![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is another word for sensory memory? |
iconic |
|
|
how can you prevent short term memory from degrading? |
rehearsal |
|
|
What was patient KF's deficits re memory? |
left parietal lesion digit span of 2 normal spatial span on Corsi blocks normal long term memory |
|
|
What was patient ELD's deficits re memory? |
right hemisphere lesion impaired spatial span normal digit span normal long term memory |
|
|
What do lesion studies suggest about spatial and digit spans? |
left hemisphere for digit span short term memory right hemisphere for spatial span STM (supported by PET in healthy humans ) |
|
|
Describe structure of Baddeley and Hitch's WM model |
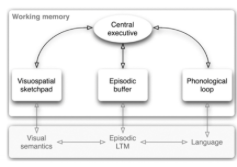
top down control fluid slave systems crystallised LTM systems (nOT PASSIVE: MANIPULATION OF CONTENTS) |
|
|
What did Owen (1999) find when comparing PET for spatial span and N-back |
Found that in spatial span (just storage) in posterior parietal cortex Top down modulation (brought in in N-back) introduced by DLPFC |
|
|
What is change blindness task an example of? |
capacity limits in Visual short term memory |
|
|
Describe Luck and Vogel's (1997) slot model of VSTM capacity? what task did they use? What evidence did Vogel find in 2001 to further back this up? |
Used change detection task show sample (e.g. with different coloured squares) - delay - target (is this display the same or different?) Found that after 3 items, the % correct dropped off rapidly suggested that we have 3 slots - and if object falls into one you can remember it, but outside of that you have to guess Vogel (2001) found that conjunction vs colour/size/orientation discriminations (feature vs conjunction) showed same detection patterns - supporting slot model |
|
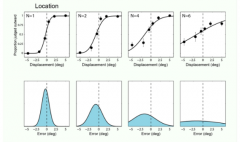
What are these results by Bays and Husain (2008) suggesting about visual short term memory? what does this provide evidence AGAINST |
x axis is the LOCATION change between sample-delay-target so testing ability to detect changes in location (results for changes in orientation e.g. of arrow are very similar) from left to right, the number of items in the array is increasing form N=1, N=2, N=4, N=6 find that more items mean that it is harder to judge changes in location (and orientation - similar results) between sample and target the fact that 2 objects is harder than 1 would suggest that the 3 slo theory is wrong - shouldn't lead to worse performance by this theory |
|
|
What did Bays and Husain (2008) say limited VSTM? How was this different to 3 slot theory? |
they said that precision to make judgments about orientation/locatoin changes of objects between sample and delay began to decline AS SOON AS sample size EXCEEDS ONE if one item neural network all dedicated to that discrimination, if two then response dedicated per object is 50%, if four then 25% etc. but importantly there is no item limit 3 slot theory says that you should have no limitation until 3 objects in array, then huge limitation |
|
|
What did Ma, Husain and Bays (2014) find modulated the precision of recall using delayed reproduction tasks? |
used continuous response space no item limit precision worsens with N cules modulate precision of recall e.g. paradigm - 3 samples (oriented lines) shown serially, each of different colour - then have to match orientation of probed colour using continuous colour wheel |
|
|
What is the CDA? (Vogel 2004) |
Contralateral delay activity electrophysiological marker that plateaus at VSTM capacity limit |
|
|
What is the involvement of the parietal cortex in VSTM? (Todd 2004) |
Finding that fMRI activity seems to increase up to item capacity limit in parietal cortex |
|
|
What 4 areas appear important for VSTM? |
Fronto-parietal (manipulation and monitoring information in STM in PFC, maintenance in parietal) visual cortex basal ganglia (gating information in and out of STM) |
|
|
What task shows that monkeys with frontal lesions have impaired STM? |
Delayed match to sample task: have to remember which tray peanut is hidden in |
|
|
What are the 3 traditional memory processes? |
encoding maintenance retrieval |
|
|
What is a delayed saccade to location task? How can you impair performance on this task? |
Show cue for spatial location delay respond by making saccade to remembered location (less binary, can look at error of saccade) |
|
|
Evidence that monkey's neurons in the ______ and _____ areas are tuned to remember spatial locations after visual stimulus extinguished |
frontal parietal |
|
|
What did Brozoski et al (1979) find devastated monkeys performance on delayed match to sample task (as mUCH as PFC lesion!) |
depletion of catecholamines in PFC catecholamines are any class of aromatic amines that includes number of NT such as adrenaline and dopamine memory fields modulated by catecholamines and monkey's spatial memory recall performance on remembered saccade task also impaired |
|
|
What has been found to improve spatial memory - damaged by chronic blockade of dopamine D2 receptors from antipsychotics? |
D1 DOPAMINE AGONISTS (given systematically) reverse haloperidol (D2 dopamine receptor agonist) induced spatial memory deficits |
|
|
what does working memory improve and decline with? |
Gathercole (2004) found that verbal storage, complex memory span and visuospatial memory all improve between the ages of 4 and 15 Reuter-Lorenz (2009) found that between the ages of 20 and 80 speed of processing,g working memory and long term memory all decline - but verbal knowledge does not decline as quickly World knowledge (vocab) increases as age - decreasing finally between 70s and 80s |
|
|
up to ____ variance of g factor (intelligence factor) can be explained by variance in _____ |
75% working memory |
|
|
What did Jaeggi (2008) find was the affect of training WM in performance on another task? |
Found that training pp to improve from 2 back to 5 back N-back task - also led to improvements in performance score on IQ test (compared pre and post) Found that control group also improved slightly, but to lesser extent this is highly controversial |
|
|
At what point is attention related to STM? (not answer just 4 possibilities) |
could be early selection pre encoding into STM - so deciding what to attend to for sensory memory encoding? Could be gatekeeper between sensory memory and STM? protecting items from interference during maintenance? 'executive control' of attention important for selection during retrieval? |
|
|
What is Cowan's model for memory? |
STM is an activated portion of LTM, with items in the focus of attention having a privileged status |
|
|
Example of spatial span task? |
Corsi's blocks |
|
|
What do Change detection tasks do? what theory did it lead to? |
use controlled stimuli to determine how many objects can be remembered with each glimpse at the visual scene (only 3 to 4 at a time?) SLOT MODEL |
|
|
Describe key features of Limited resource model (husain) |
capacity it not determined by number of items VSTM can be flexibly allocated among items - with no limit- but more items = less PRECISE the representation of each item indexed by precision of recall |
|
|
what are mnemonic (memory) fields? |
Term given to neurons in parietal and frontal regions that are tuned to remember locations of stimuli |

