![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What motion does the atlanto-occipital joint do? How many degrees? |
anterior/posterior. Such as nodding. 35 degrees. |
|
|
What are the three approaches for a sphenopalatine ganglion block? |
1) Transnasal 2) Greater palatine approach: located just medial to the gumline of the third molar on the posterior portion of the hard palate. The needle is advanced 2.5 cm through the foramen. 3) Lateral approach: through the coronoid notch. Advanced approximately 2 inches to the lateral pterygoid plate. |
|
|
What is the dural pouch lying just posteriorly to the gasserian ganglion called? |
The trigeminal cistern |
|
|
What cranial fossa contains Meckel's cave? |
the middle cranial fossa |
|
|
When performing a gasserian ganglion block, what foramen is the needle inserted through? |
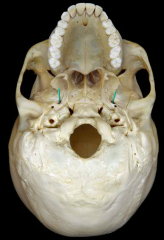
The foramen ovale (where the mandibular branch exits). |
|
|
How is a V2/V3 trigeminal nerve block done? |
through a trans-coronoid approach. Under fluoroscopy, a needle is passed perpendicularly at the coronoid notch to the lateral pterygoid plate. This will block both V2 (maxillary) and V3 (mandibular) branches. |
|
|
What are three pain pathologies that may affect the supraorbital nerve? |
1) Acute herpes zoster 2) Post herpetic neuralgia 3) Supraorbital neuralgia |
|
|
Where is the needle placed when performing a supraorbital nerve block? |
Just medial to the supraorbital foramen/supraorbital notch. Do not go into the foramen. |
|
|
Describe the technique for a radial nerve block at the elbow. |
Palpate the distal biceps tendon at the elbow. Insert a needle just lateral and aim medially and cephalad until paresthesias are felt. Aspirate. Inject ~12 ml of solution. |
|
|
Describe the technique for a medial nerve block at the elbow |
Identify the brachial artery just medial to the biceps tendon at the elbow. Go just medial to this, injecting 0.5 to 0.75 inches, aiming medially and cephalad. Aspirate. Then inject. |
|
|
Describe the technique for an ulnar nerve injection at the elbow |
The elbow is bent and arm abducted. The groove between the olecranon and medial epicondyle is palpated. Just proximal to this, a needle is advance 0.5 inches cephalad until paresthesias are felt. Inject about 5-7 ml of solution. |
|
|
Describe a radial nerve block at the wrist |
Inject medial to the radial artery and lateral to the flexor carpi radialis tendon |
|
|
Describe the technique for a median nerve injection at the wrist. |
Identify the palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis tendons approximately 2-3 cm proximal to the wrist. Insert the needle between the two, to a depth of about 0.5 inches. Aspirate. |
|
|
Describe the technique for an ulnar nerve injection at the wrist. |
Identify the FCU tendon at the crease. Insert a needle just laterally, aimed medially, about 0.5 inches. Inject. |
|
|
Describe the technique of a metacarpal nerve block |
have the patient rest their hand palm down. Identify the metacarpal head. Inject a total of 3 ml (total for entire metacarpus) anesthetic starting at the dorsal part of the head and advancing to near the palmar surface. Do this on both sides of the metacarpal head. |
|
|
Describe the technique of a digital nerve block |
Have the patient rest their hand palm down. Identify the dorsal aspect of the base of the fingers. Draw up a total of 3 ml of anesthetic for each finger. Insert the needle dorsally and slowly advance to the volar side of the bone while slowly injecting on each side. |
|
|
Describe the process of intravenous regional anesthesia |
An IV catheter is inserted into the distal extremity. Two blood pressure cuffs are applied over cotton cast padding. Inflate the upper cuff to 100 mg Hg over SBP. Inject 30-50 ml of lidocaine 0.5% for surgical anesthesia or other meds for things like CRPS. After 10 minutes, inflate the lower cuff and deflate upper. After ten minutes, deflate lower just below SBP for a few seconds then reinflate. Monitor for toxicity. |
|
|
What three nerves innervate the wrist joint? |
1) Deep branch of the ulnar nerve 2) Anterior interosseous nerve 3) Posterior interosseous nerve |
|
|
Describe the technique for a radiocarpal intra-articular injection |
Inject the area that is the junction of the lunate, scaphoid, and radius. This is just medial to the palmaris longus tendon and around the area of the groove between the thenar and hypothenar eminences. |
|
|
Describe the technique of an ilioinguinal nerve block |
Similar to a LFCN block except more medial and inferior. Identify the ASIS. Trace the inguinal ligament 2.5 inches medially and inferiorly. Insert a 1.5 inch needle toward the pubic symphysis between the external and internal oblique muscles. Inject. |
|
|
Describe the technique of an iliohypogastric nerve injection |
Similar to a LFCN block or ilioinguinal nerve block except only trace the inguinal ligament 1 inch medial and inferior from the ASIS. |
|
|
Where does the superior hypogastric plexus lie? The inferior? |
In front of L4. In front of L5. |
|
|
Describe the technique for a pudendal nerve block. |
This is not how it is described in Waldman, but how it could be done with fluoro: The pudendal nerve travels between the piriformis and coccygeus to exit out the greater sciatic foramen, go superficial to the sacrospinous ligament just medial to the ischial spine, and then back through the lesser sciatic foramen. Thus, it is likely best to block it just medial to the ischial spine with about 10-15 ml of injectate. |

