![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
water pollution |

the contamination of water bodies (e.g. lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers and groundwater). This form of environmental degradation occurs when pollutants are directly or indirectly discharged into water bodies without adequate treatment to remove harmful compounds.
|
|
|
biological oxygen demand |
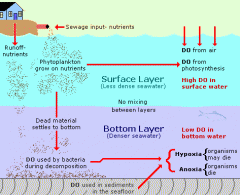
measure of dissolved oxygen required to decompose the organic matter in the water biologically (how dirty ware is test) |
|
|
environmental law |

is a system of complex and interlockingstatutes, common law, treaties, conventions, regulations and policies which seek to protectthe natural environment which may be affected, impacted or endangered by humanactivities.
|
|
|
contaminates |

to make impure or unsuitable by contact or mixture with something unclean, bad |
|
|
fecal coliform |

is a bacteria that occur naturally in human intestines and are used as a standard measure of microbial pollution and an indicator of disease potential for a water source |
|
|
point source pollution |

sources of pollution that are readily identified and stationary.( pipes, accidental spills, ect.) they are are often thought to be easier to recognize and control that are area sources. this true to certain point because some sources leak tremendous amounts of pollutants into the environmental. |
|
|
non-point source pollution |
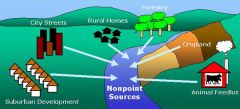
pollution sources that are diffused and intermittent and are influenced by the factors such as land use, climate, hydrology, topography, native vegetation, and geology |
|
|
primary treatment |
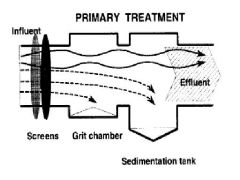
removal of large particles and organic material from waste water through screening |
|
|
secondary treatment |
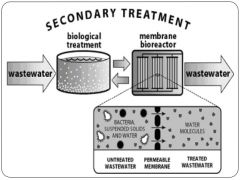
use of biological processes to degrade waste water in a treatment facility |
|
|
tertiary treatment |
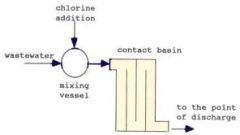
an advanced form of waste water treatment involving chemical treatment or advanced filtration (example- chlorination of water) |
|
|
effluent discharge |

any material that flows outward from something. example include waste water from hydroelectric plants and water discharged into streams from waste disposal sites |
|
|
water renovation and conservation |
the practice of applying waste water to the land. in some systems, treated waster water is applied to agricultural crops, and as the water infiltrates through the soil layer, it is naturally purified. reuse of the water by pumping t out of the ground for municipal or agricultural uses. |
|
|
Wastewater treatment |

Water treatment is any process that makes watermore acceptable for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses including being safely returned to the environment.
|
|
|
Runoff
|

the draining away of water (or substances carried in it) from the surface of an area of land, a building or structure, etc |
|
|
Watershed |

an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas
|
|
|
Eutrophication |
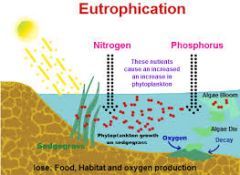
excessive richness of nutrients in a lake or other body of water, frequently due to runoff from the land, which causes a dense growth of plant life and death of animal life from lack of oxygen
|
|
|
Dead zone(s) |
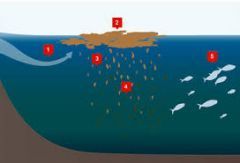
Dead zone" is a more common term for hypoxia, which refers to a reduced level of oxygen in the water. Hypoxic zones are areas in the ocean of such low oxygen concentration that animal life suffocates and dies.
|
|
|
pH |
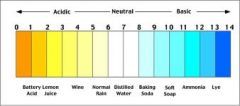
is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration; a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Aqueous solutions at 25°C with a pH less than seven are acidic, while those with a pH greater than seven are basic or alkalin
|
|
|
dissolved oxygen |

refers to microscopic bubbles of gaseous oxygen (O2) that are mixed in water and available to aquatic organisms for respiration—a critical process for almost all organisms. Primary sources of DO include the atmosphere and aquatic plants. |
|
|
chlorination |
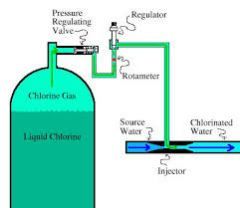
disinfection of water by the addition of small amounts of chlorine or a chlorine compound
|
|
|
aquifer |
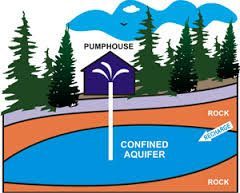
a body of permeable rock that can contain or transmit groundwater
|
|
|
Hypoxia |

oxygen deficiency in a biotic environmen
|
|
|
methane gas |

A colorless, odorless, flammable gas that is the simplest hydrocarbon. It is the major constituent of natural gas and is released during the decomposition of plant or other organic compounds, as in marshes and coal mines.Methane is the first member of the alkane series.
|
|
|
activated sludge |

aerated sewage containing aerobic microorganisms that help to break it down.
|
|
|
leachate |

noxious, mineralized liquid capable of transporting bacterial pollutants. produced when water infiltrates through waste material and becomes contaminated an polluted |

