![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
108 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diastolic pressure |
Measurement of the pressure excerpted by the blood on the artery walls while the heart ventricles are not contracting ( at rest); the lower of the two pressures; the bottom number of the b/p |
|
|
Systolic pressure |
Measurement if the pressure exerted by the blood on the artery walls while the heart ventricles are contracting; the hugest of the two pressures; the top number of the b/p |
|
|
Hypertension |
The systolic BP consistently over 140 mm Hg or the diastolic BP consistently over 90 Hg |
|
|
Hypotension |
The BP suddenly falls 20 mm Hg to 30 mm Hg below the persons Nirmal BP or falls below the low normal 90/60 mm Hg |
|
|
Orthostatic hypotension or postural hypotension |
When the position changes, it results in systolic pressure drop of 15 to 25 mm Hg or the diastolic pressure falls 10 mm Hg |
|
|
Pulse pressure |
Measurement of the difference between systolic and diastolic pressures, normally a 30-50 point difference |
|
|
Afebrile |
Without fever |
|
|
Febrile |
Fever |
|
|
Hyperthermia |
Fever |
|
|
Hypothermia |
Temperature below normal |
|
|
Pyrexia |
Fever, commonly above 105 degrees F |
|
|
S1 |
As the ventricular contraction begins, the tricuspid and bicuspid valves (AV valves) slam shut; the first heart sound; the linger, lower-priced sound; the lub lub-dub |
|
|
S2 |
As the ventricles begin relaxation, the pulmonary and aortic valves (semi lunar valves) close; a shorter, sharper sound; the dupp of lubb dupp |
|
|
Bradycardia |
Heart rate below 60 bpm |
|
|
Tachycardia |
Heart rate above 100 bpm |
|
|
Pulse deficit |
The difference between the apical and radial pulse when the radial pulse is slower than the apical pulse |
|
|
Eupnea |
Evenly spaced respiration of normal depth, between the rate of 12 and 20 breaths per minute |
|
|
Apnea |
Respiration cease or are absent |
|
|
Bradypnea |
Respiratory rate below 12/minute |
|
|
Tachypnea |
Respiratory rate above 20/minute |
|
|
Dyspnea |
Labored or difficult breathing |
|
|
Stertorous |
Noisy, snoring, labored respirations that are audible without a stethoscope |
|
|
Hypoxemia |
Decreased oxygen level in blood |
|
|
Hypoxia |
Decreased oxygen level in tissues |
|
|
Orthopnea |
Difficulty breathing unless in upright position |
|
|
Stridor |
An audible high-pitched crowing sound that results from partial obstruction of the airways |
|
|
Six vital signs |
Blood pressure (BP) Temperature (T) Pulse (P) Respiration (R) Oxygen saturation (SpO2) Pain |
|
|
Why are vital signs significant? |
Reveal how systems are functioning, provide data of overall conditon,provide a baseline against sublets changes can be measured |
|
|
What can affect the reading of a body temperature? |
Environment, time of day, physical activity and exercise, medications, food or drink, smoking, illness |
|
|
Routes used for taking temperature are: |
Oral Tymoanic Auxiliary Skin Temporal artery Rectal |
|
|
What are factors used to assess for respiratory rate? |
Rate per minute, depth, rhythm, pattern, respiratory effort |
|
|
What are some abnormal breath sounds that are discussed in the chapter. |
Adventitous, wheeze, crackles or rates, rhonchi, stridor |
|
|
Normal Sp02 level is? And where are the spots it can be taken? |
96%-100% Clip senior for fingertip, earlobe, bridge of nose, toe |
|
|
When to reassess vital signs? |
After administering IV medications, changed level of consciousness, unstable postoperative condition, uncontrolled bleeding, pale, cold, clam my skin, suspect any change, serious condition suspected, instinct |
|
|
4 circulatory qualities |
Strength of hearts contraction, blood thickness, blood volume, peripheral vascular resistance |
|
|
Normal percentage of RBC in plasma (ages) |
Newborn: 49-54 Children: 35-49 Adult females: 37-47 Adult males: 40-54 Test to measure percentage: hematocrit |
|
|
Korotkoff sounds |
First sound: clear, rhythmic tapping sound Second: soft, swishing, murmuring sound Third: sharper, crisper rhythmic sound Fourth: softening or muffling of rhythmic sound Fifth sound: silence |
|
|
Effects of hypertension; and what are some risks |
-Gradual loss of elasticity in arterial walls -Heart works harder
Genetics, smoking, stress, alcohol,obesity, elevated cholesterol |
|
|
Untreated hypertension causes |
Brain: stroke Heart: heart attack Kidneys: kidney failure Retina: loss of vision |
|
|
Temporal pulse |
Used when radial not accessible |
|
|
Carotid pulse |
Used in cardiac arrest |
|
|
Brachial pulse |
Measures BP |
|
|
Radial pulse |
Used for pulse rate assessment |
|
|
Femoral pulse |
Determines leg circulation |
|
|
Popliteal pulse |
Determines leg circulation |
|
|
Posterior tibialis pulse |
Determines foot circulation |
|
|
Dorsal Pedia pulse |
Determines foot circulation |
|
|
Adventitous sounds |
Abnormal sounds heard by listening to lungs with a stethoscope, includes wheezes, rales or crackles, rhonchi, and stridor |
|
|
Wheezes |
Musical, whistling sounds that may be audible without stethoscope |
|
|
Rales or crackles |
Short, choppy, popping, snapping, raspy sounds that may resemble rubber band sounds between index finger and thumb |
|
|
Rhonchi |
Low pitched rattling or bubbling, snoring, or sonorous wheezing sounds |
|
|
Peripheral pulse sites |
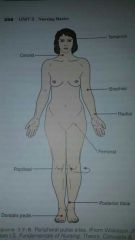
|
|
|
Peripheral pulse assessment |
Strength -absent or 0 -weak or 1+ ( may be thready) -Strong or 2+ -Bounding or 3+ Equality -equal strength bilateral lyrics - weaker than opposite side |
|
|
How does the brain regulate vital signs? |

|
|
|
What is needed to know for pain assessment? |
Site Location Characteristics (sharp,dull,stabbing,aching) Severity of pain (pain scale) |
|
|
Thermogenesis |
Way human body produces heat is through the processes occurring after ingestion of food |
|
|
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) |
Amount of heat the body produces at total rest |
|
|
Thermoregulation |
Regulation of body temperature controlled by the hypothalamus |
|
|
Circadian rhythm |
Body's "time clock" |
|
|
Oral temp advantage/disadvantage |
Advantage: more accurate, convenient, simple, no position change Disadvantage: risk body fluid exposure, affected by smoking, drinking liquids,not for children/confused/unconscious patients |
|
|
Skin temperature advantage/disadvantage |
Advantage: convenient, safe, comfortable route, good for newborns, unaffected by eating/drinking/smoking Disadvantage: affected by perspiration, reflect surface rather than core temperature, affected by severe environmental temperature |
|
|
Typanic membrane advantage/ disadvantage |
Advantage: Convenient, easy route, quick (5 sec), preformed without disturbing sleep, comfortable, unaffected by eating/ drinking/smoking Disadvantage:inaccurate if probe not pointed to Tymoanic membrane, correct placement is difficult in children, can't be used with someone with ear infections, higher cost |
|
|
Temporal artery temp. Advantage/disadvantage |
Quick (less than 5 sec) easy, comfortable, can use with chikdren, does not require positioning, not affected by eating/drinking/smoking Affected by perspiration, thick hair on artery gives inaccurate reading, high cost |
|
|
Axillary temp advantage/disadvantage |
Safe, can be used on unconscious patient Temple 1° less than core temperature, changes in Temple are slower to be reflected |
|
|
Rectal temp advantage/ disadvantage |
Most accurate, provides core temperature, reflect temp quick Embarrassment, positioning required, risk body fluid exposure, risk rectum perforation, can't have diarrhea, heroics, rectal surgery |
|
|
Internal catheter probe temp advantage/ disadvantage |
Most accurate, core temo, continual monitoring Most invasive, require sterile technique, risk vessel perforation and infection |
|
|
Uncontrolled hypertension can cause perminately damage to what organ? |
Heart |
|
|
health assessment |
comprehensive assessment of the physical, mental, spiritual, socioeconomic, and cultural status of a individual, group, or communtiy |
|
|
nursing assessments focus on.... |
the clients functional abilities and physical responses to illness and other stressors |
|
|
what are the purposes of a physical assessment? |
to obtain base line data, to identify collaborative problems, to figure out nursing diagnosis and wellness diagnosis, to monitor the status of identified problem, and to screen for health problems |
|
|
where would you do a comphrehensive assessment? |
annual physical, outpatient appointment, inpatient setting, admission onto unit |
|
|
what is a focused physical assessment? |
pertains to a particular topic, body part, or functional ability rather than an overall health status. gets added to database of the comprhensive assessment |
|
|
what is a specific system assessment? |
limited to one body system |
|
|
what is an ongoing assessment? |
performed as needed, after the initial database is completed, and idealing after EVERY interaction with a patient |
|
|
what is an head to toe approach? |
starts at the head and neck and progresses down the body |
|
|
what is a body systems approach? |
examines each system in a predetermined order (musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, neurological |
|
|
before approaching a patient ___________ yourself with the situation |
familiarize |
|
|
when to avoid doing an assessment? |
when the client is...-hungry-tired-anxious-unwilling to cooperate with assessment |
|
|
palpation is.... |
the use of touch to gather dataused to assess temperature, skin texture, moisture, anatomical landmarks (edema, masses, areas of tenderness) |
|
|
percussion is... |
tapping your fingers on the skin using short strokesuseful when assess lung sounds and abdominal issues |
|
|
ausculation means... |
the use of hearing to gather data |
|
|
direct auscultation means... |
listening without using an instrumentexample: hearing wheezing without the use of a stethoscope |
|
|
indirect auscultation means... |
listening with the help of an instrumentexample: listening to lung sounds |
|
|
olfaction means... |
the use of the sense of smell to gather data |
|
|
if a clients breath has a fruity or acetone smell, what does that mean? |
ketoacidosis! which may accompany diabetes! assess the urine for ketones |
|
|
when assessing older adults, remember SPICES which stands for... |
means the typical issues that require nursing intervention.s=sleep problemsp=problems with eating or feedingi=incontinencec=confusione=evidence of fallss=skin breakdown |
|
|
mongolian spots |
benign, blue black birthmarks found on the lower back and butt of some african american, hispanic, native american, and asian babies. usually fade by age 2 but can still persist until adolscence |
|
|
capillary hemangiomas |
"stork bites", small, irregular pink-red areas that are usually on the face and nape of neck in newborns. diasppear in infancy and can last until 5 years old |
|
|
use the __________ of the _______ to assess skin temperature |
dorsum, hand/finger |
|
|
when assessing the skin, the nurse is checking for these four things....? MTTT |
moisture, texture, turgor, temperature |
|
|
primary skin lesions are.... |
result from disease of irritation. example: acne |
|
|
secondary skin lesions are... |
develop from primary skin lesions as a result of continued illness, exposure, injury, infectionexample: crusts that form from pimples |
|
|
exceptionally dry hair may mean... |
HYPOthyroidism |
|
|
exceptionally smooth (very fine, silky) hair may mean.... |
HYPERthyroidism |
|
|
How to assess the head, acroynm: |
HEENThead, eyes, ears, nose, throat |
|
|
what is the weber test? |
assesses the sound vibrations of nerve impulses from CN VIII. placing the vibrating tuning fork on the center of the clients head-should be able to sense the vibration in both ears. |
|
|
what is the rinne test? |
uses the tuning fork to compare air conduction and bone conduction. used to assess the type of hearing problem |
|
|
what is the romberg test? |
the patient should be standing feet together and eyes closed, with minimal swaying. test neurological issues as well as ear imbalances |
|
|
an enlarged thyroid may be associated with either.... |
hyper/hypothyroidism |
|
|
pulmonary circulation means... |
oxygen depleted blood circulates from the heart into the lungs and back into the heart |
|
|
systemic circulation means... |
pumping it throughout the body |
|
|
coronary circulation means... |
circulates blood through the heart itself |
|
|
bruit means.. |
turbulent blood flow through the cartoid artery producing a whooshing sound |
|
|
carotid stenosis means... |
narrowing from plaque, increased cardiac output secondary to fluid overload, use of stimulants, and hypothyroidism |
|
|
Glasgow coma scale |
grades eye movement, motor, and verbal responses. relies heavily on verbal and vision interaction and doesn't evaluate brainstem reflexes |
|
|
lethargic |
appears drowsy, easily drifts off to sleep |
|
|
stuporous |
requires vigorous stimuli before responding |
|
|
comatose |
does not respond to verbal or painful stimuli |

