![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Wave
|
Created by a vibration; a disturbance that transfers energy throught matter and empty space.
|
|
|
Medium
|
Matter; the stuff mechanical waves travel through.
|
|
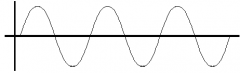
Transverse Wave
|
A wave where the medium moves perpendicular to the motion of the wave
|
|
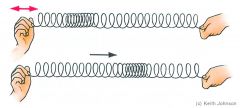
Longitudinal Wave
|
A wave where the medium moves parallel to the motion of the wave
|
|
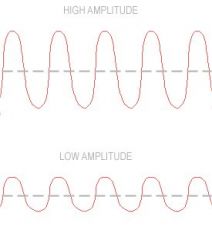
Amplitude
|
The amount of energy a wave transfers
|
|
|
Crest
|
Highest point of a transverse wave.
|
|
|
Trough
|
Lowest point of a transvserse wave
|
|
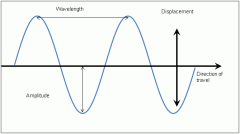
Wavelength of Transverse wave
|
The length of one wave - includes one crest and one trough. From the top of one crest to the top of the following crest.
|
|
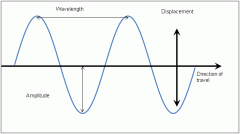
Amplitude of Transverse wave
|
The height of the crest or the depth of the trough measured from rest position of a transverse wave.
|
|
|
rest position
|
The horizontal line that show what the medium is like before the wave disturbes it.
|
|
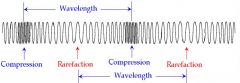
Compression
|
The dense or squeezed part of a longitudinal wave
|
|
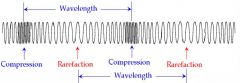
Rarefaction
|
The spread out or less dense area of a compression wave
|
|
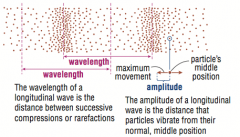
Amplitude of a longitudinal wave
|
The distance that particles vibrate from their normal, middle position
|
|
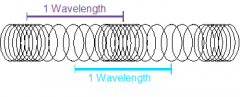
Wavelength of a longitudinal Wave
|
The distance between one compression and one rarefaction
|
|
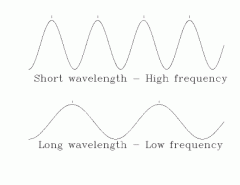
Frequency
|
the number of waves past a point in1 second. unit: hertz (hz)
|
|
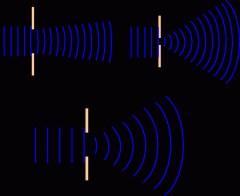
Diffraction
|
The bending of a wave when it goes around a barrier
|
|
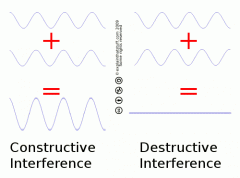
Interference
|
The combining of two or more waves. either constructive or destructive.
|
|

Refraction
|
The bending of a wave as it moves from one medium to another
|
|
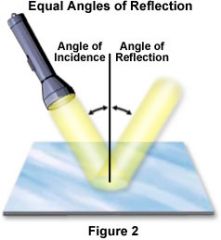
Reflection
|
The bouncing back of a wave when it hits a barrier
|
|
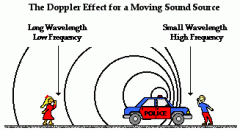
Doppler Effect
|
The change in frequency that occurs when the source of a sound wave is moving relative to the observer
|
|
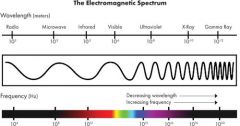
Electromagnetic wave
|
Waves created by vibrating electrons that can travel thru a vacuum or a medium. A wide variety of frequencies and wavelengths are possible, electromagnetic spectrum
|
|
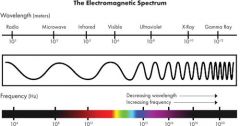
gamma ray
|
Highest energy electromagnetic wave. Very short wavelength and very high frequency
|
|
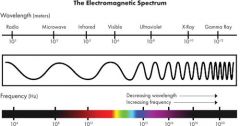
infrared wave
|
electromagnetic waves we associate with radiant heat. Wavelength and frequency just below human sight.
|
|
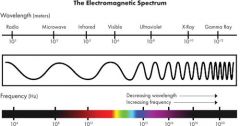
Ultra violet rays
|
electromagnetic waves with wavelengths and frequecies just above human vision. Harmful
|
|
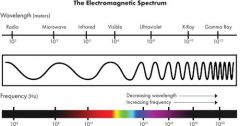
Radiowaves
|
electromagnetic wave with longest wavelenghts and frequencies
|
|
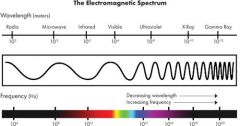
Microwaves
|
a specific type of radio wave used for cooking food and transmitting data
|
|
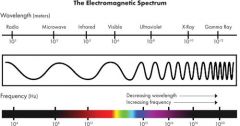
Visible light
|
The part of the electromagnetic spectrum humans can see.
ROYGBV |
|
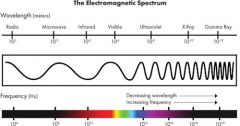
X-rays
|
electromagnetic waves with wavelengths that a just longer then gamma rays. Penetrate skin
|
|
|
translucent
|
Material that allows light to be transmitted thru it but not clearly Wax paper, frosted glass
|
|
|
transparent
|
Materal that allows to be clearly transmitted thru it.
|
|
|
Symbol for wavelength
|
λ
|

