![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are needles categorized by?
|
Needle body Needle eye |
|
|
Taper point needle
|
Sharp point pierces and penetrates the tissues without leaving small cuts Best used when a sealed suture line is needed |
|
|
Taper-cut needle |
Used with tough, fibrous tissue and some cardiovascular procedures |
|
|
Reverse cutting needle
|
Has 3 cutting edges on the point, makes a triangle, cutting edge is on the outside of the curve |
|
|
Cutting edge needle |
Has 3 cutting edge on point and body, the cutting edge is on the inside of the curve, most traumatic |
|
|
Why is cutting edge needle the most traumatic? |
The cutting edge on the inside of the curve cuts towards the edges of the wound compromising the strength of the tissue
|
|
|
Double-curve needle
|
Generally used in large animal surgery |
|
|
Halfcurve needle
|
Only half the body of the needle is curved
|
|
|
Full-curve needle |
The entire body of the needle involved in the curve |
|
|
What are the most common needle curve used? |
1/4 and 5/8 circle |
|
|
Single-eyed needles
|
Suture material passed through the needle eye Suture threaded through the eye from the inside of the curve to the outside |
|
|
French-eyed needle |
One complete eye and one split eye |
|
|
Swagged/Eyeless needle |
Needle and suture are attached to each other |
|
|
Tensile Strength
|
Amount of the force in lbs. per square inch (psi) that the suture can withstand before it breaks |
|
|
Memory |
Ability or tendency of the suture to return to its original packaged form. |
|
|
Flexibility
|
Partially determined by the size and material used to make suture |
|
|
Absorbability
|
Suture is either absorbable or non-absorbable |
|
|
Non-absorbable suture
|
remain intact for at least 2 yrs |
|
|
Absorbable suture |
Broken down by the body |
|
|
Capillarity
|
Ability of h suture to allow microbes to "wick" to the interior of the suture strand |
|
|
Multifilament/Braided |
HAs tow or more stands braided together to foem a single strand of suture |
|
|
Monofilament |
creates less frictions than multifilament making less tramatic |
|
|
Knot security
|
Some types of suture material hold knots better than other types |
|
|
Color
|
Easier identification after placement in tissue |
|
|
Criteria for selecting suture type and size |
Patient size Are of placement Strength required Healing potential of tissue Importance of appearance Cost |
|
|
How is individual packaged suture sterilized
|
Gamma radiation
|
|
|
Why would a DVM use staples |
Patient has post surgical incisional licking or tissue reaction to other suture material |
|
|
What suture type would you use instrument tie square knot?
|
Absorbable an silk, for ligation |
|
|
What suture type would you use instrument tie surgeons knot? |
Nylon polyester, and ploypropylene
|
|
|
Suture patterns are categorized by what? |
Apposing tissue edges, layer of tissue placement, method of placement (interrupted or continuous) |
|
|
SQ pattern |
|
|
|
SC Pattern
|
Placed just under the skin to eliminate the need for skin sutures |
|
|
Advantages of continuous sutures |
Minimal use of suture material and knots |
|
|
Disadvantages for using continuous sutures? |
If the line breaks whole suture is broke Bacteria can travel up the entire length of suture |
|
|
Advantages of interrupted sutures?
|
Minimized travel of bacteria |
|
|
Disadvantages of interrupted sutures?
|
More suture is used |
|
|
Dehiscence |
Rupture along surgical suture line |
|
|
Upon removal what should the LVT be looking at? |
No gaps in the incision, drainage, redness, or swelling |
|
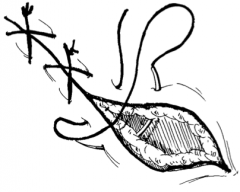
|
Cruciate matress
|
|
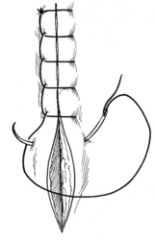
|
Ford Interlocking
|
|
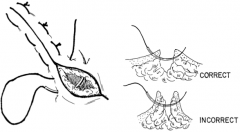
|
Horizontal Matress
|
|

|
Simple continuous
|
|
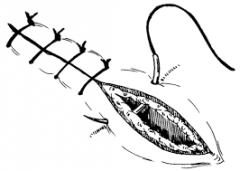
|
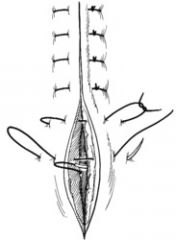
Simple Interrupted
|
|
|
Vertical Matress
|
|
|
What are the Brand name and absorbability of Nylon
|
Non-absorbable |
|
|
What are the Brand name and absorbability of Polyester
|
Non-absorbable |
|
|
What are the Brand name and absorbability of Polyglactin 910
|
Absorbable 56-70 days |
|
|
What are the Brand name and absorbability of Polyglycolic
|
Absorbable 120 days |
|
|
What are the Brand name and absorbability of Polypropylene
|
Surgilene, Prolene Non-absorbable |
|
|
What are the Brand name and absorbability of Polidioxanone
|
Absorbable 180 days |
|
|
What are the Brand name and absorbability of Silk
|
Non-absorbable |
|
|
What are the Brand name and absorbability of Chromic gut
|
Absorbable 60 days |
|
|
What are the Brand name and absorbability of Stainless steel
|
Non-absorbable |

