![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is photopic vision? |
- Vision mediated by cone cells. - Poor sensitivity to dim lights. - Excellent visual acuity. - Colour vision. |
We like the bright lights, big city colours~! |
|
|
What is scotopic vision? |
- Mediated mainly by rods. - Highly sensitive to light. - Poor visual acuity - Absence of colour vision |
‘Sc...’ is for ‘skulking in the darkness.’ |
|
|
What unit is used to denote light intensity? |
Luminance (candelas per squared meter, cd/m^2) |
Latin for candle. |
|
|
What is mesopic vision? |
A combination of both photopic and scotopic vision: where it is not too light or too dark. |
Both? Both. Both is good. |
|
|
What is the purkinje shift? |
The effect of switching from cones to rods when processing light. |
Clap on... clap off... What happens to cells? |
|
|
What is photometry? |
The science of the measurement of light. |
Science of *?* |
|
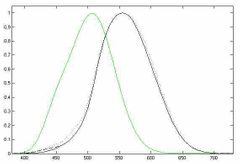
Which of these luminosity functions show photopic and scotopic vision respectively? |
Photopic is the black curve (daytime adapted). Scotopic is the green curve (night time adapted). |
The horizontal axis is the wavelength in nanometers. |
|
|
What is illuminance? What is used to denote it’s unit of measurement? |
The total luminous flux incident on a surface, per unit area. It is measured in lux (lx). |
It used to be referred to a ‘brightness’. Let’s light them up. Double rainbow... what does it mean? |
|
|
What does ‘dark adaptation’ refer to? How is it measured? |
How the eye recovers its sensitivity in the dark following exposure to bright lights. Measured by determining the absolute intensity threshold. (E.g., turning up the luminance of a test spot and asking participant to report when they see it, and measuring the luminance of the test spot) |
Just a little brighter and they might report a presence. Determining the ‘a———- threshold.’ |
|
|
What is duplicity theory of vision? |
The division in labour between rod and cone cells in the processing of vision. |
Think of difference between rod and cone thresholds. Remember how cones recover quicker than rods? |
|
|
What is light adaptation? What threshold is used to describe it? |
How the eyes adapt from darker environments to lighter environments. Happens very quickly. Weber’s Law is the threshold measurement used to describe it. |
Let there be light! (Stepping out on a sunny day) ‘.... ‘s Law’ is used to describe it. |
|
|
What happens to dark adaptation ability as we age? (Assuming the eye is healthy). |
Small decrease in capability |
Just like in presbyopia; all good things must eventually... |
|
|
What happens to the dark adaptation capability in patients diagnosed with AMD? |
Patients complain of poor vision at night or under low illumination. Rod loss and dysfunction, resulting in poor dark adaptation capability. Photostress Recovery Time (PST) is reduced in AMD patients. |
Hard to see and adjust when it’s so dark like this. |
|
|
What happens to the capability of dark adaptation of vision in patients diagnosed with retinitis pigmentosa? |
Congenital night blindness and a decrease in peripheral vision. First progressive loss of rods, followed by cone loss.
|
Dark adaptation affected early in the condition. Tunnel vision. |
|
|
What does tremor mean when referring to eye movement? |
Light jiggly movements in the head. If the eyes were paralysed, the whole visual world would become one grey blob. |
Fixation crosses and disappearing black and white smudges. |

