pressure = Stronger pressure gradient - Strong pressure gradient = Higher wind speed - Higher wind speed = More energy released |
|
|
What is a Feed Back Loop? |
- Increased vorticity = increased speed of cold front - Faster cold front results in more warm air being pushed aloft. - Faster rising air = bigger more powerful T-storms. - Tornadoes can occur. |
|
|
What is Lake Effect Snow? |
- Cold, polar air passes over relatively warm lake surface. - Lake surface heats the air and evaporates water from the surface. - Air rises due to heating and water condensing into clouds - Clouds thicken to the point where snow falls - Slight orographic lift once air reaches land is enough to produce snow. (Result of air mass coming over land) |
|
|
What conditions are required to form a tornado? |
- Cold air aloft (steep Lapse Rate) - Warm moist air near the surface - Wind shear between layers in the atmosphere
Contrast of energy (warm/moist vs cold air aloft) = T-storms Wind shear gives it the rotation. |
|
|
How does a funnel cloud form? |
Funnel clouds develop from a decrease in pressure, which induces condensation. The visible dark cloud is from dust and debris sucked up from the surface.
Usually form on the SW side of the storm.
Rain / Hail on the NE side. |
|
|
What are the 5 factors that initiate a hurricane? |
- Begin as a low pressure center (often in West Africa). Basically a group of storms that drifts out to sea. - Lack of wind shear aloft, El nino kills hurricanes. - Relatively clam winds at the surface and aloft. - Warm Water - Hurricanes can't form over land. Water temps need to be at least 78 F. - Coriolis - Hurricanes can't form at the equator because there is no coriolis. |
|
|
Coriolis and its effect on Hurricanes |
- Coriolis adds vorticity (spin) to the low pressure center. - Added spin decreases pressure and increases wind speeds - If wind is greater than 74 mph, an eye will form - Low pressure becomes strong enough to have air descend into the eye - Sinking air heats by adiabatic compression - The heat evaporates the clouds leaving clear skies in the eye. |
|
|
What is a Storm Surge? |
A sudden rise in sea level produced by low pressure, coastal topography, and wind. Doesn't include wave height on top of the surge.
Basically a tsunami. |
|
|
What are the factors of a Storm Surge? |
- Pressure: As a hurricane spins faster, the vorticity increases. - Decreased pressure on ocean surface creates a suction affect that pulls the water into the atmosphere. - 1mb pressure decrease = 1 cm sea level rise
- Coastal Topography - Broad, shallow coasts = Water pushed onto land. - Steep coasts = Water pushed up and down.
- Wind - High winds push a bulge of water in front of the hurricane, and also creates waves, which are added on top of a storm surge. |
|
|
Basics of a hurricane. |
Low pressure - cyclonic circulation Tropical Cyclone = One air mass - Warm / Very wet. |
|
|
What is the composition of the atmosphere? |
- Nitrogen: (Inert) Does nothing - Oxygen: (Extremely volatile) reacts with most everything. Burns, rusts, etc. - Argon: (Inert) Doesn't do anything |
|
|
What are Greenhouse gases? |
Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere. - Carbon dioxide - Water (variable) - Ozone (Upper and Lower) - Methane |
|
|
What are the components of Ozone? |
Upper layer - (Good Ozone) 6-30 miles into the atmosphere. Absorbs dangerous UV radiation. Broken down by CFC's with Chlorine.
Lower layer - (Bad Ozone) at the Earth's surface, created by combustion engines and is a major component of smog, which oxidizes things. - Ex. smog eats paint - O3, added oxygen molecule. |
|
|
What are Rossby Waves? |
Rossby waves are high altitude, fast moving westerly winds, which often follow an irregular path.
The path that they take changes throughout the season
The Jet Steam is the located within the core of this wavy flow. |
|
|
What is Upwelling? |
Upwelling is the rise of cold water from deeper layers of the ocean, which replace warmer surface waters as a result of wind.
Creates vertical movement of air. |
|
|
What is El Nino? |
El Nino occurs when pressures over the eastern Pacific ocean decrease, while pressures in the western Pacific ocean increase.
This causes a strong counter current to occur, pushing warm waters over to the east coast.
Wetter then normal weather on the east coast. aka south america. |
|
|
What is La Nina? |
La Nina happens when strong trade winds drive equatorial currents toward the west. This strong wind movements causes upwelling, pulling up cold water around the east coast.
Drier than normal weather conditions in mid to south america.
West coast (Australia) experience storms / wetter than normal weather. |
|
|
What is the ITCZ? |
Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), also known as the "doldrums" is the area where the northeast and southeast trade winds come together.
Area of high precipitation, and no wind. |
|
|
What are the sections of the atmosphere? |
-Troposphere "The portion between the surface and the Tropopause. We live in this layer.
- Stratosphere - "This is the layer above the Troposphere, it increases in heat because of the merging of O and O2 in the formation of Ozone, which releases heat in the process.
- Mesosphere - Temperatures generally drop with height in this layer.
- Thermosphere - Uppermost layer, This is were auroras occur. Temperatures increase here because of increased solar radiation. |
|
|
What is a Lapse Rate? |
A Lapse Rate is the rate of decrease of temperature with a change in elevation.
Temperature determines volume. |
|
|
Why does the Tropopause vary in height? |
In the tropics the tropopause is higher because the warm air increases its volume.
At the poles cold, dense air exists, this makes the air have less volume, making it lower. |
|
|
What is atmospheric pressure? |
The in a nutshell it is the weight of the atmosphere.
Pressure is measured in: - pounds per square inch lbs/in^2 - inches of mercury = 29.92 in/Hg (most accurate) - Millibars (most common) - 1013.2mb. Sea-level pressure is thought to be 1000mb. |
|
|
What are the two major components of atmospheric pressure? |
- Vertical Pressure Variation - Horizontal Pressure Variation "Causes wind and aids in storm formation". |
|
|
What is an environmental lapse rate? |
World Wide average of -3.5 degrees F per 1000 ft of elevation. |
|
|
Why do planes fly below 43,000 ft.? |
The thinner air imposes less drag on the aircraft. There is a trade-off between fuel efficiency and power, and this optimum range occurs at 30,000 to 40,000 feet.
higher we go, the better our chances are of flying above bad weather. |
|
|
What are some affects of a decrease of pressure with altitude? |
Cerebral edema - brain swells with fluid because of the physiological effects of traveling to a high altitude.
Pulmonary edema - Fluid build up from blood freezing
The Bends - dissolved gases coming out of solution into bubbles inside the body on depressurisation. |
|
|
What are 7 temperature controls? |
1. Latitude 2. Seasons, often combined with latitude 3. Albedo 4. Elevation 5. Continentality 6. Urban Heat Island 7. Atmospheric Moisture |
|
|
What are 5 precipitation controls? |
1. Convection 2. Orographic Uplift 3. Tropical Cyclones 4. Mid Latitude Cyclones 5. Convergence |
|
|
What drives all weather? |
THE SUN! |
|
|
What does the Earth's rotation = 23:56 hrs and not 24 hrs? |
This is due to the tidal effects the Moon has on Earth's rotation. |
|
|
Why is the earth not a true sphere? |
Earth is an oblate spheroid because of its rotation, which causes the Earth to bulge near the middle. |
|
|
Why does latitude have an effect on the temperature? |
Latitude mainly affects the angle of the suns rays. The higher the latitude the lower the sun will be in the sky and the sub solar point will be farther away from your location.
High Lat = Lower Temps Low Lat = Higher Temps
This means that high lats have their solar energy spread out further. |
|
|
What is the Sub Solar Point? |
The sub solar point is the point where the sun is directly overhead, 90 degrees.
Higher latitudes have less energy. |
|
|
What is the main cause for our weather and climate? |
The main reason for our weather and climate is the redistribution of solar energy through currents, storms, and air masses. |
|
|
Why do seasons occur? |
Seasons occur because the earth is tilted at 23.5 degrees. This means that the Earth is always "pointing" to one side as it goes around the sun.
This variable amount of sunlight throughout the year creates the seasons.
The north pole is always facing the sun at a 23.5 degree tilt. |
|
|
Seasons Graphic |
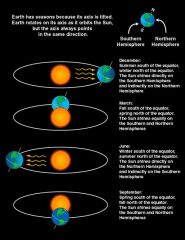
|
|
|
Earth with Tropics and Circles |
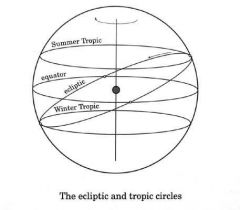
|
|
|
What is the max and min of solar zeinith? |
North pole: max = 23.5 degrees Equator: min = 66.5 degrees |
|
|
Side view of earth, what earth looks like through the seasons. |
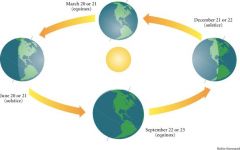
|
|
|
Does every object have a temperature greater than absolute zero? |
Yes because absolute zero is -273 celcius. The more intense the radiation the shorter the wave-length. |
|
|
What is Stefan/Boltzman Law? |
The intensity of emitted radiation is proportional to its temperature.
Shorter wavelengths have higher intensity. |
|
|
What is Wiens Law? |
The higher the temperature of a body, the shorter the wavelength of it's maximum radiation.
Hotter objects emit shorter wavelength radiation. |
|
|
What is the difference between heat and radiation? |
Heat rises, radiation goes in all directions. When you stand in front of a fire you aren't feeling heat. You are feeling radiation.
Thermal sensors used in the Gulf War detect radiation, not heat. |
|
|
What does radiation look like? |
Solar radiation is a combination of electric and magnetic energy.
Humans can see between .4 and .7u. |
|
|
What is insolation? |
Incoming solar radiation is the intensity of incoming solar radiation on an object.
Incoming Solar Radiation. |
|
|
What is Rayleigh Scatter? |
Blue Sky, Sunsets, Blue ligh reflects off of atmospheric molecules "about .4u" |
|
|
What is Mei Scatter? |
Fog "Absorbs blue, green, and red light". |
|
|
What do green trees reflect and absorb? |
Reflection is what we see, trees reflect green light, absorb red and blue. |
|
|
What do white and black reflect / absorb? |
Thats why when you wear a black shirt in the summer you feel a lot hotter then a white shirt. In the visible spectrum, white reflects light and is a presence of all colors, but black absorbs light and is an absence of color. |
|
|
What is the difference between solar and Earth radiation? |
Solar radiation has short wavelengths Earth radiation has long wavelengths |
|
|
What is the Greenhouse Effect? |
Earth's atmosphere does the same thing as the greenhouse. Gases in the atmosphere such as carbon dioxide do what the roof of a greenhouse does. During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere. Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight. At night, Earth's surface cools, releasing the heat back into the air. But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. That's what keeps our Earth a warm and cozy 59 degrees Fahrenheit, on average. |
|
|
What is the Energy Budget? |
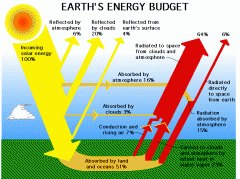
|
|
|
What is the most efficient absorber and re-emitter of long wave radiation? |
Water! |
|
|
Do clouds absorb radiation? |
Clouds are very efficient at absorbing long wave and re-radiating it back to the ground.
Example, Cloudy nights are warmer. |
|
|
What is Albedo? |
The amount of short wave energy reflected by a surface? |
|
|
What are the 3 stages of solar radiation? |
1. Reflected - bounces of things like snow or clouds 2. Transmitted - passes through things without change "aka window". 3. Absorbed - changed to another form of energy - heat, latent, or chemical. |
|
|
How much solar energy is reflected at different latitudes? |
The higher the latitude, the more solar radiation is reflected.
The lower the sun angle, the more solar radiation is reflected. |
|
|
What are three types of radiation energy? |
Heat energy - sensible heat "i.e. temperature" Latent energy - condensation and evaporation Chemical energy - Photosynthisis |
|
|
What is Specific Heat? |
Heat Capacity / Mass
The ratio of heat absorbed or lost by a system "surface" to the corresponding temperature increase or decrease.
|
|
|
Maritime Climates |
Water has a greater heat capacity than land. The depth of mixing layers helps contribute to the moderating climates found near the coast. It takes more energy to heat water and water sotres energy more efficiently than land. Partially due to the depth of mixing. |
|
|
Elevation and Climate |
For every 1000 ft of elevation increase is a 300 mile change in latitude.
Pressure decreases exponentially with height. As pressure decreases the air will expand and cool at a dry and wet rate. |
|
|
What is an Environmental Lapse Rate? |
The lapse rate is the change of temperature with a change in elevation.
The world average is +- 3.5/1000ft of elevation change. |
|
|
What makes Urban Heat Islands so hot? |
The combination of less available water because of evapotranspiration, low albedo surfaces, and structures that trap long wave radiation can combine to produce some miserably high temperatures. |
|
|
What is a squall line? |
A squall line is a line of thunderstorms that can form along or ahead of a cold front. |
|
|
What is the Bergeron Process? |
Ice crystals provide a migration point and physically attract these super cooled cloud particles through a vapor pressure gradient.
This happens with dust particles, pollution, works in a similar manner = Acid Rain. |
|
|
What is Orographic Uplift? |
1. High humidity air blows onshore from ocean 2. Air strikes the Mtns. and is forced to rise - cools at what rate? 3. Air cools to the dew point "LCL", saturated, RH = 100%,. Condensation begins and releases heat, clouds form, most likely area for rain (rain removes h2o from air mass) 4. Air begins to descend - Heats via compression. 5. Air, heated by compression, is hotter and drier than the original air mass. |
|
|
What is convection? |
The movement of heat by the transfer of a mass or substance, can only occur in fluids. |
|
|
What is a convection cell? |
A thunderstorm - Circulation that develops due to uneven heating of a fluid, where the warmer parts expand and rise due to bouyancy and the denser colder parts. |
|
|
What are the stages of a Thunderstorm? |
1. Initiation - Ground heating - Frontal Uplift - Orographic Uplift
2. Mature - Updrafts - Downdrafts - Rain, Ice, Hail - Gust Front - Anvil - Jetstream - Stratosphere
3. Old Thunderstorm - Light Rain - Light downdrafts
|
|
|
What is a supercell? |
A supercell is a very violent mature thunderstorm. - Often produces hail and or tornados - Self sustaining - Severe - heavy rain, hail, and wind |
|
|
What is a micro burst? |
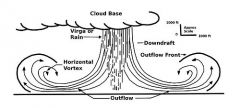
Micro bursts are the product of severe downdrafts.
1. Head wind 2. Sudden downdraft 3. Tail wind
|
|
|
What are the different types of clouds? |
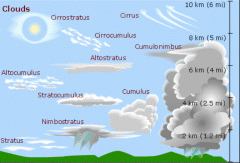
|
|
|
What is the Bernulli Effect? |
Air that is squeezed between mountains or hills. An increase of velocity results in a decrease of pressure. |
|
|
What is a Rotor wave? |
A cloud that develops on the lee side of mountains particularly when mountain chains are parallel to each other. |
|
|
What brings the most energy to an air mass? |
Adding moisture to an air mass gives it abundant energy. |
|
|
What are the 2 components of available moisture? |
1. The amount of water vapor in the air - has a high Specific Heat - energy storage capacity. - an efficient Greenhouse Gas - absorbs and re-radiates long wave energy.
2. Surface water - absorbs up to 75% of insolation - only 25% of solar energy available for sensible heat (increased air temp.) |
|
|
What are the four phases of matter? |
Solid - Ice Liquid - Water Gas - Vapor Plasma - Like the sun, needs lots of heat. Gives the sun its solid apearance
Lightning - heats the atmosphere to a plasma. |
|
|
How does phase change and latent energy work? |
Energy is required before matter (water) can undergo a phase change.
From solid to liquid - doesn't take much energy From liquid to gas - heat is released. 540 cal From solid to gas - (Sublimate) Occurs when temps are below freezing.
The phase change works in reverse as well. |
|
|
When water changes to a lower energy phase, heat is released in these forms. |
To freeze 1.0gm of ice releases to condense 1.0gm water releases Sublimate 1.0gm ice releases |
|
|
Information about Phase change |
Water can absorb or release large amounts of energy as "latent heat" without a change in temperature. |

