![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
156 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are plasma membranes?
|
Specialized biological membrane which separates the cell from the outside world.
|
|
|
What are organelles?
|
Secondary compartments within the cytoplasm
|
|
|
What are ribosomes? How are they identified histiologically?
|
Organelles which translate mRNA to protein product; intensely basophilic.
|
|
|
How are ribosomes found within cells?
|
Free (or soluble); translate protein destined for use by cell
OR Attached (insoluble); translate protein to be exported |
|
|
What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum? Describe structure, function and staining properties.
|
Continuous membrane shaped into flattened cisternae , saccules which can expand and contract as necessary for protein synthesis. Location of protein synthesis, ribosomes are located so as proteins grow they are inserted into the RER. Stains basophilic.
|
|
|
What is the Smooth endoplasmic reticulum? What do they stain?
|
Tubular/non continuous membraneous cisternae, contain enzymes for metabolism, detox, fatty acid conversion, hormone/lipoprotein synthesis.
Stains eosinophilic |
|
|
What is epithelial tissue?
|
Tissue that lines almost every surface of organs and tissue with a high density. Avascular tissue that functions to protect, absorb, excrete, secrete.
|
|
|
What are the types of epithelial tissue?
|
Simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, stratified squamous, pseudostratified columnar, Transitional
|
|
|
What is the types of simple squamous epithelial tissue?
|
Thin cells with bulging nuclei; can be mesothelial (line inner structures and organs) and endothelium (line blood vessels, heart and lymphatic)
|
|
|
What are the edges of epithelial cells called?
|
Apical, basal, lateral
|
|
|
What are simple cuboidal epithelial cells?
|
Are as tall as they are long; centrally located nucleus, are in a single layer. Line secretory or absorptive tissues
|
|
|
What are simple columnar epithelial cells?
|
Taller than long, centrally located nucleus, arranged in single layer. Line secretory and or absorptive surfaces and ducts (intestinal)
|
|
|
What are stratified squamous epithelial cells?
|
Multiple layers of thin cell stacks, basal cells thicker than apical cells. Resists friction/abrasion (skin)
|
|
|
What are pseudostratified columnar cells?
|
Single layer of epithelial cells where all cells touch basilar surface, but not touch apical surface.
|
|
|
What is significant about the pseudostratified columnar cells?
|
In times of stress (colds) tissue can become stratified squamous to better protect system.
|
|
|
What are transitional epithelial cells?
|
Cells that accommodate stretching; Cells can slide all over one another and can have many layers to one. They appear scalloped and cobblestoned. Seen in the bladder.
|
|
|
What are desmosomes?
|
Plaque (filaments) between adjacent cellular membranes; intermediate filaments mechanically anchor the plaque.
|
|
|
What are tight junctions?
|
Fused membranes The outer layer of contiguous cells is shared.
|
|
|
What are the functions of tight junctions?
|
To create an effective barrier against materials passing from lumen to basilar sides between adjacent cells near apical border.
|
|
|
What are gap junctions?
|
Connection between contiguous cells with very small openings that allow electrolytes to pass through.
|
|
|
What are zonular adherins?
|
Similar to desmosomes, intermediate filamentsact as anchors at attachment site; circumscribe whole cells and can withstand some stretching (think of wire in a pipe cleaner)
|
|
|
What is a terminal bar?
|
Representation of groups of various junctions; they are dark staining spots at the apical pole of adjacent epithelial cells.
|
|
|
What is a basal lamina?
|
Layered structure that is specialized connective tissue matrix adjacent to the basilar surface of epithelial.
|
|
|
What are hemi-desmosomes?
|
Structures allowing cell to attach to the basal lamina
|
|
|
How are basal lamina noted on a slide?
|
Because they have many complex sugars they can easily be stained as eosinophilic
|
|
|
What are microvilli?
|
Tiny finger like projections at apical pole of cell. Create a brush border. They can extend and retract to create more/less surface area.
|
|
|
What are stereocilia?
|
Non motile tubular surface projections; VERY long microvilli
|
|
|
What are kinocilia?
|
Highly motile wide surface projections, composed of microtubules. Can move things away from lining (ie mucus)
|
|
|
What are the types of connective tissue?
|
Bone, Cartilage, Connective tissue proper
|
|
|
Why is connective tissue unique?
|
It's ability to change and respond frequently to inflammation and other environmental changes.
|
|
|
What are the elements found in connective tissue?
|
Fibers, water, molecules that hold water in place (complex sugars)
|
|
|
What is used to identify the specific classifications of connective tissue?
|
Differing amounts of cells, fibers and space
|
|
|
What is loose irregular connective tissue?
|
Tissue that has more "space" than fibers.
The cellularity varies; few fibers In life it is soft and pliable Irregular directions of fibers |
|
|
What is dense irregular connective tissue?
|
More fibers than space,
fewer cells, Large amounts of wavy fibers in many directions In life, firm and resistant to compression, withstands forces in multiple directions (like soles of feet) |
|
|
What is dense regular connective tissue?
|
More fiber than space
Fibers arranged in parallel, few cells in life. Example; tendons, ligaments Irregular force at tangental directions can cause problems In life very firm, resistant to strong directional force |
|
|
What is Adipose tissue?
|
Predominant feature is adipocyte (fat cell)
Location is dependent to conservation of heat and mechanical cushioning Energy storage |
|
|
What are the functions of connective tissue proper?
|
1. Connect, suspend and form shape
2. Insulate and cushion (adipose) 3. Storage (adipose) 4. Repair and regeneration |
|
|
What is mesenchyme?
|
Embryonic cells that lack fibers; not typically found in adults. Are pluripotent. Where stem cells found.
|
|
|
What is a fibroblast?
|
Elongated cells, with oval shaped nucleus. They make connective tissue elements and can signal to other connective cells for other cellular needs. Play large role in final process of healing. Active cells enlarge to rounded cells (ER expanded)
|
|
|
What is a fibrocyte?
|
Fibroblast that is quiescent
|
|
|
What is a macrophage?
|
Large cell with an irregular to round shape that originate from monocytes of the immune system. Phagocytic function and producer of many other connective tissue elements and inflammatory responses. Cytoplasm typically contains debris, and lysosomes.
|
|
|
What are plasma cells?
|
Small in size, dark round eccentrically located nucleus and a large area not stained (or lightly eosinophilic). This area produces immunoglobin which accounts for enlarged golgi apparatus . Derived from B cells in immune cell. Found where there is antigenic challenge (Gi tract, respiratory system).
|
|
|
What are pericytes?
|
Cells found wrapped around vessels and capillaries' surrounded by basement membrane adjacent to endothelial cell. Capable of migrating away from the vessel and differentiating into other CTs (due to cytokines or other signals). It is protected by a basal layer, but very responsive.
|
|
|
What are the types of fat cells an how to they differ?
|
White fat cells, Brown fat cells.
White fat has large lipid droplet; brown fat has multiple fat droplets and is found in young and hibernating animals. Brown fat has a central round nucleus. White fat has a nucleus that is flattened at the edge. |
|
|
What are mast cells?
|
Large cell with round nucleus. Cytoplasm is completely filled with granules. Found near blood vessels and organ tubes near smooth muscle. Are involved in epithelial secretory activity, smooth muscle responses to antigenic activity and complex inflammatory activity.
|
|
|
What are the types of chemicals found in mast cells?
|
Heparin (anti-clotting factors), histamine (smooth muscle tone), proteases, esterases
|
|
|
What are lymphocytes?
|
Typically B cells, immune surveillance cells found in epithelial tissue.
|
|
|
What are reticular cells?
|
Found in lymphoid cells; form a reticulum or network to form a structure. They only make reticular fibers, type III collagen. Very large nucleus with extending fibers. Create a filter for blood and lymph to be passed through.
|
|
|
What are melanocytes?
|
Pigment producing cells found within epithelial cells.
|
|
|
What are collagen fibers?
|
Thick fibers; several types exist. Most popular type of fiber.
|
|
|
What are elastic fibers?
|
Thin, pliable fibers.
|
|
|
What are the functions of the biological membrane?
|
Selective permeability, compartmentalization, structural integrity, recognition, etc
|
|
|
What is a plasma membrane?
|
Specialized cell membrane which separates the cell from the environment. Not visible with light microscope
|
|
|
What is the Golgi complex?
|
Flattened stacks of membrane cisternae and vesicles. Modifies newly translated proteins for their target destination. The fedex of the cell! Is chromophobic.
|
|
|
What are peroxisomes?
|
Vesicles that contain neutral active enzymes (catalase) that regulate oxygen; important for metabolism and detox functions.
|
|
|
What are lysosomes?
|
Basophilic (they are acidic) vesicles that contain enzymes for degradation and metabolism. Recycling center of the cell.
|
|
|
What are mitochondria?
|
Organelles that convert energy within the cell (ATP). Large amount of membraneous folds.
|
|
|
What are microtubles?
|
Structural proteins that contribute to the cytoskeleton, cell shape and polarity. Also control and stabilize intracellular organelle traffic.
|
|
|
What are centrioles?
|
Subunits are three microtubles, the center of microtuble assembly and movement
|
|
|
What are is the function of intermediate filaments?
|
Orientation of structural elements and anchoring of structures to the cell surface
|
|
|
What is the function of microfilaments?
|
Contractile proteins that act as structural links between other molecules. Involved in muscle contraction, cell locomotion, etc
|
|
|
What is heterochromatin and what does it stain?
|
Highly condensed, transcriptionally INACTIVE DNA complexed with histone proteins.
Stains BASOLPHILIC |
|
|
What is euchromatin?
|
Less condensed transcriptionally active DNA complexed with histone proteins
|
|
|
What are the phases of mitosis?
|
Prophase: chromatin condenses
Metaphase: chromosomes align in center of nucleus Anaphase: Chromosomes split to centrioles Telophase: Chromatin uncoils, cytoplasm divides. Interphase: duplication of cytoplasmic organelles |
|
|
Define Parenchyma
|
The cells that make up an organ
|
|
|
What is the histologic appearance of collagen fibers?
|
Orange to orange PINK by H and E staining. Typically wavy, interlacing strands of varying thickness
|
|
|
What is the histologic appearance of elastic fibers?
|
Pale pink with H and E.
|
|
|
Where are reticular (Type III) collegen fibers typically located?
|
Lymph nodes and organs, bone marrow. Require special stain to see.
|
|
|
What are chondroblasts?
|
cartilage cells capable of division and matrix production; very active.
|
|
|
What are chondrocytes?
|
cartilage cells do not divide, maintain the matrix.
|
|
|
What are chondroclasts?
|
specialized cartilage cells that break down matrix, fused blood borne monocytes
|
|
|
What are fibroblasts?
|
Found along periphery of cartilage; divide and produce matrix
|
|
|
What type of fibers dominate the matrix of cartilage?
|
collagenous type II
|
|
|
Is cartilage vascular or avascular?
|
AVASCULAR
|
|
|
What type of tissue is cartilage?
|
Connective tissue
|
|
|
Why are you unable to see collagen fibers in cartilage?
|
It is very high density
|
|
|
How can you determine chondroblasts from chondrocytes?
|
The euchromatin and heterochromatin
|
|
|
What is the perichondrium?
|
Lies along the edge of cartilage next to other connective tissue. Typically are able to see connective tissue
|
|
|
What is hyaline cartilage?
|
Bone forming sites of developing animals. Matrix composed of collagen fibers, dense regular CT and ground substance
|
|
|
What cells are found in hylaine cartilage?
|
Chondrocytes
|
|
|
What are some examples of hyaline cartilage?
|
Articular surfaces, respiratory tract, larynx, nose
|
|
|
What cells are present within elastic tissue?
|
Chrondrocytes
|
|
|
How is elastic cartilage differentiated from hyaline cartilage?
|
The visible elastic fibers stain BRIGHT pink with H&E
|
|
|
Where is elastic cartilage typically present?
|
External ear, auditory canal, epiglottis
|
|
|
What is the lacunae?
|
The clear area surrounding the nucleus of a chrondroblast and chondrocyte
|
|
|
What is fibrocartilage?
|
Specialized cartilage that is never found along (no perichondrium). Extremely strong, and arranged in orderly fashion.
|
|
|
How is fibrocartilage differentiated from other cartilage?
|
They contain large amount of Type II collagen fibers.
|
|
|
Where is fibrocartilage present?
|
Intervertebral discs, ligament/tendon attachments, joint menisci, pubic symphesis
|
|
|
What is interstitial growth in cartilage?
|
Chondroblasts divide and secrete matrix between daughter cells or along the perichondrium
|
|
|
What is appositional growth?
|
Growth occurs along edges of pre-existing outer and cartilage boundary
|
|
|
What are osteoblasts?
|
Large bone forming cells capable of dividing. Found along the bone forming surface.
|
|
|
What type of collagen do bones cells produce?
|
Type I cartilage
|
|
|
How and where are osteoblasts located?
|
Appear almost cuboidal; along bone forming surface
|
|
|
What are osteocytes?
|
Celled embedded in the boney matrix; cellular processes make contact with adjacent osteocytes
|
|
|
What are osteoclasts?
|
Cells within the bone that have brush borders; they break down mineralized inorganic matrix. Surrounded by erosion lacunae
|
|
|
Where are osteocytes located within a bone?
|
A columns around the vessels within the bone
|
|
|
What are osteoblasts?
|
Large bone forming cells
Capable of dividing Found along a bone forming surface |
|
|
What are osteocytes?
|
Cells embedded in the bony matrix
Cellular processesmake contact with adjacent osteocytes/blasts through canaliculi |
|
|
What are osteoclasts?
|
Cells within bone that break down mineralized inorganic matrix with hydrolytic enzymes and acids.
Surrounded by erosion lacunae |
|
|
What are the components of the matrix of the bone?
|
Fibers and ground substances
|
|
|
What is an osteoid?
|
Organic component of the matrix; Composed of collagen type I
Provides tensile strength |
|
|
What is ground substance?
|
The inorganic components of the bone matrix
Provides the compressive strength of the bone |
|
|
What are the two major types of bone?
|
Lamellae
Woven Bone |
|
|
What are the types of lamellar bone?
|
Compact and spongy
|
|
|
What is an osteon?
|
A tubular unit within compact bone which contains the lamellae (layers), and haversian canals (containing blood vessels)
|
|
|
What is a volkman canal?
|
Perforating branches of the osteon which connect to other osteons
|
|
|
What are canaliculi?
|
Connect neighboring lacunae of osteocytes and allow cell to cell contact
|
|
|
What is the lining of all inner surfaces of compact bone referred to as?
|
Endosteum
|
|
|
What is the periosteum?
|
Specialized outer covering of compact bone. Highly vascularized and innervated
|
|
|
How is spongy bone characterized?
|
Contains more non-bony space than bone
Bony trabeculae or spicules of bone are found within large areas of space |
|
|
How is spongy bone an adaptation?
|
It provides strength while not adding weight, very advantageous for birds
|
|
|
What is woven bone?
|
Immature bone that under normal circumstances is always replaces by lamellar bone
|
|
|
What are the zones of ossification within the epiphysis?
|
Zone of resting (non dividing cartilage)
Zone of Proliferation (wedge shaped actively dividing) Zone of Maturation (columns of maturing chondrocytes) Zone of Calcification (large cells with thin intercellular membranes) Zone of Ossification (Ossifies matrix partially eroded by perivascular cells) |
|
|
What is articular cartilage?
|
3 layered cartilage (superficial, intermediate, deep). Has no periosteum.
|
|
|
What does the tide line differentiate? Where is it found?
|
Non mineralized and mineralized matrix; found within the deeper zones of articular cartilage
|
|

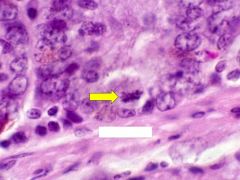
What are the structures indicated?
Why do they stain basophilic? |
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes located on the rough ER have high amounts of RNA (an acid) which stains intensely basophilic) |
|
|
What are the eosinophilic regions indicated?
|
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|

What is the eosinophilic region indicated?
|
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|

What are the chromophobic regions indicated?
|
Golgi Apparatus
|
|

What structures are indicated?
|
Lysozymes
|
|

|
1. Euchromatin
2. Heterochromatin 3. Nucleolus |
|

|
Prophase
|
|
|
Metaphase
|
|

|
Anaphase
|
|

|
Telephase
|
|

|
Simple Cuboidal
|
|

|
Simple Squamous
|
|

|
Simple columnar
|
|

|
Stratified Squamous
|
|

|
Transitional
|
|
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar
|
|
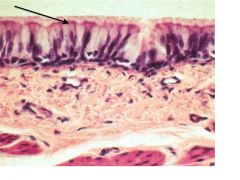
|
Pseudostratified Columnar
|
|

|
Terminal Bar
|
|

|
Terminal Bar
|
|
|
|
Basal Laminae
|
|

|
Basal Laminae
|
|

|
Kinocilia
|
|

Name this tissue
|
Loose irregular Connective tissue
|
|
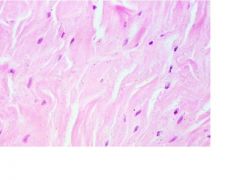
Name the type of tissue
|
Dense irregular connective tissue
|
|

Name the type of tissue
|
Dense Regular Connective tissue
|
|

What cells are indicated?
|
macrophages
|
|

What cells are indicated?
|
Plasma cells
|
|

What fibers are shown?
|
Elastic Fibers
|
|

What cells are shown?
|
Fibroblasts
|
|

What cells are shown?
|
Lymphcytes
|
|

What type of tissue is shown?
|
Brown fat
|
|

What are the cells shown?
|
Mast cells
|
|

What tissues are shown?
|
Reticular fibers
|
|

Label the image
|
1. Chondroblasts
2. Lacunae 3. Cell Nest 4. Perichardium |
|

|
Elastic fibers of elastic cartilage
|
|

|
Lacunae
|
|

|
Fibrocartilage
1. Cells (chondrocytes) 2. Fibers |
|

What type of cartilage is shown?
|
Fibrocartilage
|
|

What type of tissue is shown?
Label the indicated structures |
Compact Bone
1. Central Canals 2. Osteocytes, with Lacunae |
|

What tissue is shown?
What type of cells are shown? |
Spongy bone
Osteoblasts |
|
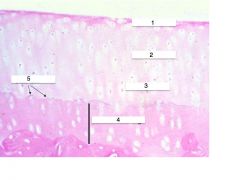
What type of tissue is shown?
Label the indicated structures or areas |
Articular Cartilage
1. Superficial 2. Intermediate 3. Deep 4. Calcified Cartilage 5. Tide Line |

