![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epidemiology
|
The study of how disease is distributed in populations and the factors that influence or determine the distribution
|
|
|
Objectives of epidemiology
|
1. Identify the cause of disease
2. Determine the extent of disease 3. Study the natural history of disease 4. Evaluate preventative measures, therapies, etc. 5. Science-based public policy |
|
|
Test sensitivity
|
How well does the test identify those with disease?
|
|
|
Test specificity
|
How well does the test rule out those who do not have disease?
|
|
|
Primary prevention
|
Protecting the non-infected
|
|
|
Secondary prevention
|
Detecting the pre-clinical
|
|
|
Tertiary prevention
|
Reducing the impact of clinical disease
|
|
|
Endemic
|
The usual occurrence of a disease within a given area
|
|
|
Sporadic
|
Separate or scattered disease incidents occurring at low frequency
|
|
|
Epidemic/Outbreak
|
More disease than expected for a given time and place
|
|
|
Pandemic
|
Epidemic affecting several continents
|
|
|
Incubationary carrier
|
Pre-clinical, many organisms being shed
|
|
|
Convalescent carrier
|
Continues to harbor and shed organisms for a variable period of time following recovery
|
|
|
Transient carrier
|
Subclinical but may shed organisms for variable periods
|
|
|
Chronic carrier
|
Organisms are shed for long periods of time
|
|
|
Reservoir
|
Any animal, arthropod, plant, soil, or inanimate matter in which an infectious agent normally lives and multiplies or on which it depends primarily for survival and reproduces in such a way that it can be transmitted to a susceptible host
|
|
|
Nidus
|
A localized reservoir that persists over a very long time period
|
|
|
Vehicle
|
An object, substance, or non-receptive living being serving as an intermediary in transmitting a pathogen from the organism hosting it to a receptive host
|
|
|
Vector
|
A living creature which acquires a pathogen from one living host and transmits it to another
|
|
|
Fomite
|
An object or material that can transfer pathogens on its surface
|
|
|
Incubation period
|
The time between exposure to the pathogen and the onset of clinical signs
|
|
|
Latent infection
|
Inapparent infection that has the potential to develop signs of disease
|
|
|
Source of infection
|
The animal, person, or object from which an infectious agent passes immediately to the host
|
|
|
Intrinsic host factors
|
"From within" host factors
1. Species 2. Age 3. Breed 4. Gender 5. Physiological state 6. Disease history |
|
|
Extrinsic host factors
|
"Outside" host factors
1. Use of animal/occupation in humans 2. Husbandry in animals/socio-economic status in humans |
|
|
Infectivity
|
An agent factor
Ability of the agent to ledge and multiply within the host; minimum number of infectious particles required to establish an infectious |
|
|
Infectiousness
|
An agent factor
The ease with which the agent is transferred to another |
|
|
Pathogenicity
|
An agent factor
The ability to produce disease |
|
|
Virulence
|
An agent factor
The degree of pathogenicity; the disease-evoking power of a microorganism in a given host |
|
|
Host range
|
An agent factor
The range of hosts in which an agent can survive |
|
|
Viability
|
An agent factor
Ability of an infectious agent to survive in the environment |
|
|
Environmental factors
|
Physical aspects of the environment: temp, pressure, humidity, etc.
Biological aspects of the environment: presence of reservoirs, vectors, herd immunity |
|
|
Horizontal transmission
|
Transmission of disease among peers
|
|
|
Vertical transmission
|
Transmission of disease between generations
|
|
|
Direct transmission
|
Person to person, animal to animal, person to animal
|
|
|
Indirect transmission
|
Transmission via a common vehicle or vector
|
|
|
Expiratory droplet
|
Direct transmission
Produced by a cough or sneeze and deposited in the respiratory tract according to size |
|
|
Droplet nuclei
|
Indirect transmission
Truly airbourne, evaporated expiratory droplets and other fluids that are inhaled into the alveoli Ten times more infectious than expiratory droplets |
|
|
Disease
|
An abnormality of structure or function that interferes with the well-being of the individual animal or results in decreased production, growth, or efficiency
|
|
|
Clinical disease
|
Outward manifestation of disease (signs or symptoms)
|
|
|
Pre-clinical disease
|
Not yet clinically apparent but will be in the future
|
|
|
Subclinical disease
|
Not clinical and will not be in the future
|
|
|
Herd immunity
|
Resistance of an "at risk" population to an attack by a disease to which a large proportion of the group are immune
|
|
|
Epidemic
|
An increase in the number of cases in a given time and place over the number expected
|
|
|
Index case
|
The first recognized case of a disease in an outbreak
|
|
|
Retrospective cohort study design
|
Determine exposures among each individual in the entire population at risk and determines whether or not disease occurred in each individual
|
|
|
Case-control study design
|
Identify a group of individuals from the population at risk with the disease and find out about their exposures. Compare to a group of individuals from the same population at risk WITHOUT disease and find out about their exposures.
|
|
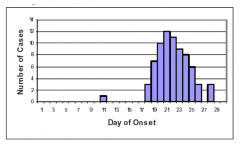
|
Common source outbreak with point source exposure
|
|
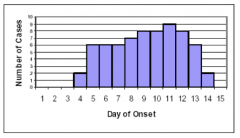
|
Common source outbreak with continuous exposure
|
|
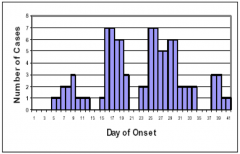
|
Common source outbreak with intermittent exposure
|
|
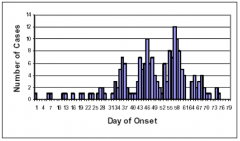
|
Propagated outbreak
|

