![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Viruses |
-are not considered alive -they are acellular (not mad out of many cells) -they cannot reproduce on their own |
|
|
how do viruses work? |
-viruses have very specific cells that only they can effect. For ex: HIV virus infects only immune cells (T cells and macro-phages) -every different virus can only effect specific cells in specific organisms. -there are virusus that can infect every kind of organism Ex: plant, fungi, animal and bacterial viruses. |
|
|
Structure of a typical virus |

Caspid-protien cast Nucleic acid |
|
|
how do viruses reproduce? |

The viral DNA uses nucleotides and enzymes of the host cell to replicate itself. 1st phase (Lysogenic phase)- the virus attaches to the bacterial cells and injects its DNA into the bacterial cell. The bacteria will now use the DNA from the virus to build new viruses parts. 2nd phase (Lytic phase)- all bacterial cells that have virus DNA in them start to transcribe and translate of the virus genes to make virus parts. So many viruses are assembled that the bacterial cell ruptures. The new viruses infect other cells. |
|
|
Capsid
|
The protein shell that encloses a viral genome. It may be rod-shaped, polyhedral, or more complex in shape.
|
|
|
Phage
|
A virus that infects bacteria; also called a bacteriophage.
|
|
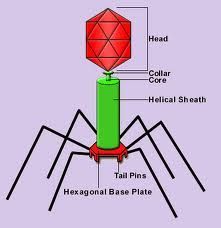
What is shown on the picture?
|
T4 phage virus.
|

