![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the water's physical properties? |
Water temperaturepH water Turbidity Dissolved oxygen Hardness |
|
|
Water that has more free hydrogen ions is acidic, whereas water that has more free hydroxyl ions is basic |
Ph water |
|
|
It is a measure of the cloudiness of water |
Turbidity |
|
|
It is breathed by fish and zooplankton and is needed by them to survive. |
Dissolved oxygen |
|
|
is a measure of the amount of calcium and magnesium salts in water. Calcium and magnesium enter water mainly through the weathering of rocks. |
Hardness |
|
|
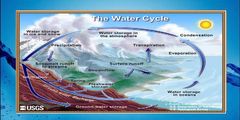
The hydrologic cycle, collects, purifies, and distributes the earth's fixed supply of water. |
Water cycle |
|
|
It is powered by energy from the sun and involves three major processes - evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. |
Water cycle |
|
|
States of water cycle |
Evaporation Condensation Precipitation Surface runoff Infiltration Transpiration |
|
|
It is the process of a liquid's surface changing to a gas. In the water cycle, liquid water (in the ocean, lakes, or rivers) evaporates and becomes water vapor. |
Evaporation |
|
|
It can happen high in the atmosphere or at ground level. Clouds form as water vapor condenses, or becomes more concentrated (dense). Water vapor condenses around tiny particles called cloud condensation nuclei . Cloud Condensation Nuclei can be specks of dust, salt, or pollutants. Clouds at ground level are called fog or mist. |
Condesation |
|
|
It describes any liquid or solid water that falls to Earth as a result of condensation in the atmosphere. Precipitation includes rain, snow, and hail. |
Precipitation |
|
|
It describes a variety of ways liquid water moves across land. Snowmelt, for example, is an important type of runoff produced as snow or glaciers melt and form streams or pools. |
Surface runoff |
|
|
It is the process by which precipitation or water soaks into subsurface soils and moves into rocks through cracks and pore spaces. |
Infiltration |
|
|
It is the process by which moisture is carried through plants from roots to small pores on the underside of leaves, where it changes to vapor and is released to the atmosphere. Transpiration is essentially evaporation of water from plant leaves. |
Transpiration |
|
|
Draw the water cycle |
|

