![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Development of Self Hint: self-image etc. |
A journey from: physical self recognition and self-awareness To Self description and self evaluation To Knowledge of standards and emotional response to wrongdoing |
|
|
Describe self concept/ a sense of self What does Cooley theory talk about? What does Erikson theory talk about? |
An individual actively thinks about themselves as a person, as distinct or seperate from other people. Cooley (1902): Looking-glass self How do others percieve How am I expected to act Erikson (1950, 1968): Stages of psychosocial development |
|
|
Role of the MPFC -Medial Prefrontal Cortex -Hippocampus |
-decision making, long term memory -decoding emotions, social communication -self regulation- modulates amygdala responses -links to emotional networks, memory networks -the MPFC lights up in scans when thinking about the self |
|
|
Infants
What helps infants increase their self awareness ? |
Cognitive development and social interaction (family) |
|
|
Infants develop Categorical self Understanding gender (age) When do infants become aware of their gender? |
Categorical self Begin to be aware of gender, age and other characteristics Eg. I am a boy, you are a girl. I am goof Understanding gender (18 months) By age 2, began to behave differently Boys: cars, trucks Girls: dolls, toys 2.5 - 3 yrs, they can verbally state it |
|
|
What age do toddlers begin to use personal pronouns? |
Age 2 |
|
|
Development of competence and self-esteem is due to? |
Secure relationship with primary caregiver. Which can give trust, autonomy, competence and self-esteem. |
|
|
PARENTING STYLES
Authoritative styles Pessimisive Authoritarian style |
Authoritative: -Reward child -Negotiate -Warm and loving have good grades According to Baumrind Pessimisive -loving and nuturing -give complete freedom without consequences
Authoritarian style -strict and give no attention -high standards -punitive -controlling |
|
|
Childhood How do they present themseleves? (describe themseleves) Preschool Middle childhood End of middle childhood |
Preschool -Concrete and physical -Base their ideas of set on observable features and behavioural characteristics Eg. I am a boy. I live in a big house. I like pizza. During Middle childhood Psychological & social qualities are incorporated into children's self-description by age 8. -personality trait terms eg. funny, smart -forming social identities eg. I am a second grader at XX school -more capable of social comparison eg I am faster at swimming than.. End of middle childhood Children are better able to integrate different traits and ideas about themseleves and awareness of context leading to selves |
|
|
Self esteem Self esteem becomes more differentiated or multi-multi-dimensional with age. -Preschoolers 2 aspects of self-eseem -Mid-elementary school -As children age |
-Preschoolers distinguish two aspects of self esteem: -Their competence (physical and cognitive) -Their personal and social adequacy (social acceptance) -By mid-elementary school, children differentiate among five apects of self-worth (Harter, 1996) -As children age, they combine their self perceptions in 5 distinct domains to form an overall, abstract sense of self-worth. |
|
|
What do we know about personality change? McCrae Roberts & Wood |
McCrae: personality traits "follow intrinsic paths of development essentially independent of environmental influences" Roberts & Woods: "personality traits in particular, remain open systems that can be influenced by the environment at any age" Personality change is an ongoing process through the life span |
|
|
Harter 1996 Multi-dimensional and Hierarchical |
[Overall self-worth] < > •Scholastic competence •Social acceptance •Behavioural conduct •Athletic competence •Physical appearance
The accuracy of childrens self-evaluations increases over the elementary school years. |
|
|
What is an ideal self |
A sense of what they "should" be like
•with age, the gap between the real self and the ideal self increases; which contributes to a decrease in average self-esteem from early to middle childhood |
|
|
What influences of self-esteem? |
-Heredity -Competence -Social feedback -Secure attachment to warm, democratic parents Self esteem is stable over the elementary school years |
|
|
Compared to childrens self-descriptions, those of adolescents become: |
-Less physical and more psychological -Less concrete and more abstract -Less generalised and more differentiated -Are more integrated and coherent -Are more self aware and reflective (eg which groups they fit into) |
|
|
Self esteem between childhood and early adolescence tends to decrease due to: |
-school transitions -puberty -social context and comparisons |
|
|
What is the process of identity formation? |
Experimentation with different roles and activities, discovering what fits their personality and what does not.
In the process of experimentation, identity evaluation occurs.
Period of psychological moratorium -> developmental "time out" explained by: Changing bodies -Cognitive growth that permits -systematic thinking -Social demands to grow up |
|
|
Draw Marcia's Identity Status Model |
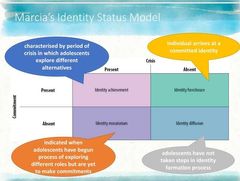
|
|
|
Erikoson -The adult-Psychosocial Growth Explain what is generativity vs stagnation- middle adulthood. |
Generativity: making use of time and helping others guide the mext generation. Stagnation: refers to failure to find way to contribute. Eg is everything going as planned. |
|
|
Erikson Old age: Integrity vs despair |
Finding a sense of meaning in life
Integrity: I've had a successful life Despair: I havent done what I wanted to do. |
|
|
How do older adults maintain positive self image |
Reduce the gap of ideal self and real self Changing standards of self evaluation |
|
|
The temperament in infants
Types of temperament in infants |
-Pre-determined at birth but environmentally influenced -Respond in predictable ways to events -Basis for later personality
Thomas and Chess -Easy temperament 40% -Difficult temperament 10% -Slow to warm up temperament 15% |
|
|
What is Continuity Discontinuity |
Continuity: individuals retain their rankings within a group Eg person who is extrovert as a young adult is more like to stay extroverted when old. Discontintuity: people change systematically in common directions over the years. |
|
|
What makes a personality stable over the life span? |
Heredity Lasting effects of childhood experiences Stable environments Gene-environment correlations |
|
|
What causes changes in personality over the life span? |
-Diseases that cause nervous system deterioration can cause moodiness, irritability
-Changes in the environment
-Poor for between person and environment |

