![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is some of the other names of Thiamin?
|
Vitamin B1, Aneurine, Thiamine
|
|
|
Can phosphlorylated thiamin be absorbed?
|
No
|
|
|
What happens to Phosphorylated thiamin in the intestines?
|
The intestinal phosphatases hydrolyse the phosphate group prior to absorption.
|
|
|
What are the 2 active names of thiamin?
|
Thiamin pyro phosphate (TPP) & thiamin diphosphate (TDP)
|
|
|
What is required for the conversion of free thiamin to thiamin pyro phosphate?
|
Magnesium & ATP
|
|
|
Where is free thiamin converted to it's coenzyme form?
|
In the liver
|
|
|
What is the definition of a co-enzyme?
|
An organic non-protein molecule, often phosphorylated derivative of a water soluble vitamin
|
|
|
What is phosphorylation?
|
The addition of phosphate group usually transferred from ATP
|
|
|
What form is 80-90% of total thiamin in the body?
|
Exists as TPP
|
|
|
Is thiamin saturated at high or low concentrations in the body?
|
Low
|
|
|
T/F is thiamine absorption at high or low doses by active transport?
|
Low 2mg.
|
|
|
What factors inhibit absorption of thiamin?
|
Alcohol,
conditions such as diarrhoea/vomiting, ulcerative colitis, neoplasia (abnormal proliferation of cells) hepatic disease, achlorhydria (absent or low gastric acid) |
|
|
What is the free thiamin bound to whilst circulating in blood?
|
Bound to protein- usually albumin
|
|
|
Are there any storage sites in the body for thiamin?
|
No,so daily uptake is important
|
|
|
What level of thiamin is usually contained in the body?
|
25-30 mg of thiamin
|
|
|
How is an excess of thiamin excreted for the body?
|
Via urine
|
|
|
What conditions can cause a significant loss of thiamin?
|
Diuresis (excessive urine production) and sweating
|
|
|
When there is a thiamin deficiency does urinary excretion increase or decrease?
|
Decreases, indicating that there is renal conservation mechanism
|
|
|
What are the 2 main roles of thiamin?
|
Co-enzyme and component of neural membranes
|
|
|
What are the functions of thiamin as a co-enzyme?
|
1. Synthesis and metabolism of neurotransmitters.
2. ATP production in krebs cycle. 3. Metabolism of carbohydrates 4. Metabolism of branched chain amino acids and lipids 5. Production of RNA and DNA and niacin coenzyme |
|
|
What are the functions of thiamin as a component of neural membranes?
|
Nerve transmission and activation of ion transport in nerve membranes
|
|
|
Name some of the neurotransmitters that thiamin is important for?
|
Acetylcholine, GABA, glutamate and aspartate
|
|
|
How many coenzymes is thiamin part of?
|
At least 24 enzymes
|
|
|
What are the two most important coenzymes that thiamin assists in the functioning of?
|
Dehydrogenase enzyme complex, transketolase enzymes
|
|
|
What is the biochemical role of dehydrogenase enzyme complex
|
Catalyses decarboxylation - removal of carboxyl groups - COOH
|
|
|
What is believed to be the function of thiamin triphosphate in the neuronal channels?
|
Activates high conductance chloride and sodium channels
|
|
|
Explain the absorption process of thiamin
|
Free thiamin is absorbed from the proximal jejunum of the small intestine
|
|
|
Why is thiamin important in the kreb cycle
|
Thiamin catalysts pyruvate to form Acetyl COA, catalyses alpha ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA, both of which are integral parts of the kreb cycle.
Thiamin also assists with pentose shunt pathway which provides glucose which is the beginning of the krebs cycle |
|
|
List four sub clinical signs of thiamine deficiency
|
Nervous system mainly affecting lower extremities, headaches, muscle wasting and tiredness
|
|
|
What population group is most at risk of thiamin deficiency?
|
Alcoholics
|
|
|
List 5 other groups at risk of developing WKS
|
Anorexics, diabetics, those on dialysis, diets of highly polished rice, and long term parenteral therapy
|
|
|
What is the dosage for dysmenorrhea ?
|
100mg daily
|
|
|
Is there conclusive evidence for the therapeutic use of thiamin in Alzheimer's disease?
|
No - the results have been insufficient in some individuals
|
|
|
Give 5 rich food sources of thiamin?
|
Wheat germ, peas, lean pork, lentils, fortified breakfast cereals
|
|
|
Are there toxicity issues with thiamin? WHat does this suggest about it's safety?
|
There are no reported issues with oral toxicity but adverse affect noted from high doses parenteral nutrition. Appears very safe for consumption.
|
|
|
Where are thiaminases and where are they found?
|
Thiaminase is an enzyme found in some fish which affects the uptake of thiamin
|
|
|
T/F An excess intake of sugar and white bread increase the need for thiamin
|
True - even though a small amount of thiamin is added back into Bread the overall impact of eating too much flour and sugar increases the need for thiamin
|
|
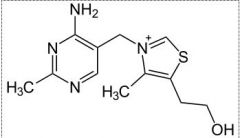
What Vitamin is this?
|
Thiamin
|

