![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
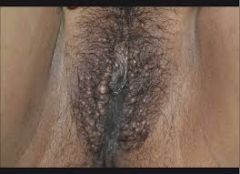
What does this image of the vulva show? what will the patient complain of? |
Fox-fordyce disease (series of pruritic, raised, yellowish retention cysts, resulting from keratin plugged apocrine glands) patient will complain of itch |
|
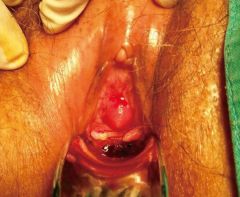
what does this image show? what will the patient complain of? when is it most commonly seen? |
There is inflammation and red growth on the distal edge of the urethra the patient will complain of vulvodynia (pain at vulva) usually found in children who have spontaneous prolapse of urethral epithelium, or in post menopausal women (vaginal epithelium contracts and leads to eversion of epithelium) |
|
what is this? when will the patient get this? what are the complaints and complications? |
vulvar varicosity Usually found during pregnancy or post partum patient will complain of discomfort at vulvar area There is a risk of thrombosis |
|
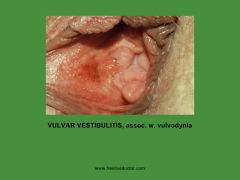
what is this? what will the patient present with? how to manage? |
vulvar vestibulitis (look out for multiple small eythematous dots, which are very tender on palpation) Severe introital dyspareunia and vulvar pain manage by giving topical estrogen cream, corticosteroids. Last option is surgical excision of glandular area |
|
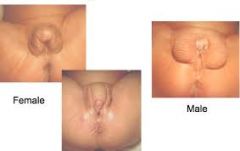
what is this? |
pictures showing ambiguous genitalia |
|
|
what is the approach to ambiguous genitalia? |
1) find out the genotype. It should be either: 46XX (F) 46XY (M) or, mosaic: 45XO/46XY 2) if patient is phenotypically female, and genotypically male: suspect androgen insensitivity syndrome 3) if patient is phenotypically male, but genotypically female: suspect congenital adrenal hyperplasia, or androgen producing tumor, or exogenous androgen |
|
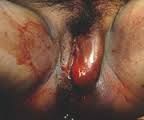
what is this? what is the treatment? why? |
vulvar hematoma Needs emergent surgical exploration and drainage, because blood loss can be extensive, tracking into large potential spaces of the ischiorectal fossae |

