![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Structure of Water |
●Small dipolar molecule made up of 2 hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to 1 oxygen atom ●The electrons in water are not shared evenly between hydrogen and oxygen ●Large Oxygen pulls electron close towards it to become delta negative And the hydrogen be omes delta positive ●Slight charges attract 1 another to form a weak interaction called a hydrogen bond. These are continually broken and reformed |
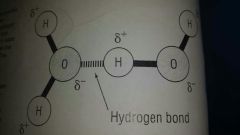
Many Hydrogen bonds in water make it a polar molecule |
|
|
Metabolic Role |
●Condensation and Hydrolysis reactions involve water such as joining amino acids or splitting disaccharides |
|
|
|
High Latent heat of vaporisation |
●Due to many hydrogen bonds it requires a lot of energy to evaporate water. ●Water evaporates from a surface it 'removes' heat and has a cooling effect E.g. SWEATING & TRANSPIRATION |
|
|
|
High boiling point |
●Continuous making and breaking of hydrogen bonds in water means it is a liquid not gas ●Difficult for water molecules to escape liquid which means it has a high boiling point compared to other similar sized molecules |
|
|
|
Low Density of Ice |
●As water is cooled,molecules slow down to form more H bonds to firm a crystalline structure which is less dense than liquid water. ●This means that ice floats on water and insulates organisms beneath it |
|
|
|
High Specific Heat capacity-Thermostability |
●H bonds in water prevent the movement of water molecules so large amounts of energy Is needed to increase temp ●Therefore has a high specific heat capacity ●large bodies of water are thermostable during large external fluctuations of temperature. |
|
|
|
Cohesion |
●H bonds cause water molecules to stick together ●results in surface tension at surface of water ●allows organisms to walk on water E.g. pond skaters ●●Water can be transported up the xylem in the transpiration stream as cohesion between molecules make long thin columns of water difficult to break |
|
|
|
Solvent |
●polar makes water really good solvent ●any polar mols like ions will dissolve well ●Negative ions will be attracted to positive end of water and VICE VERSA ●Water mols cluster around charged parts of solute;allows metabolic reactions like photosynthesis and respiration to take place in solution in cytoplasm |
|
|
|
Transport Medium |
●Water is a good solvent and remains liquid over wide range of temp means water is a good transport medium ●plasma in blood Mineral ions in xylem |
|

