![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
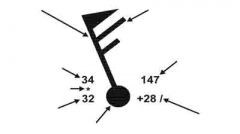
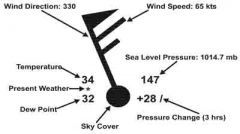
Identify each arrow
|
|
|
|
How is wind direction expressed?
|
the direction from which it is blowing
|
|
|
What is a station model?
|
Method to annotate wind on a chart
|
|
|
What are the left two numbers and middle marker on a station model?
|
Temperature (top) and Dew Point (bottom). Present weather may be in middle.
|
|
|
What are the right two numbers on a station model?
|
Sea Level Pressure (top) and Pressure Change over the last three hours (bottom)
|
|
|
What does the flag indicate on a station model?
|
Wind direction and speed - Pennant = 50kts, long barb = 10kts, short barb = 5kts
|
|
|
What does the circle / square indicate on a station model?
|
Sky Cover in eigths, square = automated, circle = manual
|
|
|
On the station model chart, what does the dot, comma, or star mean?
|
Rain, Drizzle or Snow
|
|
|
On the station model chart, what is the sea level pressure expressed in?
|
3 digits to represent tenths of millibars
|
|
|
On the station model chart, what is the time frame of the pressure change?
|
past three hours
|
|
|
Which direction does wind flow around high pressure areas?
|
clockwise
|
|
|
Which direction does wind flow around low pressure areas?
|
counterclockwise
|
|
|
What does the spacing of isobars indicate?
|
Rate of pressure change = pressure gradient = pressure gradient force (PGF)
|
|
|
What causes the Coriolis force?
|
Earth's rotation
|
|
|
What does the Coriolis force do?
|
Diverts air to the right with respect to its initial direction of motion
|
|
|
Where are gradient winds found?
|
Above 2,000 feet
|
|
|
How do gradient winds flow?
|
Parallel to Isobars, CCW around Lows, CW around highs
|
|
|
When must surface friction be considered in determining wind direction?
|
Below 2,000 feet
|
|
|
What are the 3 forces that must be balanced below 2,000ft to determine wind direction?
|
PGF, Coriolis force, and Friction
|
|
|
What is Buys Ballot's Law?
|
If the wind is at your back, the area of low pressure is to your left (slightly forward of left if standing on the earth's surface
|
|
|
Where is the Jet Stream?
|
around 30,000 feet
|
|
|
What are the wind speeds of the Jet Stream?
|
Over 50 kts, usually 100-150 kts, up to 250 kts
|
|
|
How big is the jet stream?
|
1000-3000 miles long, 100-400 miles wide, 3000-7000 feet deep
|
|
|
What happens to the jet stream in the winter?
|
Moves south, higher, faster
|
|
|
When does a sea breeze occur and where does it come from?
|
Day, from sea, 15-20 kts
|
|
|
When does a land breeze occur and where does it come from?
|
Night, from land, faster and shorter than sea breeze
|
|
|
When does a mountain wind occur and where does it come from?
|
Night, from the mountain
|
|
|
When does a valley wind occur and where does it come from?
|
Day, from the valley
|
|
|
When does saturation occur?
|
When air contains a maximum amount of water vapor for a given temperature: dew point = air temperature
|
|
|
What is the dew point?
|
the temperature at which saturation occurs
|
|
|
What does the dew point indicate?
|
amount of mosture in the air (potential)
|
|
|
What happens with a higher dew point / narrow dew point depression?
|
visible moisture in the form of dew, frost, fog or clouds
|
|
|
What is the RH when the dew point spread reaches 4 degrees F?
|
90%
|
|
|
What are three characteristics of precipitation and corresponding cloud type?
|
Showers (cumuliform), Continuous (stratiform), Intermittent (cumuliform or stratiform)
|
|
|
What are common types of precipitation (7 listed)?
|
Drizzle, freezing drizzle, rain, freezing rain, hail/graupel, ice pellets/sleet, snow/snow grains
|
|
|
What are clouds made of?
|
Condensed water vapor, consisting of water droplets or ice crystals
|
|
|
What are condensation nuclei?
|
Dust, salt crystals, ash, particles, etc. that water vapor can condense upon to create clouds
|
|
|
What are the four groups of clouds?
|
Low, Middle, High, Special
|
|
|
What is the height range of low clouds?
|
Surface to 6,500' AGL
|
|
|
What is the height range of middle clouds?
|
6,500' to 20,000' AGL
|
|
|
What is the height range of high clouds?
|
Above 20,000' AGL
|
|
|
What is the height range of special clouds?
|
Extensive vertical development, usually from low to middle clouds through high cloud category
|
|
|
What determines the classification of clouds?
|
The cloud base
|
|
|
What are the two prinicpal cloud forms?
|
Cumuliform and Stratiform
|
|
|
What is a cumuliform cloud?
|
Lumpy & billowy with a definite pattern/structure to the base
|
|
|
What is a stratiform cloud?
|
Uniform base with horizontal sheet-like layers
|
|
|
What is the primary composition of low clouds?
|
Water droplets
|
|
|
What is the special prefix attached to low clouds?
|
No special prefix attached
|
|
|
What does the prefix nimbo or numbus indicate?
|
Violent or heavy precipitation
|
|
|
What type of cloud is a nibostratus cloud and what type of precipitation does it produce?
|
A stratiform cloud that produces heavy steady precipitation (Low cloud in example)
|
|
|
What are risks of low clouds?
|
Visibility of terrain, faster icing, low turbulence, light precipitation
|
|
|
What is the primary composition of middle clouds?
|
Ice crystals, water droplets or a mixture of the two
|
|
|
What is the special prefix attached to middle clouds?
|
Alto-
|
|
|
What is visibility in middle clouds?
|
1/2 mile to a few feet
|
|
|
What are risks of middle clouds?
|
Low visibiltiy, turbulence, icing, rain and snow
|
|
|
What is Virga and where is it found?
|
Rain or snow that evaporates before reaching the ground; can be encountered below middle clouds
|
|
|
What is the special prefix attached to high clouds?
|
cirro- or the word cirrus
|
|
|
What are characteristics of high clouds?
|
Little effect, moderate turbulence, limited visibility, no precipitation, not an icing hazard
|
|
|
What is the primary composition of high clouds?
|
ice crystals
|
|
|
What types of clouds are included in the Special Clouds with Extensive Vertical Development?
|
Towering cumulus and cumulonimbus
|
|
|
What type of clouds are shown in Figure 2-14?
|
Stratus
|
|
|
What type of clouds are shown in Figure 2-15?
|
Altocumulus
|
|
|
What type of clouds are shown in Figure 2-16?
|
Cirrus
|
|
|
What type of clouds are shown in Figure 2-17?
|
Cumulonimbus
|
|
|
What are the risks of towering cumulus clouds?
|
Nearing the thunderstorm stage, heavy rain, moderate tubulence, icing
|
|
|
What are the risks of cumulonimbus clouds?
|
Thunderstorms, extreme turbulence, hail, icing, lightning
|
|
|
What type of weather stability does Figure 2-22 (left) indicate (colder air settling when lifting action is removed)?
|
Stable condition
|
|
|
What type of weather stability does Figure 2-22 (middle) indicate (air is pushed up and continues to rise)?
|
Unstable condition
|
|
|
What type of weather stability does Figure 2-22 (right) indicate (air is pushed up and stays at that level)?
|
Neutral
|
|
|
What are the four methods of lifting?
|
Convergence, frontal, orographic and thermal
|
|
|
What is Convergence?
|
Two air masses converging and forcing air upwards
|
|
|
What does a cold front Do as it moves through an area?
|
Lift the air ahead of the cold air mass
|
|
|
What is Orographic lifting?
|
Force of the wind against a mountainside pushing air upward
|
|
|
What is thermal lifting?
|
convective lifting, cool air heated by a warm surface and pushed upward
|
|
|
Identify the four lifting methods in Figure 2-23
|
Convergence, frontal, orographic and thermal
|
|
|
What stability conditions do cumuliform clouds indicate?
|
Unstable conditions
|
|
|
What stability conditions do stratiform clouds indicate?
|
Stable conditions
|
|
|
What type of turbulence indicates stable / unstable atmosphere?
|
Smooth / Rough
|
|
|
What type of visibility indicates stable / unstable atmosphere?
|
Poor / Good (outside clouds)
|
|
|
What type of winds indicates stable / unstable atmosphere?
|
Steady / Gusty
|
|
|
What type of precipitation indicates stable / unstable atmosphere?
|
Steady / Showery
|
|
|
What type of icing indicates stable / unstable atmosphere?
|
Rime / Clear
|
|
|
What type of air mass indicates stable / unstable atmosphere?
|
Warm / Cold
|
|
|
What type of front indicates stable / unstable atmosphere?
|
Warm / Cold
|
|
|
What are additional signs in the sky that indicate stable air?
|
Temperature inversions, low fog, stratus clouds
|
|
|
What are additional signs in the sky that indicate unstable conditions?
|
Thunderstorms, showers, towering clouds, dust devils, rapidly decreasing air temperature while climbing
|

