![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is dew and when does frozen dew form |
Did forms on objects when they cool below the dew point temp -frozen dew, cools below 0 and freezes |
|
|
|
What is frost |
-happens when dew point is is less then or equal to freezing -see point is below 0 |
|
|
|
How much water does dew contribute annually |
12-50mm |
|
|
|
What are condensation nuclei |
Particles suspended in air which water may condence -most favourable 0.1um or greater -very light, suspended for days |
|
|
|
What are the 2 kinds of condensation nuclei |
Hygroscopic- have an affinity for water, see condensation with RHmcu lower than 100% Hydroscopic- repell water; resist condensation with RH above 100% |
|
|
|
What is dry and wet haze (haze=light scattering by particles in air) |
Dry haze- late afternoon,low RH, blue or yellow tint Wet haze- air cooks overnight, RH rises to 75%, dull grey or white, condensation on hygroscopic nuclei |
|
|
|
What is fog |
-forms near ground -air cools near surface becomes saturated, cools below dew point, addition of moisture by evaporation |
|
|
|
What are the 5 types of fog |
-radiation fog -advection fog -upslope fog -mixing fog -evaporation fog |
|
|
|
What is radiation fog |
-clear night, dry air above, moist air near ground -conditions promote radiation cooling - light breeze less than 2.5m/s helps -morning, for evaporates (surface heats, raising air temps, lower RH) |
|
|
|
What is advection fog |
-warm sir moves horizontally over cool surface |
|
|
|
What is fog drip |
Source of moisture in some regions -drinking water in Chile -giant redwood trees in California |
|
|
|
What is upsole fog |
-most air flows up barrier -gets cooler as it goes higher in atmosphere |
|
|
|
What is mixing fog |
Moist but unsaturated air masses become saturated when mixing together (Seeing someone's breath) |
|
|
|
What us evaporation fog |
Cold air in contact with a warmer water surface warmed by the water and become saturated from evaporation -layer of air at surface mixes with cooler air above,saturating it and making fog |
|
|
|
What are the factors for describing clouds (form as air rises and cools) |
Cloud levels - High (cirro) -mid (alto) -low (doesn't have anything) 2 types of cloud -stratiform =strato or stratus (layer cloud) -cumuliform= cumulo or cumulus (puffy cloud) 10 genera (principle cloud forms) |
|
|
|
What are the different kinds of clouds |
Cirrus clouds ( Ci, high) Cirrocumulus (Cc, cumuliform, high) Cirrostratus (Cs, stratiform, high) Altocumulus (Ac, cumuliform, mid) Altostratus (As, stratiform, mid) Himbostratus (Ns, stratiform, nimbo=precipitation) Stratocumulus (Sc)
|
|
|
|
What are stratus cloud |
-1 step up from fog -dosent go to surface - not a lot of rain -drizzle -St -low level cloud |
|
|
|
What are cumulus clouds and cumulus congestus clouds |
-Low level -see on summer day -Cu Cumulus congestus clouds -size and shape -higher and thicker - see with rain -Tcu |
|
|
|
What are cumulonimbus clouds |
-give thunderstorms -flat tops -Cb -strong upper level winds blowing from right it left to produce shape |
|
|
|
How to use a ceilometer to det34mine sky conditions |
-measures height of cloud base -uses laser beam aimed at clouds - measures the delay between transmitted and reflected signal |
|
|
|
What are geostationary satellites |
-orbit 36,000km over spot on equator -monitors 1 area -makes images every 7.5-15 mins -transmits as soon as image is made |
|
|
|
What are polar orbiting satellites |
-orbits paths along lines of longitude -14 revolutions a day -850km above surface -higher detail |
|
|
|
What is visible light image |
Standard image of clouds and surface -show think clouds as bright white areas |
|
|
|
What are infrared image |
Temperature of cloud tops, used to infer cloud top height -10-12um -show high clouds as bright areas and low clouds as grey areas |
|
|
|
What are water images |
-6.5-6.9um -provide info on the water vapour content in atmosphere |
|
|
|
The importance of stability and cloud development |
-release heat to atmosphere -help refylatr energy balance -indicators of physical processes |
|
|
|
What is adiabaric process |
Change in temp and size of an air parcel without addition or removal of heat |
|
|
|
What are the dry adiabatic rate and saturated adiabatic lapse rate |
Vertical motion is often adiabatic Dry -10°c per 1000m Saturated -6°C per 1000. |
|
|
|
How to determine stability |
Comparing temp of a rising air parcel to the temp of the surrounding environment |
|
|
|
What is environmental lapse rate |
-observed decrease in the air temp with elevation -observed using a radiosonde |
|
|
|
What is stable and unstable when determining stability |
Stable -an air parcel displaced upward will tend to descend back to its initial level Unstable -air parcel displaced upward will continue to rise |
|
|
|
Determining stability |
-air parcel cooler then surrounding air sink -air parcel warmer than surrounding air are buoyant and rise - if temp decreases faster then temp of rising air parcel, local environment is unstable |
|
|
|
What is an absolutely stable environment |
ELR is less than saturated adiabatic lapse rate -warmer air over cooler -inversion( temp increases with hight) |
|
|
|
What is neutral stability |
ERL= dry lapse rate -parcel of unsaturated air cooks and warms at same rate of environment -ERL = saturated lapse rate for saturated air |
|
|
|
What is an absolutely unstable atmosphere |
ELR is greater than dry lapse rate -air parcel will rise -when air is saturatedbit forms a vertical cloud -cool air over warm -thunderstorms, servere weather |
|
|
|
What is a conditionally unstable atmosphere |
-depends if air parcel is saturated -ELR is between saturated lapse rate and dry lapse rate (Stable for unatayratef air parcel) (Unstable for saturated parcels) |
|
|
|
What are the caused for instability |
Cooling of air aloft -advection -radiatitive cooking of clouds Warming of the surface -isolation -advection -warm surface Mixing -mixing a stable layer tends to increase lapse rate |
|
|
|
How do coulda develop |
- as air parcel rises and cools to its dew point condensation happens -air currents counteract force of gravity (terminal velicity) on water droplets and ice crystals (particles fall and evaporate is upward currents not enough) |
|
|
|
What causes air to rise so clouds form |
- surface heating (free convection) -uplift along topographic obstacles -ascent due to horizontal convergence -uplift along weather fronts |
|
|
|
Convention of clouds |
-isolation created high surface temp -differential heating -air above warmer surface heats to firm bubble -bubble (thermal) grows and detaches |
|
|
|
Topography and clouds |
-orographic uplift -orographic clouds -windward, leeward, and rain shadow -wave and testicular clouds |
|
|
|
What is precipitation |
Any form of water that falls from the cloud and reaches the surface |
|
|
|
What are cloud droplets |
-average size 20um or 0.02mm -unable to fall as precipitation or evaporates in the dryer air below clouds -larger ones survive the journey to surface |
|
|
|
What is vapour pressure involved in cloud droplet growth |
-when a cloud droplet is in equilibrium with its surroundings -when condensation = evaporation |
|
|
|
What is curvature effect in cloud droplet growth |
-water molecules are less strongly attached to curved (convex) water surface (higher evaporation) -pure water condenses when RH is greater than 100% |
|
|
|
What is solute effect in cloud droplet growth |
-dissolving of hygroscopic nuclei and lowering equilibrium vapour pressure -promotes condensation -inhibits evaporation -water can condence before EH reaches 100% -droplets grow and impact the solute diminishes |
|
|
|
Smaller and larger droplets with solute and curvature effects |
Smaller (solute effect more important) Larger (curvature effect more important) Curvature(equilibrium of droplet requires RH greater than 100%) Solute (small droplets grow with RH less than 100%) |
|
|
|
What is the growth of condensation |
-responsible for the formation of cloud droplets - to slow for the drops to grow to precipitation sizes |
|
|
|
What is the Collison and coalescence process |
-important in warm clouds -larger droplets fall fast - terminal velocity (rain drops stop accelerating) -faster drops collide and coalesce with smaller droplets |
|
|
|
Waht are the results of collision and coalescence process |
Coalesced drops -bigger, faster, collect smaller droplets more efficiently) Thinker clouds -larger sized drops, more collisions Thin clouds produce drizzle |
|
|
|
What is the Ice crystal process (bergeron) |
Important in cold clouds and mid to high latitudes -cloud composed of supercooled droplets and ice crystals -equilibrium vapour pressure is lower over ice than water |
|
|
|
Ice crystal process |
-vapour diffuser from droplet area or ice crystals -ice crystals grow to sizes that allow for them to fall as individual crystals -crystals may collide and join together forming snowflakes |
|
|
|
What is rain (precipitation types) |
-falling drop a of liquid water -drizzle is smaller than o.5 mm -rarely larger than 6mm -virga (drops that evaporate before reaching surface |
|
|
|
What are the measures of rain intensity |
Light is smaller or equal to 2.5mm per hour Moderate is 2.6-7.5mm per hour Heavy is greater or equal to 7.6mm per hour |
|
|
|
Know Most precipitation starts as snow |
-summer freezing leave about 3600m -snowflakes melt to drops about 300. Below freezing level |
|
|
|
What are fallstreaks |
Ice crystal that fall from cirrus clouds -may sublimate or seed lower clouds |
|
|
|
Snow flakes and snowfall (precipitation type) |
-ice crystals for depends on temp -dendrite crystal most common Types -plate -column -dendrite -needle |
|
|
|
What are the specific blizzard requirements |
-duration -wind -visibility |
|
|
|
What is the visibility of snowfall descriptions for snowfall intensity |
Light (greater than 1/2 mile Or 800m) Moderate (greater than 1/4, less than or equal to 1/2 mile Or >400m <800m) Heavy (less than or equal to 1/4 mile Or 400m) |
|
|
|
What is the temperature profile for ice pellets and freezing rain |
-temp at surface less than 0 -inversion at surface, temp increases with hight yo greater than 0 -Above inversion, temp decreases with hight |
|
|
|
What are ice pellets |
Raindrop that travels through deep subfrezing layer and freezes before the surface |
|
|
|
What is freezing rain |
Supercooled liquid drops freeze on contact with cold surface creating a clear ice glaze |
|
|
|
What is rime |
Supercooled cloud/fog droplets freeze onto objects making opaque white ice covering |
|
|
|
What is snow grains |
Small, flat, elongated - less than 1mm -neither bounce nor shatter on hard surface -fall from stratus clouds |
|
|
|
Description of snow pellets of graupel |
-larger than snow grain (less than 5mm) -brittle and easily break on hard surface -fall from towering cumulus clouds |
|
|
|
What is hail (precipitation type) |
-prices of ice greater to or equal to 5mm -transparent ice -made by cumulonimbus clouds -hailstone frie by accretion -accumulation of supercooled droplets on hailstone embryo -strong updrafts make large stones |
|
|
|
The process of hail |
Hailstones start as embryos -suspended by updrafts -ice particles collide with supercoolediquid droplets -freeze on contact -ice particles grow and fall to ground |
|
|
|
How is rain measured |
Measured as depth in mm -standard rain gauge -tipping bucket rain gauge -weighing type rain gauge |
|
|
|
How to measure snow depth |
Average depth at greater or equal to three representative locations -ruler, sonic technology |
|
|
|
How to measure snow water equivalent |
-typical fresh snowpack 10:1 ratio (10cm of snow =1 cm of water) -ranges from..... 6:1 for wet snow 30:1 for dry snow |
|
|
|
What is a Doppler radar |
-transmits microwaves toward target -ruptured energy (echo)measured and displayed -brightness of echo=intensity of rain or snow Measured horizontal speed if Iran and snow moving toward it away from radar antenna |
|
|
|
What are polar orbiting satellites |
-designed to assess clouds and rainfall rated |
|
|
|
What are the kinds of polar orbiting satellites |
TRMM- precipitation rates in tropics and subtropics GPM-like TRMM but up to 65° north and south CloudSat- very sensitive radar, looks at cloud droplets and ice particles |
|
|
|
What are horizontal pressure variations |
-short column of dense, cold air exerts the same pressure as a taller column of less dense warm air -warm air aloft is associated with hight atmospheric pressure -cold air aloft with low atmospheric pressure |
|
|
|
What causes horizontal pressure variations |
Heating and cooling of air columns -aloft and at surface |
|
|
|
What does pressure gradient force air to do |
To move from areas of hight to areas of low pressure -air slowly sinks above surface high -air slowly rises about the surface low |
|
|
|
How to get air pressure |

|
|
|
|
What are daily pressure variations |
-most intense in topics, lesser in high latitudes -driven by absorption of solar e edgy by soon and water vapour - mid latitude variations primarily driven by transitory pressure cell |
|
|
|
What is s mercury (hg) barometer |
- hight of Hg in glass tube -another common term to report air pressure -Measured in mm or inches |
|
|
|
What is the standard atmospheric pressure |
1013.24hPa =29.92 inches Hg = 760mm Hg = 1013.25mb |
|
|
|
What are android barometers |
Contain small flexible metal box that depends or contracts |
|
|
|
What is a altimeter |
Calibrated to measure altitude |
|
|
|
What is a barograph |
Continuously documents sure pressure over time |
|
|
|
What are pressure reading corrected for and how |
Corrected for temp, gravity and surface tension -converts station pressure to seal level pressure (+10 hPa for every 100 m above sea level) |
|
|
|
What are isobars in sea level pressure charts |
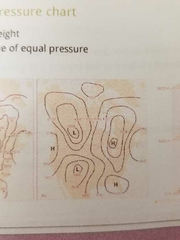
Lines that connect equal pressure -constant height |
|
|
|
Constant pressure surface |

Trough are dips Ridges are high |
|
|
|
What are newtons law of motions |
1) an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue moving in a straight line at constant speed unless an external force acts on object 2l force exerted on an object equals it's mass times acceleration -refer to all (net) forces acting on object -will always accelerate toward net force |
|
|
|
What are newtons horizontal forces affecting air movement |
horizontal pressure graient force (causes horizontal motion) Coriolis force (motion changes wind direction) Centripetal force (imbalance in other forces changes wind direction) Friction (decreases wind speed near surface) |
|
|
|
What are newtons vertical forces (affecting air movement) |
Vertical pressure gradient force (causes upward or downward vertical motion) Gravity (causes downward vertical motion) |
|
|
|
How to find pressure gradient |

From high to low |
|
|
|
How to find pressure gradient force |

Causes wind to blow Close=steep pressure gradient=strong pressure gradient force= High wind |
|
|
|
What is coriolis force |
-force due to earth s roatation -wind deflects (right in northern hemisphere, left in southern hemisphere) -only influence direction -stronger wind=greater deflection - Not at equator -max at poles -over long distances |
|
|
|
What does coriolis force depend on |
Amount for deflection depends on -velocity -latitude -earth rotation rate (7.29 ×10-5 radian s-1) |
|
|
|
What is straight flow aloft (geographic winds) |
-lows to the left of geostrophix flows, hight to the right -spacing of isobars indicate wind speed (close= fast, far=slow) -travels parallel to isobars |
|
|
|
What are curved flow aloft (gradient winds) |
Cyclonic -counterclockwise in northern hemisphere Anticyclonic- clockwise in northern hemisphere - gradient wind parallel to curved isobars |
|
|
|
What is centripetal force |

-inward directed force so winds keep moving in circular path -magnitude of centripetal force is dependent on (wind velocity, radius of the winds curved path) |
|
|
|
What is centripetal acceleration |
directed at right angles to the wind -if object is accelerating a net force is acting on it |
|
|
|
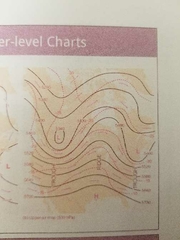
What are winds omg upper level chats |
-winds parallel to contour lines -generally flow west to east -heights decrease from South to north -larger temp contrasts= larger hight gradients= stronger winds |
|
|
|
What is friction |
-reduces wind speed, decreasing the coriolis force -weaker coriolis force no longer balances PGF -winds cross the isobars= 30° -depends on terrain roughness (friction force) |
|
|
|
Winds and vertical air motions |
-air converges towards surface low, then rises-no change in surface pressure if converting air is balanced by diverging air at upper level -falling air diverges away from surface high |
|
|
|
What are the 2 veerial forces in atmosphere |
Gravity pulls down Pressure gradient force pushes upward -PGF causes winds in atmosphere -PGR pushes upward from high to low pressure at the surface and gravity pushes back down -this created hydrostatic balance |
|
|
|
When does Pressure gradient force happen |
-PGF happens where pressure differences exist in a fluid -causes fluid to move from high to low pressure |
|
|
|
What is hydrostatics |
The study if stationary fluids |
|
|
|
What is the equation for hydrostatic |

-change in pressure with hight is directly proportional to the density of the fluid -pressure decreases more quickly in cold air |
|
|
|
What is hypsomety |
Relationships between pressure and hight - pressure surface is a shape where the pressure is the same everywhere -thinness of a layer of air is the difference in hight between two pressure surfaces -warmer temp mean thinker layers |
|
|
|
Know |

|
|

