![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

glacier
|
a large mass of ice formed over many years that moves very slowly over land
|
|

freshwater
|
water that is not salty
|
|

runoff
|
Water will run off surfaces like paved sidewalks and roads to collecting places such as rivers, streams, or lakes.
|
|
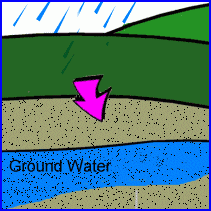
infiltration (infiltrate)
|
Water slowly soaks into the soil. Some of the water stays in the surface soil. Some water seeps deep into the soil where it is stored as groundwater.
|
|

reservoir
|
a place where water collects and is stored
|
|
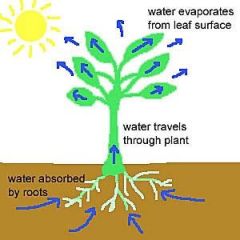
transpiration (transpire)
|
moisture is carried through plants from roots to small pores on the underside of leaves, where it evaporates and is released to the atmosphere
|
|
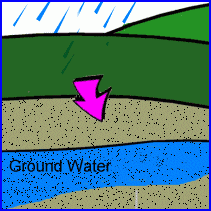
groundwater
|
water stored deep beneath the ground
|
|
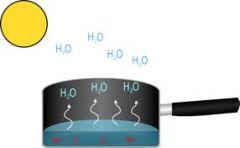
evaporation
|
changing from water (liquid) to water vapor (gas)
|
|

condensation
|
changing from water vapor (gas) to water droplets (liquid)
|
|
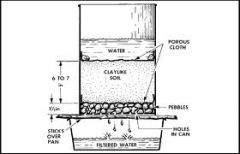
filter
|
a special tool used to clean water
water moves through the filter slowly so the dirt and chemicals can be removed when water moves through the soil, it is filtered naturally |
|

precipitation
|
any water that falls from the sky
|
|
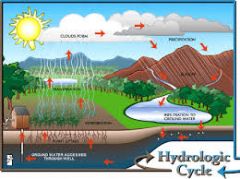
solar energy
|
energy from the sun
Energy from the sun drives the processes of the water cycle (melting, evaporating, sublimating) |
|

icecap
|
a very large and thick sheet of ice that covers the North Pole, the South Pole, or another region
|
|

melting
|
changing from ice (solid) to water (liquid)
|
|

freezing
|
changing from water (liquid) to ice (solid)
|
|
|
Freezing Point |
0 degrees Celcius (32 degrees fahrenheit) |

