![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Alopecia
|
Alopecia
Deficiency of the Hair |
|
|
Pruritis
|
Pruritis
Itching |
|
|
Dermatitis
|
Dermatitis
Inflammation of the skin |
|
|
Necrosis
|
Necrosis
death of living tissue |
|
|
Histology
|
Histology
The science concerned with the minute structure of tissues and organs in relation to their function. |
|
|
Trauma
|
Trauma
A serious bodily injury or shock, as from violence or an accident. |
|
|
Abscess
|
Abscess
a localized collection of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue |
|
|
Ulcer
|
Ulcer
a break in skin or mucous membrane with loss of surface tissue,disintegration and necrosis of epithelial tissue, and often pus |
|
|
Laceration
|
Laceration
A jagged wound or cut. |
|
|
Excision
|
Excision
surgical removal or resection |
|
|
Cyanosis
|
Cyanosis
A bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes resulting from inadequate oxygenation of the blood |
|
|
Biopsy
|
Biopsy
The removal and examination of a sample of tissue from a living body for diagnostic purposes. |
|
|
Mycosis
|
Mycosis
infection with or disease caused by a fungus |
|
|
Systemic
|
Systemic
Relating to or affecting the entire body or an entire organism |
|
|
Cancer
|
Cancer
a malignant tumor of potentially unlimited growth that expands locally by invasion and systemically by metastasis |
|
|
Benign
|
Benign
Not life-threatening or severe, and likely to respond to treatment, as a tumor that is not malignant. |
|
|
Plantar
|
Plantar
Of, relating to, or occurring on the sole. |
|
|
Palmar
|
Palmar
of, relating to, or involving the palm of the hand |
|
|
Rostral
|
Rostral
situated toward the oral or nasal region |
|
|
Caudal
|
Caudal
Of, at, or near the tail or hind parts; posterior. |
|
|
Cranial
|
Cranial
of or relating to the skull or cranium |
|
|
Distal
|
Distal
situated away from the point of attachment or origin |
|
|
Proximal
|
Proximal
situated next to or near the point ofattachment or origin |
|
|
Dorsal
|
Dorsal
Of, toward, on, in, or near the back |
|
|
Ventral
|
Ventral
Relating to or situated on or close to the abdomen |
|
|
Abduction
|
Abduction
the movement of a limb away from the midline of the body |
|
|
Adduction
|
Adduction
Movement of a limb toward the midline of the body |
|
|
Rotation
|
Rotation
the turning of a body part about its long axis as if on a pivot |
|
|
Flexion
|
Flexion
a bending movement around a joint in a limb |
|
|
Extension
|
Extension
a forward raising of the arm or leg by a movement at the shoulder or hip joint |
|
|
Lateral
|
Lateral
of or relating to the side |
|
|
Medial
|
Medial
lying or extending in the middle |
|
|
Recumbency
|
Recumbency
the state of leaning, resting, or reclining |
|
|
Dorsal Recumbency
|
Dorsal Recumbency
denoting a position more toward the back surface than some other object of reference |
|
|
Ventral Recumbency
|
Ventral Recumbency
lying on abdomen with front legs folded under the body |
|
|
Exfoliation
|
Exfoliation
Detachment and shedding of superficial cells, in flakes |
|
|
Ecdysis
|
Ecdysis
the act of molting or shedding an outer cuticular layer |
|
|
Dorsoventral
|
Dorsoventral
extending from the back to the belly |
|
|
Ventrodorsal
|
Ventrodorsal
extending from a ventral to a dorsal surface |
|
|
Intra-
|
Intra-
A prefix meaning "inside" or "within," as in intravenous, within a vein. |
|
|
Inter-
|
Inter-
Between; among |
|
|
Extracellular
|
Extracellular
Located or occurring outside a cell or cells. |
|
|
Purulent
|
Purulent
Containing, discharging, or causing the production of pus. |
|
|
Four types of tissue:
|
Four types of tissue:
Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial tissue |
|
|
Types of Muscle Tissue:
|
Types of Muscle Tissue:
Skeletal Smooth Cardiac |
|
|
Where the Nervous Tissues is Found:
|
Where the Nervous Tissues is Found:
brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves |
|
|
What Does Mucus Membrane Color Indicate?
|
What Does Mucus Membrane Color Indicate?
Oxygenated Hemoglobin in the Blood |
|
|
What does CRT Indicate?
|
What does CRT Indicate?
Blood Pressure |
|
|
Steps of Healing Tissue:
|
Steps of Healing Tissue:
Inflammatory Phase Proliferative Phase Remodeling Phase |
|
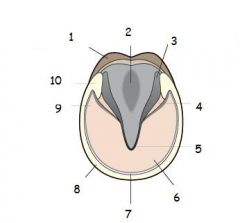
Name the parts of the Hooves:
|
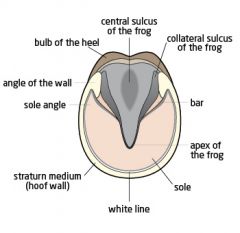
Name the parts of the Hooves:
|
|
|
Composition of Reptilian Skin:
|
Composition of Reptilian Skin:
Epidermis: characterized by complete covering of keratin 3 Layers in the Epidermis: Stratum corneum: heavily keratinized outer layer. Intermediate zone: composed of stratum germinativum cells in various stages of development. Stratum germinativum: the deepest layer, consisting of cuboidal cells. Undergoes mitosis to form the intermediate zone. Dermis: consists of connective tissue. |
|
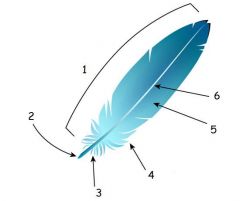
Composition of Feathers:
|
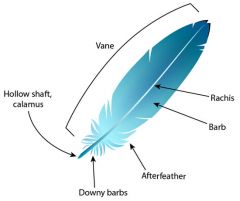
Composition of Feathers:
|
|
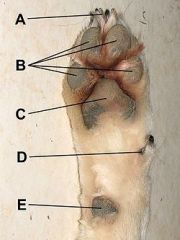
Composition of Paw Pad:
|
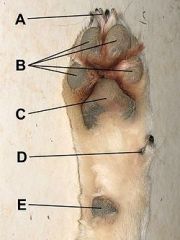
Composition of Paw Pad:
A) Claw, B) Digital Pads, C) Metacarpal Pad, D) Dew Claw, E) Carpal Pad. |
|
|
Composition of Dog Hair:
|
Composition of Dog Hair:
Undercoat: Keeping warm Guard Hair: Protect the skin from superficial injuries and form an additional layer of insulation to protect the dog from cold weather. Whiskers: Function as sensory structures for the dog. Double Coat: Dogs provided with extra insulation bred for freezing conditions. |
|
|
What Do Mast Cells Release During an Allergic Reaction?:
|
What Do Mast Cells Release During an Allergic Reaction?:
Histamine |
|
|
Sensory Receptors of Snakes:
|
Sensory Receptors of Snakes:
Jacobson’s organ: The tongue flicks out, picking up odors and carrying them to the roof of the mouth into contact with a sensory receptor Electromagnetic: Vibrations detected of prey in rattlesnakes Thermoreceptors: Some snakes hunt their prey using body heat. |
|
|
Polled Breeds:
|
Polled Breeds: The use of polled genetics in breeding programs
|

