![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Crater |
Funnel-shaped opening at the top of a volcano |
|
|
Caldera |
Formed when a part of a wall collapses following an explosive eruption |
|
|
Viscosity |
Liquid's thickness and stickiness |
|
|
Temperature of magma affects it's viscosity |
The higher the temperature of magma is, The lower its viscosity is. |
|
|
Silica content of magma affects it's viscosity |
Magma's with high silica content are more vicious than those with low silica content |
|
|
Gas of magma affects it's viscosity |
Gas dissolved in magma tends to increase its ability to flow. Loss of gases makes magma more vicious |
|
|
Phreatic or Hydrothermal |
Hot rocks come in contact with water |
|
|
Phreatomagmatic |
Contact between water and magma |
|
|
Strombolian |
Fountain lava |
|
|
Vulcanian |
Tall eruptions that reach up to 20km high |
|
|
Plinian |
Excessively explosive type of eruption of gas and pyroclastics |
|
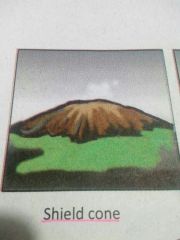
Shield volcanoes |
Formed by the accumulation of lava |
|

Cinder cone |
Built from ejected lava fragments |
|
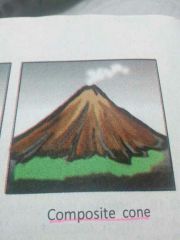
Composite cones |
Nearly perfect sloped structure. Solidification of both lava and pyroclastic deposits |
|
|
Geothermal Energy |
Source of energy that is in the heat from the earth's interior |

