![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
131 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define HCM
|
Felines -concentric thickening of L ventricular and septal myocardium w/decreased ventricular complicance and dysfunction during systole
|
|
|
Why does CHF occur in HCM?
|
LV thickens and loses compliance> vol builds up in LA and dilates>mitral valve regurg
|
|
|
How do you get (systolic/diastolic (pick one)) failure with HCM?
|
Hyptertrophy of LV>decreased ventricular compliance>diastolic dysfunction>dilated LA>pulmonary edema
|
|
|
What is SAM, and what does it cause?
|
Systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve causes mitral regurg and obstruction of the LVOT.
|
|
|
What is HOCM?
|
Hypertrophy of the LV with obstruction of outflow of the LV. Blocks bloodflow, decreasing ventricular compliance (can't hold as much blood or pump as well.
|
|
|
Name 4 diseases that can cause 2ndary LV Hypertrophy in cat
|
Hypertension
Hyperthyroid Aortic Stenosis Acromegaly |
|
|
How diagnose DCM in a cat?
|
rads - globoid heart
|
|
|
Does Feline DCM result in systolic or diastolic failure, and how is it treated?
|
Systolic
Pimo Furosemide Aspirin Taurine |
|
|
How do you treat pulmonary edema of Felines?
|
Cage rest
Lasix Nitroglycerine Aspirin |
|
|
How do you treat HCM or CHF in cats?
|
Diltiazem
Altenolol Aspirin Enalapril |
|
|
What does diltiazem do?
|
V HR
dilates arteries relax heart SID |
|
|
What does Altenolol do?
|
V HR
Antiarrhythmic Relieves outflow obstruction |
|
|
Name 8 major 2ndary causes of canine cardimyopathy.
What's the primary cause? |
Taurine
Carnitine - (cockers/boxers) Endocardial Fibroelastosis Doxorubicin-induced myocardial failure Tachycardia-" " Parvo Trypanosoma cruzi Neoplasia Idiopathic |
|
|
How is DCM diagnosed?
|
HF signs
acute wt. loss 85% will have Afib Generalized cardiomegaly dilated A/V on Echo |
|
|
What causes sudden death with DCM? How is it treated?
|
Ventricular arrhythmias; lidocaine
|
|
|
Tx for primary DCM in dogs
|
Lasix
Cage rest dig or pimo + inotropes Vasodilators |
|
|
Name some + inotropes
|
dopamine
dobutamine Amrinone |
|
|
Name some vasodilators
|
nitrol ointment
nitroprusside Hydralazine enalapril |
|
|
How do you treat DCM in dogs LONG TERM?
|
Lasix
Pimobendan Enalapril Mexilitine/Sotalol Taurine in Goldens, Newfies, and Cockers |
|
|
How to treat pulmonary edema from DCM?
|
Vasodilators
|
|
|
What common arrhythmias occur with DCM?
|
Ventricular arrhythmias (boxers, dobies)
Afib - 85% Sinus tach when start HF |
|
|
About Doberman DCM
|
Autosomal Dominant gene
die w/in 3mos of diagnosis heart is enlarged but not globoid diffuse pulmonary edema Super Sensitive to digoxin Poor prognosis - sudden death from VPCs (tx with Altenolol/Sotalol) Holter monitor yearly after 3yo |
|
|
Cocker DCM
|
Only small/med dogs that get DCM
Super prone to endocardiosis of mitral valve Have to echo to differentiate. Tx w/ Lasix Dig/pimo enalapril Taurine L-carnitine May be able to wean off drugs |
|
|
Boxer Cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
|
Autosomal Dominant inheritance
Ventricular arrhythmias syncope/collapse are main signs ECG - vent arrhythmias Dx with rads/Holter monitor with proper tx, 50% alive longer than 1 yr |
|
|
What are the DDx for ARVC (boxer cardiomyopathy)?
|
DCM
Tumor Seizures |
|
|
How do you treat ARVC?
|
Acute: Lidocaine
Long term: Mexiletine+/-altenolol If SVa, add dig to start and transition to diltiazem/altenolol. |
|
|
Myocarditis and causes
|
inflamm'n of the myocardium (LA)
Causes: Anything. Bacterial Viral Parasitic Degenerative Tumors |
|
|
How tx Myocarditis?
|
Rest for >1 mo, abx for infections
|
|
|
DCM in LA?!?
|
Yeah. Think monensin in horses. Pooooor prognosis.
Think glue factory. |
|
|
Causes of systemic hypertension
|
Will appear normal!
CRF Hyperthyroid Neurogenic Pheochromocytoma Arteriosclerosis Cushing's DM |
|
|
Treatment for systemic hypertension
|
Amlodipine +/-enalapril/benzalapril
B-blockers (-lols) DO NOT USE DILTIAZEM! |
|
|
Pulmonary hypertension?
|
increased pulmonary vasuclar resistance due to factors preventing a decrease in resistance or thick, stiff, non-compliant pulmonary arteries.
|
|
|
Aterioschlerosis vs. Atheroschlerosis?
|
Arterio - loss of elasticity of arterial lumen
Athero - build up of plaque along walls of arteries - Heart attacks (dogs don't get because different coronary aa supply and develop collateral circulation) |
|
|
Species that get atheroschlerosis?
|
Pigs
Birds Man |
|
|
What is cor pulmonale?
|
RV Hypertrophy and dilation due to pulm hypertension> leading cause is HWD.
|
|
|
What is pulmonary hypertension? What does it do? What causes it? How dx?
|
increased BP in pulmonary vasculature due to lack of resistance or thickened, stiff pulmonary arteries.
Causes a Pressure overload on RV>RVE (dilation+hypertrophy)> RAE measure pulm aa pressure with swan-gatz |
|
|
HW
Life cycle IH Adult life span Season |
Life cycle - temp dependent; 50F for 2 weeks to develop
IH mosquito Life span 5-7 yr Season April - Dec |
|
|
Mech for lung problems with HWD
|
Ag from female irritates pulmonary tissue> eosinophilic pneumonitis>coughing>pulmonary hypertension
leads to: pulmonary fibrosis pneumonia Pruning of lobar arteries Cor pulmonale |
|
|
Changes with CHF
|
RV will dilate and hypertrophy
Glomerulonephritis Dermatitis Vascular mechanical obstruction |
|
|
Severity of HWD depends on what?
|
Number of HW
stage/location of HW Severity of host reaction |
|
|
HWD causes __ HF?
|
Right (>ascites, venous distention)
|
|
|
What tests do you use to detect HWD?
|
Knott's
ELISA for female antigen Fluorescent Ab test is worthless. |
|
|
When would a dog have adult worms with no microfilaria?
|
Immature adults (<6mo infection)
All one sex Immune response against microfilaria sequestration monthly preventative >6 mos (kills microfilaria, sterilizes adult females) |
|
|
About Ivermectin
|
Effective against all stages. ONLY preventative that kills adults. Dog must be cage rested for 2 years.
Kills adults slowly. kills microfilaria in 90% of dogs in 21d Give at preventative dose to kill all over 3-6 mos: sterilizes females Not for cats! protects against rounds/hooks |
|
|
Pros/cons to immiticide split dosing?
|
Kills 90% worms, 98% immatures
decreased incidence THE increased efficacy and safety decreases insult to lung Don't have to stage Decreases wolbachia inflamm'n Costs more Total dose higher more exercise restriction |
|
|
ELISA will remain positive for how long?
|
>4 months. Recheck @ 6 if positive.
|
|
|
Milbemycin
|
Super safe
Sterilizes adult females protects against rounds, hooks, whips. |
|
|
Selamectin
|
don't use in sick animals
kills ear mites, fleas, sarcoptes, ticks, hooks, rounds |
|
|
Moxidectin
|
6 mo injectable
don't use in sick dogs caution with allergies Don't give within 1 mo of other tax Don't give if adult HW present |
|
|
What is post-caval syndrome mech? Signs?
|
Acute HW syndrome
Huge # of worms occluding post-cava>cardiac return from liver & kidney are reduced>congestion occurs>organ failure. Shocky Biliuria Hemouria Azotemia |
|
|
How tx post-caval syndrome?
|
Immediate removal of worms in jug vein w/ local anesthetic/alligator forceps.
Cage rest for life Lasix |
|
|
Prognosis of post-caval syndrome?
|
Poor. Death w/in 48hrs if not tx.
|
|
|
Allergic pneumonitis 2ndary to HWD?
|
moist rales
TTW shows eosinophils Txt - Steroids, ABx |
|
|
About HWD in cats
|
Lower #
Shorter lifespan prolonged PPP lower microfilaria fewer adults |
|
|
DDx for HWD in cats
|
Asthma
Bronchitis Lung worm Hairball Cardiomyopathy Toxo Pleural effusion |
|
|
Dx of HWD in cats
|
Rads - Increased caudal lobar pulmonary arteries
Ag/Ab test |
|
|
Tx of HWD in cats
|
Put on preventative (not Ivermectin) and let worms die over time.
Will kill more with the Ivermectin than cure. |
|
|
Functions of pericardial sac?
|
limit acute dilation
maintain optimal heart geometry reduce external friction |
|
|
Causes of transudate/mod-transudate with pericardial effusion?
|
Hypoproteinemia
CHF PPDH Neoplasia obstructing lymphatics Heartbase tumor |
|
|
DDx for hemorrhage of pericardial sac?
|
Erosive neoplasia (hemangiosarc)
Trauma LA rupture Clotting problems iatrogenic |
|
|
DDx for sterile inflammatory pericardial effusion
|
idiopathic
uremia post-traumatic pericarditis Neoplasia |
|
|
DDx for Septic pericardial effusion
|
Bacteria
pasteurella - everything clostridia/coliforms - cattle Salmonella, Hemophilia porcine viral pneumonia - pigs Strept - cats, horses Anaerobics - dog, cat Foreign body (hardware disease) pulmonary abscess (horse) Nocardia (dogs/cats) Systemic infections |
|
|
Common primary tumors of the heart
|
HSA
MTA FSA CSA AdCA |
|
|
2 DDx for pericardial effusion w/o apparent cause
|
idiopathic
Neoplasia |
|
|
Heartbase tumors?
|
originate from thyroid, parathyroid, btw aorta & pulmonary artery in pericardial sac
Typically aortic body tumors or chemodectomas. Typically seen in bostons and boxers |
|
|
Mech: pericardial effusion> V BP
|
effusion ^ intrapericardial pressure>increased resistance to coronary artery flow>myocardial necrosis>impeded filling of A & V > decreased CO, BP
R side MOST affected>R CHF |
|
|
Fibrinous pericarditis/exhudative pericarditis?
|
FP - leakage of inflammatory cells into pericardium
EP - cause of constrictive pericaritis |
|
|
PPDH = ?
|
What - congenital defect of ventral diaphragm and pericardial sac resulting in their fusion and communication
PE - venous distention, R CHF, ascites, muffled heart sounds |
|
|
Cow with pericardial disease?
|
Hardware Disease
Standing hunched, won't move Off feed, off milk Grunt test Tamponade Elbows abducted Increased HR/decreased heart sounds splashing/friction rubs |
|
|
DDx for a dog with ascites
|
DCM
Pericardial dzs HWD Neoplasia Hypoproteinemia Tricuspid dysplasia Large VSD |
|
|
DDx for a cow with brisket edema
|
Bacterial endocarditis
Pulmonary hypertension LSA |
|
|
DDx for a horse with dependent edema
|
pulmonary hypertension from chronic pneumonia
Bacterial endocarditis |
|
|
DDx for ECG changes related to pericardial effusion (small QRS or electrical alternans)
|
QRS:
Diaphragmatic hernia Fat Pleural effusion Tumor Pericardial effusion EA: pericardial effusion BBB SVT |
|
|
Tests to diagnose Pleural Effusion?
|
ECG
NS Angiocardiography CVP (will be >20) |
|
|
Tx for PE?
|
Drain ~ 5th ICS
Remove pericardial sac Chemo ABx Steroids NO DIG or PIMO!!! |
|
|
How does mitral regurg cause a systolic murmur?
|
during systole, the AV valves close>blood pumped out of heart so, if mitral valve is leaky, get blood flow back through causing turbulence> murmur
PMI = Mitral area (L Apex), but radiates Can be caused by DCM HCM and PDA. |
|
|
Rank Order of occurence of valvular problems
|
SA: M>A>>T>P
H: A>M Cow: T |
|
|
About Jet lesions
|
endocardial sclerosis due to mechanical irritation of regurgitant streams of blood in the LA signifying chronicity of damage to endocardium
Leads to short, thickened valve leaflets Fibrosis of papillary muscle Dilatation of LA/LV Decreased CO LHF becausenot getting enough blood to body or coronary aa and myocardium gets ischemic> can't pump. |
|
|
How dx endocardiosis?
|
Thoracic rads - look for increase plum vv size
|
|
|
12 Ddx for older coughing dog with mitral murmur that radiates to tricuspid
|
LHF
LAE (compresses bronchus) Tracheal collapse URT problem (bacterial, fungal, etc) LRT problem (pneumonia) HWD Pulmonary neoplasia Congenital Heart Dzs Pericardial effusion Myocardial neoplasia Mediastinal mass compressing trachea Lungworms Hilar lymphadenopathy compressing trachea |
|
|
Tx for Systolic mitral murmur w/cardiomegaly
|
ACEI
Dietary restriction |
|
|
Tx for dog with endocarditis w/LHF? RHF?*
|
Lasix
cage rest pimo remove ascites Acute: Na Nitroprusside Nitro ointment ACEI Chronic: Lasix Enalapril Pimo B-blockers when out of HF low Na diet Spironolactone* Afib? Dig, B-blockers, Ca Channel blockers Cough suppressants, bronchiodilators |
|
|
How does bacterial endocarditis occur & how treat?
|
Septicemia>organism invades heart>colonize and ulcerate valve leaflet>vegetations from over platelets adhered to collagen>vegetations organize and fibrin forms over them (shielding from ABx)>shortened, deformed valves>eat holes in valves>valves weaken and tear>regurg
Tx: long course of bactericidal ABx (Ags or Enrofloxacin (bartonella = gentamycin+doxy)) |
|
|
What causes bacterial endocarditis?
|
SA, horse - strep, staph
Cows - Corynebacterium pyogenes Pig - strept, coryne, erysipelothrix Sheep - entero, strep, E. coli |
|
|
Dx of Bacterial endocaritis?
|
Positive blood culture. Will look like endocardiosis on echo (it's not. That's small dogs ONLY)
Negative blood culture doesn't rule out! |
|
|
Congenital heart defects in dogs?
|
PDA
SAS PS PRAA VSD Tetralogy of Fallot ASD |
|
|
Congenital heart defects of cats?
|
ASD
Persistent common AV canal Neonatal endocardial fibroelastosis Tetralogy of fallot VSD |
|
|
Congenital heart defects of horses?
|
VSD
Valvular defects Multiple defects |
|
|
Congenital defects without murmur?
|
Vascular ring anomalies
Endocardial fibroelastosis PPDH Pectus Excavatum Ectopia cordis Reverse PDA |
|
|
Tx PRAA? PPDH?
|
Euthanasia or SX
|
|
|
DDX of puppy with L base systolic murmur
|
Aortic - Bacterial endocarditis, AStenosis
Pulmonic - PSten, TofF, ASD, VSD (radiates here) |
|
|
What does ASten do to the heart?
|
Increases diastolic pressure in LV and LA>LHF
Causes Concentric hypertrophy Leads to syncope and sudden death |
|
|
Tx of SAS?
|
Altenolol
Exercise restriction Balloon dilation |
|
|
Which dogs get PSTEN, and what does it cause? Clinical signs?
|
Pressure overload of RV
English bulldogs Terriers Chihuahuas Labs Mastiffs Newfies Boxers Usually none |
|
|
Tx Psten?
|
Balloon dilation before 1 yo. (except bulldogs/boxers)
|
|
|
What are the 4 defects of Tetralogy of Fallot?
|
VSD
Pulmonic Stenosis Overriding Aorta RV Hypertrophy |
|
|
Tx for Tetralogy of Fallot?
|
Phlebotomy for polycythemia
Hydroxyurea inhibits bone marrow Altenolol for Psten |
|
|
How are ASDs tx?
|
Tx for HF
Refer for Open Heart Sx Canine Ductal Occluder |
|
|
ASD in cattle = ?
How Dx? |
patent Foramen Ovale
Echo is the only way! |
|
|
VSD is what kind of overload of where? Found in what?
PMI? |
Volume of LV (really depends on where the VSD is).
Westies and anything that starts with English. Right! |
|
|
Tx for VSD?
|
Sx
Ductal occluder Medical management |
|
|
Most common congenital heart defect in Horses, Sheep?
|
VSD!
|
|
|
Holosystolic murmur loudest on R side, but heard on L?
|
VSD, muthafucka.
|
|
|
Tall peaked Ts with an absence of the Ps?
|
I'm hyperkalemic for you.
|
|
|
Diastolic murmur =
|
Aortic or pulmonic valves are leaking
or Mitral or tricuspid may be stenotic. |
|
|
Tricuspid dysplasia details
|
malformed valves with short chordae
prognosis poor Treat HF with spironolactone and Lasix Autosomal dominant |
|
|
PDA is defined as ___.
|
connection between MPAS and Aorta present during gestation that remains open after birth. Normally functionally closes within 12 hours, and anatomically closes w/in 21 days. Will lead to volume overload > eccentric hypertrophy > LHF
|
|
|
Common breeds for PDA
|
Poodles, Collies, Poms, Cockers, Irish Setters, GSD
|
|
|
PDA Rads =
|
PASE
Aortic bulge LAE & LVE Over-circulate lung fields |
|
|
Tx for PDA
|
Sx
Ductal occluder (if >10lb) 60% die w/in 1 yr if not tx |
|
|
Small breeds most commonly have
|
Pulmonic Stenosis
Endocardiosis (mitral regurg) VSD |
|
|
Lg Breeds most commonly have
|
Bacterial Endocarditis
Mitral Valve Dysplasia Subaortic Stenosis |
|
|
Systolic murmurs
|
Ab Pact
AS BEndocarditis PS ASD CVHD (mitral regurg) T of F |
|
|
Diastolic Murmurs
|
MT - sten
PA - regurg |
|
|
Continuous murmurs
|
PDA
AV fistula |
|
|
Congenital murmurs
|
Mitral valve dysplasia
Tricuspid dysplasia PDA Subaortic Stenosis Pulmonic stenosis PRAA VSD ASD T of Fallot |
|
|
Acquired murmurs
|
Endocarditis/Endocardiosis
|
|
|
Dominant inheritance
|
ASten
Tricuspid dysplasia |
|
|
Murmurs you can hear in the Mitral area
|
Mitral regurg
CVHD BE MVDysplasia |
|
|
Murmurs you can hear in the Left Base (Aortic and Pulmonic)
|
BEndocarditis of Aortic valve
ASten PSten T of F ASD PDA Aortic Regurg |
|
|
Murmurs you can hear in the Tricuspid (right) area
|
Tricuspid endocardiosis
VSD Tricuspid dysplasia Common AV canal |
|
|
Murmurs that are referred to the mitral area
|
VSD
PDA Tricuspid NSF |
|
|
Murmurs referred to Left Heart base (Aortic and pulmonic)
|
VSD
|
|
|
Murmurs referred to the Tricuspid area
|
Mitral endocarditis/osis
PSten |
|
|
DDx for myocarditis
|
Parvo
Protozoal (Neospora) Hairy Vetch WNile in Birds FMD |
|
|
DDx for myocardial necrosis
|
Infarct
Toxic Monensin/gossypol Cassia occidentalis Doxorubicin Nutritional Vit E/Selenium deficiency White Muscle Disease - ruminants Mulberry heart disease - piglets |
|
|
Ddx for this:
|
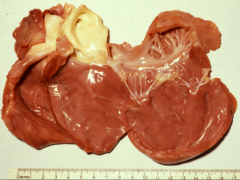
Monensin or Gossypol
DCM |
|
|
2 types of dogs that get juvenile onset DCM
|
Toy Manchesters
Portuguese Water Dogs |
|
|
Name 3 factors that influence the development of edema
|
^ Hydrostatic
V Osmotic Obstructed Lymph drainage |
|
|
Equine pericarditis is caused by exposure to __.
|
Tent caterpillar
|
|
|
Etiologies of Vasculitis
|
FIP
Fibrinoid vasculitis Arteritis (meningial/verminous) Phlebitis |

