![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

bending of waves around a barrier
|
diffraction
|
|

What type of wave is this?
|
longitudinal/compressional wave
|
|

an object at rest will remain at rest or an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an outside force
|
Newton's 1st Law of Motion
|
|
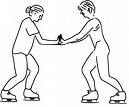
an object acted on by an unbalanced force will accelerate in the direction of the force
|
Newton's 2nd Law
|
|
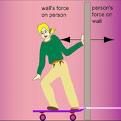
for every action there is an equal but opposite reaction
|
Newton's 3rd Law
|
|

bending of a wave as it moves from one medium into another
|
refraction
|
|
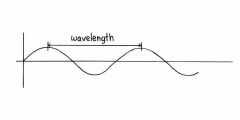
What kind of wave is this?
|
Transverse wave
|
|
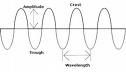
What is being measured?
|
Wavelength
|
|
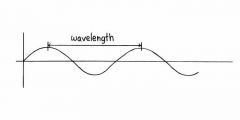
Name the part of the wave found at letter A?
|
crest
|
|
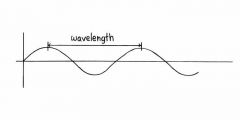
Name the part of the wave found at letter B?
|
trough
|
|
|
a push or a pull
|
force
|
|
|
the state at which one object's distance from another is changing
|
motion
|
|
|
forces that are equal but opposite in direction, that can cancel each other out and cause no change in the object's motion
|
balanced forces
|
|
|
describes unequal forces acting on an object, which results in a change in the object's motion in the direction of the larger force
|
unbalanced force
|
|
|
any force that resists motion
|
friction
|
|
|
occurs when an object speeds up, slows down, or changes direction
|
acceleration
|
|
|
measures the distance and direction from a starting point to an ending point
|
displacement
|
|
|
distance traveled divided by the time needed to travel that distance
|
speed
|
|
|
rhythmic disturbance that carries energy but no matter
|
wave
|
|
|
a type of mechanical wave in which energy causes matter in the medium to move up and down or back and forth at right angles to the direction the wave travels
|
transverse wave
|
|
|
type of mechanical wave in which matter in the medium moves forward and backward in the same direction that the wave travels
|
longitudinal/compressional wave
|
|
|
highest point of a transverse wave
|
crest
|
|
|
lowest point of a transverse wave
|
trough
|
|
|
place in a longitudinal wave where the molecules are spread far apart
|
rarefaction
|
|
|
place in a longitudinal wave where the molecules are squeezed close together
|
compression
|
|
|
distance between two adjacent crests or the bottoms of two adjacent troughs
|
wavelength
|
|
|
distance from the centers of adjacent rarefactions
|
wavelength
|
|
|
distance the wave rises above or falls below its normal level, which is related to the energy that the wave carries
|
amplitude
|
|
|
number of wavelengths that pass a given point in 1 second
|
frequency
|
|
|
unit of measurement for frequency
|
hertz
|
|
|
both wavelength and frequency determines the __________
|
pitch
|
|
|
highness or lowness of a sound
|
pitch
|
|
|
waves are created by ___________
|
vibrations
|
|
|
transverse waves that can travel through matter or space and are produced by the motion of electrically charged particles
|
electromagnetic waves
|
|
|
type of wave that can travel only through matter
|
mechanical wave
|
|
|
material through which waves can travel
|
medium
|
|
|
List the three kinds of media
|
solid, liquid, and gad
|
|
|
Which type of wave can travel in space?
|
electromagnetic
|
|
|
unit of measurement for force
|
Newton
|
|
|
occurs when a wave strikes an object or surface and bounces off
|
reflection
|
|
|
ability of two or more waves to combine and form a new wave when they overlap
|
interference
|
|
|
when the crest of a wave overlaps with the crest of another wave creating a larger amplitude
|
constructive interference
|
|
|
when the crest of a wave overlaps the trough of another creating a smaller amplitude
|
destructive interference
|

