![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
External Water Treatment types |
Evaporating - Heat to evaporate water to remove dissolved solids Reverse Osmosis - High pressure to force water through membrane Deaerating - Heat to drive off dissolved gases (ex. oxygen, carbon dioxide) |
|
|
Internal Water Treatment types |
Adding chemicals to treat water - removes residual oxygen - removes hardness - adjusts pH - adjusts TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) - disperses sludge - reduces foam - removes scaling - protects condensate system from corrosion |
|
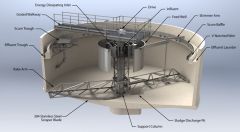
Clarifiers purpose? |
Remove suspended solids from water by allowing them to settle by gravity. (commonly used to treat river water) |
|
|
Coagulations purpose? |
Used in conjunction (occurs same time) with settling tanks/clarifiers Removes fine particles by gathering them together to form larger particles. |
|
|
Coagulants 3 more common are? |
Aluminum sulfate, Al2(SO4)3 Sodium Aluminate, Na2Al2O4 Aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)₃
|
|
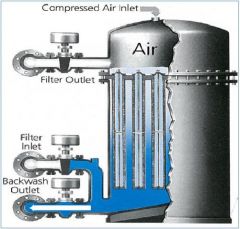
Filter aid tubular filters The cages are covered with? |
Socks of dacron or polyethylene |
|
|
cartridge filter purpose |
Used in conjunction with settling tanks to remove fine particles |
|
|
Cold Lime Soda Softening |
Uses lime (calcium hydroxide) Ca (OH)2 and soda (sodium carbonate) Na2CO3, to precipitate hardness from solution. |
|
|
Ion Exchange |
Exchanging calcium Ca2+ and magnesium Mg2+ cations against Na+ or H+ cations |
|
|
Sodium Zeolite Water Softeners |
When Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions containing hard water is passes through a bed of sodium zeolite, the sodium ions are replace by the calcium and magnesium ions.
Na2Z + Ca(HCO3)2 → 2NaHCO3 + CaZ Na2Z + MgSO4 → 2Na2SO4 + MgZ |
|
|
Cation Exchange |
Hardness causing magnesium and sodium cations removed TDS(Total dissolved solids) does not change |
|
|
Hydrogen zeolite softeners *** |
-Replace all cations with hydrogen -Regenerate using acid (sulfuric acid) -Dissolved solids in water are converted to acids |
|
|
Resins purpose? (2) *** |
One resin replaces cations with hydrogen (Cation resin) One resin replaces anions with hydroxide (Anion resin) |
|
|
Cation resin is regenerated with _? *** |
Sulfuric acid (H2S04) |
|
|
Anion resin is regenerated with _? *** |
Caustic soda (NaOH) |
|
|
Mechanical deaeration purpose and the important gases? |
-Removes dissolved gases from water -Important gases are oxygen and carbon dioxide |
|
|
Mechanical deaeration steps (3) |
-Divide water up into small droplets (Heats up quickly) -Heat water droplets to drive off dissolved gases -Scrub gases away from water |
|
|
Pressure is controlled by? *** (Deaerator) |
Regulating steam flow to deaerator |
|
|
Level controlled by? (3) (Deaerator) |
Regulating water flow to deaerator Overflow valve High and low level alarm |
|
|
temperature controlled by? (Deaerator) |
Controlled by steam pressure |
|
|
Deaeration controlled by? (Deaerator) |
By a manual vent at top of unit |
|
|
Deaerator purpose (3) |
Remove dissolved gases Provide storage area for treated feedwater To heat feed water and reduce thermal shock |
|
|
Cations and anions examples? |
cations- H,Mg,Na,Fe,Cu etc. Anions- Cl,OH,SO4,PO4,CO3 etc. |
|
|
Purpose of deaerator (3) |
- remove dissolved gases - storage for treated feed water - heat feed water and reduce thermal shock |
|
|
Internal water treatment |
Treat water (add chemicals) and to prevent corrosion, scale and sludge formation, foaming and possible failure |
|
|
Mechanical deaeration steps (3) |
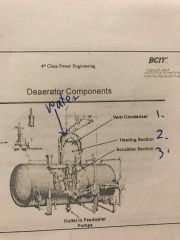
1. Divide water into smaller droplets 2. Heat water droplets to drive off dissolved gases 3. Scrub gases away from water so they cannot redissolve |
|
|
Point of addition depends on? (2) |
Results and reactions between chemicals |
|
|
***How is foaming controlled? |
Blowoff and adding defoamer |
|
|
Caustic embrittlement results from? And hows it treated? (2) *** |
Results from High concentrations of caustic soda Treated by: Not adding caustic into water Adding sodium nitrate***,tannings, lignins |
|
|
Hydrogen Zeolite Softners examples |
NaCl (Sodium Chloride) + H2Z (Hydrogen Zeolite) -> Na2Z (Sodium Zeolite) + HCl (Hydrochloric Acid) CaCO3 (Calcium Carbonate) + H2Z (Hydrogen Zeolite) -> CaZ (Calcium Zeolite) + H2CO4 (Carbonic Acid) |
|
|
Chemicals may be added where? (4) |
Boiler steam drum, condensate system, steam lines, deaerator (storage section) |
|
|
Scaling is a result of? |
Hardness |
|
|
pH must be maintained at? *** |
10.5 to minimize acid corrosion |
|
|
pH level may be increased in the steam drum and feed water system by adding what? *** |
Caustic soda and sodium phosphate |
|
|
Oxygen scavenging reactions |

2Na2SO3 (Sodium sulfite)+O2 (dissolved oxy)->2Na2SO4 (sodium sulfate) N2H4 (hydrazine)+02(dissolved oxy)->N2 (nitrogen)+2H2O (water) |
|
|
sludge is removed by what and why is it bad? |
It sticks onto metal and is removed in the blowoff. Chemicals (organic) used are: -starch from corn/potatoes -Lignin and tannin from wood -Alginates from seaweed |
|
|
Oxygen scavengings purpose and what chemicals are used? |
To remove oxygen to avoid corrosion Chemicals used: -hydrazine (carcinogenic (causes cancer)) - sulfite (increases dissolved solids) |
|
|
Demineralizers remove all _? |
Inorganic dissolved solids to produce clean water. Ex Cation resin regenerates w/ sulfuric acid (H2SO4), Anion resin regenerates w/ Caustic soda (NaOH) |
|
|
Foaming may be caused by? (4) |
High dissolved/suspended solids, organic matter or oils |
|
|
Water treatment to prevent? (4) |
Prevent: -Sludge formation (On boiler surfaces), Scale (On heating surfaces), Corrosion (Boiler metal), carryover of impurities (in boiler water) |
|
|
Impurity problems in boiler water (3) |
Suspended solids, dissolved solids, and dissolved gases |
|
|
Suspended solids are? & How to remove them? |
Solid material that don't dissolve in the water ex. mud clay, sand etc. Removed from boiler blowdown. |
|
|
Dissolved solids are? & how are they tested? |
Solids that dissolve in water and the concentration dissolved is measured by testing the water conductivity. |
|
|
Dissolved gases concerns & why? |
Gases dissolve in water but the two concerns are oxygen (forms iron oxide rust & corrosion) and carbon dioxide (produce carbonic acid which lowers ph & corrosion results in grooving.) |
|
|
Hardness consists of what salts? |
Calcium and Magnesium. Ex. Calcium Bicarbonate Ca(HCO3)2, Magnesium Bicarbonate Mg(HCO3)2, Calcium sulfate CaSO4, Magnesium Sulfate MgSO4 |
|
|
Temporary hardness are? & how to remove? |
Bicarbonates which are removed by heating water to 100 degrees Celsius. Calcium bicarbonate and magnesium bicarbonate form. |
|
|
Permanent hardness are from? |
Other calcium and magnesium salts Ex. Calcium and magnesium sulfate, calcium and magnesium chloride. |
|
|
Scaling results in? |
Dissolved solids that settle on heating surfaces causing tube metals to overheat. |
|
|
pH levels and what is recommended? |
pH less than 7.0 = acidic, pH at 7.0 = neutral, pH greater than 7.0 = alkaline or basic, pH is recommended to be above 10.5 |
|
|
pH depends on? |
Temperature. (pH cooled is higher than pH of same water) |
|
|
Water treatment required depends on? (2) |
Water source and boiler pressure. (Higher pressure, more pure water must be) |
|
|
Sources of boiler water (2) |
Surface water, Ground water |
|
|
Demineralizer Reactions (Cation) |
Cation: 1. CaSO4 (Calcium Sulfate) + H2Z (Hydrogen Zeolite) -> CaZ (Calcium Zeolite) + H2SO4 (Sulfuric Acid) 2. Ca(HCO3)4 (Calcium Bicarbonate) + H2Z (Hydrogen Zeolite) -> CaZ (Calcium Zeolite) + H2CO3 (Carbonic Acid) 3. Carbonic Acid Breakdown H2CO3 (carbonic acid) -> H20 + CO2 (carbon dioxide) Anion: H2SO4 (Sulfuric Acid) + Z(OH)2 (Anion zeolite) -> ZSO4 (zeolite sulfate) + 2H20 |
|
|
Demineralizer Reactions (Anion) |
Anion 1.H2SO4 (Sulfuric acid) + Z(OH)2 (anion zeolite) -> ZSO4 (zeolite sulfate) + 2h20 (water) 2. HCl (Hydrochloric Acid) + Z(OH)2 (Anion Zeolite) -> ZCl2 (Zeolite chloride) + 2H20 (water) |
|
|
Amines used for? |
Combat return line corrosion by neutralizing amines ( Raise pH of condensate) and filming amines ( Coat piping to protect it) |
|
|
Chemical Feed pumps use _ displacement pumps. |
Positive |
|
|
Gravity Drip feeder is used for what chemicals? |
Feeds powered and liquid chemicals into water line by gravity |
|
|
Water testing methods for hardness are? |
Soap test - add soap solution drop by drop Titration test - Hardness buffer is added, hardness indicator turns red, add hardness reagent drop by drop til colour goes red to blue, # of drops = total hardness. |
|
|
Phenolphthalein determines alkalinity from? (2) |
Hydroxide and carbonates only |
|
|
Methyl Orange determines alkalinity from? |
All alkaline dissolved solids |
|
|
Dissolved solids causes solution to ___ better. |
Conduct electricity better (TDS can be determined) |
|
|
Sodium sulfite is tested to ensure no __ remains. |
Ensures no 02 (oxygen) remains |

