![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
129 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Viral genetics |
1- Recombination 2- Reassortment 3- Complementation 4- Phenotype mixing |
|
|
|
3 component of a virus |
1- Nucleic acid (DNA/RNA) 2- Capsid- protection 3- Envelope |
|
|
|
Naked virus |
No envelope |
|
|
|
Hilical capsid |
All have envelope |
|
|
|
Recombination viral genetics |
Exchange of genes between 2 chromosome |
|
|
|
Reassortment vial genetics |
When virus with segmented genomes exchange genetic material |
|
|
|
Complementation viral genetics |
When 1 of 2 virus that infect a cell is mutated results in non functional protein |
|
|
|
Phenotype mixing |
Occurs with simultaneous infection of a cell with 2 virus |
|
|
|
Pseudovirion |
Genetic material of one virus coated by surface protein of a different virus |
|
|
|
DNA viral genome |
1- All DNA virus have dsDNA except parvovirus (ssDNA) 2- All are linear except papilloma, polyoma and hepadenovirus (circular) 3- 7 types HHAPPPPy 1- Hepadenovirus 2- Herpes virus 3- Adenovirus 4- Papilloma virus 5- Polyoma virus 6- Parvovirus 7- Pox virus 4- Replicated in nucleus except Pox virus 5- Are icosahedral except pox virus
|
|
|
|
RNA viral genome |
1- All RNA virus have ssRNA except Reovirus (dsRNA) 2- Positive stranded RNA 1- Retro virus 2- Toga virus 3- Flav virus 4- Corona virus 5- Hepe virus 6- Calici virus 7- Picorona virus |
|
|
|
Naked viral genome infectivity |
1- Purified nucleic acid of dSDNA (except parvaovirus and HBV) and positive strand ssRNA are infectious 2- Naked nucleic acid of dSDNA and negative strand ssRNA are not infectious 3- They require polymerases contained in the complete genome |
|
|
|
Viral envelope |
1- Acquire envelope from plasma membrane when they exist the cell except herpes virus acquire envelop from nuclear membrane |
|
|
|
Naked virus |
Naked RNA 1- Calicivirus 2- Picorona virus 3- Reovirus 4- Hepevirus Naked DNA- 1- Papilloma virus 2- Polyoma virus 3- Adenovirus 4- Parvovirus |
|
|
|
Envelope DNA virus |
1- Hepadenovirus 2- Herpes virus 3- Pox virus |
|
|
|
Pox virus |
1- Envelope 2- dsDNA and linear 3- Small pox eradicated world wide by the use of live attenuated vaccine 4- Molluscum contagiosum- Flesh colored papilla with central umbilication 5- Cow pox - milkmaid blisters |
|
|
|
Hepadenovirus |
1- Envelope 2- dsDNA and linear 3- HBV- 1- acute or chronic hepatitis 2- Not a retrovirus but have reverse transcriptase |
|
|
|
Adenovirus |
1- No envelope 2- dsDNA and linear 3- Cause 1- Febrile pharyngitis 2- Acute hemorrhagic cystitis 3- Conjunctivitis 4- Pneumonia 5- Gastroenteritis 6- Myocarditis |
|
|
|
Papilloma virus |
1- No envelope 2- dsDNA and circular 3- Causes 1- HPV warts 2- CIN 3- Cervical cancer (16,18) |
|
|
|
Polyoma virus |
1- No envelope 2- dsDNA and circular 3- Cause J virus - progressive multi focal leukoencephalopathy (PML) in HIV BK virus - transplant patient, commonly target kidney |
|
|
|
Parvovirus |
1- No envelope 2- ssDNA and linear 3- Causes 1- parvovirus B19- Aplastic crises in sickle cell disease 2- Slapped cheek rash in children (with erythema infectiosum or fifth disease) 3- Infect RBC precursors and endothelial cells- RBC destruction- hydrops Gerald and death in fetus 4- Pure red cell aplasia 5- Rheumatoid arthritis like symptoms in adults |
|
|
|
Which DNA virus have the smallest and largest structure |
Smallest- parvovirus Largest - pox virus |
|
|
|
Herpes simplex virus 1 |
1- Respiratory secretion, Saliva 2- Causes 1- Keratoconjunctivitis 2- Gingivasomatitis 3- Cold sore herpes labialis 4- Esophagitis 5- Temporal love encephalitis 6- Erythema multiforme 7- Herpetic whitlow of the fingers 3- Latent in trigeminal ganglion 4- Can cause sporadic encephalitis 1- Altered mental status 2- Seizure 3- Aphasia
|
|
|
|
Herpes simplex virus 2 |
1- Sexual contact, Perinatal 2- Cause 1- Herpes genitalia 2- Neonatal Herpes 1- Conjunctivitis 2- Meningitis 3- Latent in sacral ganglion 4- Viral encephalitis more common in HSV2 than HSV1 |
|
|
|
Varicella zoster virus (HHV 3) |
1- Respiratory secretion, contact with fluid from vesicle 2- Cause 1- Chicken pox 2- Shingles- Post herpetic neuralgia 3- Pneumonia 4- Encephalitis 3- Latent in dorsal root or trigeminal ganglion 4- CN 5 branch 1 involvement causes Herpes zoster opthalmicus |
|
|
|
Epstein Barr virus HHV 4 |
1- Respiratory secretion, saliva 2- Causes 1- Mononucleosis 1- Fever 2- Pharyngitis 3- Lymphadenopathy (posterior cervical nodes) 4- Hepatosplenomegaly 3- Avoid contact sports until resolution due to risk of splenic rupture 4- Associated with lymphoma 1- Burkitts lymphoma 2- Primary CNS lymphoma in HIV patients 3- Hodgkin lymphoma 4- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma 5- Infected B cells through CD 21 6- Atypical lymphocytes (cytotoxic T cells) seen in blood smear 7- Positive mono spot test - Heterophil antibody detected by agglutination of sheep or horse RBC 8- Amoxicillin in mononucleosis can cause a characteristic maculopapular rash |
|
|
|
Epstein Barr virus HHV 4 |
1- Respiratory secretion, saliva 2- Causes 1- Mononucleosis 1- Fever 2- Pharyngitis 3- Lymphadenopathy (posterior cervical nodes) 4- Hepatosplenomegaly 3- Avoid contact sports until resolution due to risk of splenic rupture 4- Associated with lymphoma 1- Burkitts lymphoma 2- Primary CNS lymphoma in HIV patients 3- Hodgkin lymphoma 4- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma 5- Infected B cells through CD 21 6- Atypical lymphocytes (cytotoxic T cells) seen in blood smear 7- Positive mono spot test - Heterophil antibody detected by agglutination of sheep or horse RBC 8- Amoxicillin in mononucleosis can cause a characteristic maculopapular rash |
|
|
|
Cytomegalovirus HHV 5 |
1- Sexual contact, Perinatal, saliva, urine, transplant 2- Cause 1- Mononucleosis in immunocompetent individual (negative monosomy test) 2- AIDS retinitis (hemorrhage, Colton wool spot and vision loss) 3- Esophagitis 4- Congenital CMV 3- Latent in nonnuclear cells 4- Infected cells have owl eyes intranuclear inclusions |
|
|
|
Epstein Barr virus HHV 4 |
1- Respiratory secretion, saliva 2- Causes 1- Mononucleosis 1- Fever 2- Pharyngitis 3- Lymphadenopathy (posterior cervical nodes) 4- Hepatosplenomegaly 3- Avoid contact sports until resolution due to risk of splenic rupture 4- Associated with lymphoma 1- Burkitts lymphoma 2- Primary CNS lymphoma in HIV patients 3- Hodgkin lymphoma 4- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma 5- Infected B cells through CD 21, latent in B cells 6- Atypical lymphocytes (cytotoxic T cells) seen in blood smear 7- Positive mono spot test - Heterophil antibody detected by agglutination of sheep or horse RBC 8- Amoxicillin in mononucleosis can cause a characteristic maculopapular rash |
|
|
|
Cytomegalovirus HHV 5 |
1- Sexual contact, Perinatal, saliva, urine, transplant 2- Cause 1- Mononucleosis in immunocompetent individual (negative monospot test) 2- AIDS retinitis (hemorrhage, Colton wool spot and vision loss) 3- Esophagitis 4- Congenital CMV 1- Seizures 2- Hearing loss 3- Petechial rash 4- CNS deficit 3- Latent in nonnuclear cells 4- Infected cells have owl eyes intranuclear inclusions |
|
|
|
Human Herpes virus 6 and 7 |
1- Saliva 2- Cause 1- Roseola infantum (exanthem subitum) 1- Fever for several days that can cause seizures follows by diffuse macular rash (starts on the trunk then spread to extremities) 3- HHV 7 less common cause of roseola |
|
|
|
Human herpes virus 8 HHV 8 |
1- Sexual contact 2- Cause 1 Kapossi sarcoma 1- Seen in HIV and transplant patients 2- Dark/violaceous plaque or nodules representing vascular proliferation 3- Can also affect GI tract and Lungs |
|
|
|
Herpes simplex virus identification |
1- Viral culture for skin/genitalia 2- CSF or PCR for herpes encephalitis 3- Tzanck test- a smear of an open skin vesicles to detect multinuclear giant cells seen in HSV-1 HSV-2 and VZV 4- OCR for skin lesion is the test of choice 4- Intranuclear Eosinophilic cowdry inclusion also seen with HSV-1 HSV-2 and VZV |
|
|
|
Post herpetic neuralgia |
Painful lesions in dermatomal distribution caused by shingles (VZV) |
|
|
|
From what cell does kaposi sarcoma arise |
Endothelial cells |
|
|
|
What 3 herpesvirus are transmitted in respiratory secretion |
HSV- 1 VZV EBV |
|
|
|
What 3 organs are affected b kapossi sarcoma |
Skin GI tract Lungs |
|
|
|
What 3 herpesvirus are transmitted via sexual contact |
HSV-2 CMV HHV-8 |
|
|
|
Receptors used by virus |
1- CMV- Integrin (heparan sulfate) 2- EBV- CD 21 3- HIV- CD4, CXCR4, CCR5 4- Parvovirus- P antigen on RBC 5- Rabies - nicotinic AChR 6- Rhinovirus- ICAM-1 |
|
|
|
Reovirus |
1- No envelope 2- dsDNA, linear 3- Icosahedral 4- Causes 1- Coltivirus - Colorado tick fever 2- Rotavirus - Fetal diarrhea in children |
|
|
|
Picornavirus |
1- No envelope 2- ssRNA, linear 3- Icosahedral 4- Causes 1- Poliovirus- polio- Salk/sabin vaccine IVP/OPV 2- Echovirus - aseptic meningitis 3- Rhinovirus - common cold 4- Coxsackievirus - 1- aseptic meningitis 2- Hand foot and mouth disease 3- Herpangina (mouth blister, fever) 4- Myocarditis 5- Pericarditis 5- HAV- acute viral hepatitis
|
PERCH |
|
|
Hepevirus |
1- No envelope 2- ssRNA, linear 3- Icosahedral 4- Causes - HEV |
|
|
|
Calicivirus |
1- No envelope 2- ssRNA, linear 3- Icosahedral 4- Cause- Noravirus- acute gastroenteritis |
|
|
|
Flavivirus |
1- Envelope 2- ssRNA, linear 3- Icosahedral 4- Cause 1- Dengue 2- Yellow Fever 3- Zika 4- West Nile encephalitis 1- meninocoencephalitis 2- Flaccid paralysis 5- St. Louis encephalitis 6- HCV |
|
|
|
Toga virus |
1- Envelope 2- ssRNA, linear 3- Icosahedral 4- Causes 1- Chickungunya 2- Rubella 3- Eastern and western equine encephalitis |
CREW |
|
|
Retrovirus |
1- Envelope 2- ssRNA, linear 2 copies 3- Icosahedral (HTLV-1) complex conical (HIV) 4- Cause 1- HTLV-1 T cell leukemia 2- HIV/AIDS |
|
|
|
Coronavirus |
1- Envelope 2- ssRNA circular 3- Icosahedral 4- Cause 1- common cold, SARS, MERS |
|
|
|
Orthomyxovirus |
1- Envelope 2- ssRNA linear 8 segment 3-Helical 4- Causes influenza virus |
|
|
|
Paramyxovirus |
1- Envelope 2- ssRNA, linear , non segment 3- Helical 4- Cause 1- Parainfluenza- coup 2- RSV- bronchiolitis in children 3- Measles and mumps |
|
|
|
Rabdovirus |
1- Envelope 2- ssRNA, linear 3- Helical 4- Causes 1- Rabies |
|
|
|
Filovurus |
1- Envelope 2- ssRNA, linear 3- Helical 4- Cause Ebola/Marburg hemorrhagic fever |
|
|
|
Arenavirus |
1- Envelope 2- ssRNA, circular 2 segment 3- Helical 4- Cause 1- LCMV - lymphocytic choronimeningitis virus 2- Lassa Fever encephalitis- spread by rodents |
|
|
|
Bunyavirus |
1- Envelope 2- ssRNA, circular 3 segment 3- Helical 4- Causes 1- California encephalitis 2- Crimeon Congo hemorrhagic Fever 3- Sandfly/Rift Bally Fever 4- Hantovirus 1- hemorrhage, fever and Pneumonia |
|
|
|
Delta virus |
1- Envelope 2- ssRNA circular 3- Helical 4- Cause HDV - a defective virus require the presence of HBV to replicate |
|
|
|
Which 2 RNA virus do not replicate in the cytoplasm |
Retrovirus Influenza virus |
|
|
|
In which family do virus have ssRNA circular and both positive and negative strand |
Arenavirus |
|
|
|
What 3 virus families have circular RNA structures |
Arenavirus Bunyavirus Delta virus |
|
|
|
Negative stranded RNA virus |
1- Virion bring its own RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 2- Examples 1- Orthomyzovirus 2- Paramyxovirus 3- Rhabdovirus 4- Filovirus 5- Arenavirus 6- Bungavirus |
|
|
|
Segmented virus |
1- All are RNA virus 2- Examples 1- Reovirus - 10-12 segments 2- Orthomyxovirus- 8 segment 3- Arenavirus- 2 segments 4- Bunyavirus - 3 segments |
Now BOARing flight 382 in 10-12 minutes |
|
|
Picornovirus |
1- Example PERCH 2- RNA is translated into 1 large polypeptide that is cleaves by virus encoded protease into functional viral protein 3- All causes aseptic meningitis except rhinovirus and HAV 4- All are enterovirus except rhinovirus and HAV 5- Spread Fecal- orally 6- Enteric virus affect GI tract |
|
|
|
Rhinovirus |
1- A picornavirus 2- No envelope 3- Cause common cold >100 serological types colonized nasal mucosa 4- Heat labile- inactivated by gastric acid therefore does not the GI tract |
|
|
|
Yellow fever |
1- A flavavirus, arbovirus 2- Transmitted by Aedes mosquito 3- Virus has a monkey or human reservoir 4- Symptoms 1- High Fever 2- Black vomit 3- Jaundice 4- May see Counsilman bodies (eosinophilia apoptotic bodies) on liver biopsy |
|
|
|
Rota virus |
1- A Reovirus (dsRNA) 10-12 segments 2- Villous destruction and atrophy leads to decrease absorption of Na and loss of K 3- Cause acute diarrhea in united state in winter especially in day care centers or kindergarten 4- Vaccination of all infants except those with a history of intussusception or SCID 5- Spread Fecal- oral |
|
|
|
Rubella |
1- A toga virus 2- Cause mild disease in children but serious congenital disease (a TORCH infection) 3- Congenital rubella finding blue berry muffin appearance due to dermal extramedullary hemopoiesis 4- Symptoms 1- Fever 2- Tender Periauricular and other lymphadenopathy 3- Arthralgia 4- Fine maculopapular rash that starts in the face then spreads centrifugally to the trunk and extremities 5- Spread respiratory droplets and trans placental |
|
|
|
Congenital rubella syndrome |
1- Congenital cataract/visual impairment 2- Sensorineural hearing loss 3- PDA |
|
|
|
Influenza |
1- Orthomyxovirus 8 segments 2- Envelope 3- Contain hemagglutin ( binds sialic acid and promote your virus entry) and neuroaminidase ( promote progeny virion release) antigen 4- Reformulated vaccine (flu shot) contain viral strain most likely appear during the flu season due to virus rapid antigen changes 5- Killed vaccine is used. Live attenuated vaccine contain temperature sensitive mutants and replicated in the nose but not the lungs given intranasally 6- Risk of superinfection with 1- S. Aureus 2- S. Pneumonia 3- H. Influenza 7- Treatment- Supportive +/- neruaminidase inhibitor (oseltamivir, zonaminvir) |
|
|
|
Antigenic shift |
1- Infection of 1 cell by 2 different segmented virus 2- Dramatically different virus 3- Major global outbreak (pandemic) |
|
|
|
Antigenic drift |
1- Random mutation in hemagglutin or neuraminidase genes 2- Minor change (genetic drift) 3- Local outbreak (epidemic) |
|
|
|
Paramyxovirus |
1- Causes 1- Parainfluenza- coup 2- RSV- bronchiolitis in children 3- Measles and Mumps 4- Human metapneumovirus - Respiratory tract infections in infants 2- All contain F (Fusion) proteins that causes respiratory epithelial cells to fuse and form multinucleated cells- syncytial 3- Palivizumab (monoclonal antibody against F protein) prevent pneumonia caused by RSV infection in premature infants |
|
|
|
Acute laryngotracheobronchitis coup |
1- Cause by parainfluenza virus 2- Contain hemagglutin (bind sialic acid and promote virus entry) and neuroaminidas (promote progeny viral release) antigen 3- Cause seal like barking cough and inspiration strider 4- Steeple sign on x ray - narrowing of upper trachea and subglottis 5- Sever strider can result in pulses paradox secondary to upper airway obstruction |
|
|
|
Mumps |
1- Uncommon due to effectiveness of MMR vaccine 2- Symptoms 1- Parotitis 2- Orchitis (inflammation of testes) 3- Meningitis (aseptic) 4- Pancreatitis 5- Can cause sterility especially after puberty |
POMP |
|
|
Measles |
1- Presentation Fever with 1- Cough 2- Coryza 3- Conjunctivitis 4- Koplike spot (bright red spot with blue-white centers on buccal mucosa) 2- Following 1-2 days later maculopapular rash that starts on the face/neck then spread downward 3- Lymphadenitis with warthin Finkeldey giant cells (fused lymphocytes) in a background of Paracortical hyperplasia 4- Sequels 1- Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) 1- Perinality changes 2- Dementia 3- Autonomic dysfunction 4- Death 2- Encephalitis (1:1000) - occurs within few days of rash 3- Giant cell pneumonia ( rare occurs in immunosuppressed individuals) 5- Vitamin A supplementation can reduce mortality and morbidity especially in malnourished children 6- Pneumonia most common cause of measles associated death in children
|
|
|
|
Rabies |
1- Infection from bat, raccoon or skunk bite than from dog bite in the united state 2- Aerosol transmission possum eg bat cave 3- Bullet shape virus 4- Negri bodies (cytoplasmic inclusion) commonly found in purkinje cells of cerebellum and hippocampal neurons 5- Long latency periods (weeks to month) before symptom onset 6- Post exposure prophylaxis include wound cleaning, immunization with killed vaccines and rabies immunoglobulin |
|
|
|
Passive active immunity of rabies |
1- Travel to the CNS by migration in a retrograde fashion (via dynein motors) up nerve axons after binding to ACH receptors |
|
|
|
Progression of rabies virus |
1- Fever 2- Malaise 3- Agitation 4- Photophobia 5- Hydrophobia 6- Hypersalivation 7- Paralysis 8- Coma 9- Death |
|
|
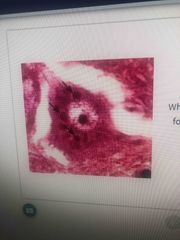
Diagnosis |
Negri bodies (cytoplasmic inclusions) commonly found in purkinje cells of cerebellum and hippocampal neuron |
|
|
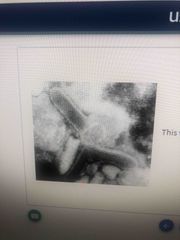
Diagnosis |
Rabies |
|
|
|
Ebola |
1- A Filovirus 2- Incubation period 21 days 3- Targets endothelial cells, phagocytes and hepatocytes 4- Transmission 1- Direct contact with bodily fluid and fomites 2- Infected bats and primates (ape,monkey) 3- High incidence of nosocomial infection 5- Symptoms 1- Flu like symptoms 2- Fever 3- Diarrhea/Vomiting 4- Myalgia 6- Complication 1- DIC 2- Diffuse hemorrhage 3- Shock 7- Diagnosis with RT- PCR within 48 hrs of symptom onset 8- Supportive care, isolation of infected patients and barrier practice for healthcare workers 9- High mortality rate |
|
|
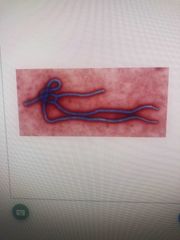
Diagnosis |
Filovirus Ebola |
|
|
|
Zika virus |
1- A flavavirus 2- Transmitted Aedes mosquito 3- Symptoms 1- Low grade fever 2- Conjunctivitis 3- Itchy rash in 20% of people 4- Complications during pregnancy 1- Congenital Microcephaly 2- Miscarriage 3- Occular anomalies 4- Motor abnormalities (spasticity, seizures) 5- Sexual and vertical transmission possible 6- Diagnosis by RT-PCR or serology 7- Outbreak more common in tropical and subtropical climates 8- Supportive care |
|
|
|
Chikungunya virus |
1- A toga virus alpha virus 2- Transmitted by Aedes mosquito 3- Symptoms- 1- High grade fever 2- Headache 3- Inflammatory poly arthritis that can be chronic 4- Maculopapular rash 5- Lymphadenopathy 4- Diagnose with RT-PCR or serology 5- Supportive care |
|
|
|
Dengue |
1- A flavavirus virus 2- Transmitted by Aedes mosquito 3- Symptoms 1- Dengue Fever 1- Fever 2- Rash 3- Headache 4- Myalgia 5- Arthralgia 6- Neutropenia 2- Dengue hemorrhagic Fever - Dengue Fever + bleeding and plasma leaking due to thrombocytopenia and extremely low or high hematocrit 3- Dengue shock syndrome- Plasma leaking leading to circulatory collapse) 4- Dengue hemorrhagic Fever most common in patients infected with a different serotype after Initial infection due to antigen dependent enhancement of the disease 5- Complication 1- Neutropenia 2- Thrombocytopenia 3- Hemorrhage 4- Shock 5- Death 6- Live recombinant vaccine uses yellow fever vaccine as the backbone to insert gene from envelope and premembrane protein of the dengue virus have been inserted |
|
|
|
What is the most common mosquito borne viral disease in the world |
Dengue virus |
|
|
|
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
1- SARs- COV2 2- Cause coronavirus 3- Transmitted by respiratory secretion and aerosol 4- Host cell entry occur by attachment of viral spike protein to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor on cell membrane 5- Symptoms 1- Asymptomatic 2- Fever 3- Dry cough 4- SOB 5- Fatigue 6- Loss of taste and smell 6- Complication 1- Respiratory failure 2- Hyper-coagulation 3- Shock 4- Organ failure 5- Death 7- Risk factors for increase hospitalization 1- Increase age 2- Obesity 3- Diabetes 4- Hypertension 5- CKD 6- Cardiopulmonary disease 8- Diagnosis RT-PCR, antigen or antibody test 9- Treatment in hospital 1- Remdesivir (nucleoside analog) 2- Convalescent plasma 3- Dexamethasone |
|
|
|
Hepatitis A virus |
1- RNA Picornavirus 2- Fecal- oral transmission (shellfish, traveler, daycare) 3- Short incubation 4- Symptoms 1- Asymptomatic in children 2- Acute and self limiting in adults 5- Good prognosis 6- Not associated with HCC 7- Liver biopsy 1- Hepatocytes swelling 2- Mononuclear infiltrate 3- Counsilman body 8- No carrier state |
|
|
|
Hepatitis B virus |
1- DNA Hepadenovirus 2- Sexual, Perinatal and Parental transmission 3- Long incubation 4- Symptoms 1- Fever 2- Rash 3- Arthralgia 5- Prognosis adults- mostly full resolution Children- worst prognosis 6- Associated with HCC 7- Liver biopsy- 1- Granular eosinophilic ground glass appearance 2- Cytotoxic T cells mediate damage 8- Carrier state common |
|
|
|
Hepatitis C virus |
1- RNA flavavirus 2- Blood transmission 3- Long incubation 4- Symptoms 1- Cirrhosis 2- Carcinoma 5- Prognosis majority develop stable chronic hepatitis C 6- Associated with HCC 7- Liver biopsy 1- lymphoid aggregated with focal area of macro vascular steatosis 8- Carrier state common |
|
|
|
Hepatitis C virus |
1- RNA flavavirus 2- Blood transmission 3- Long incubation 4- Symptoms 1- Cirrhosis 2- Carcinoma 5- Prognosis majority develop stable chronic hepatitis C 6- Associated with HCC 7- Liver biopsy 1- lymphoid aggregated with focal area of macro vascular steatosis 8- Carrier state common |
|
|
|
Hepatitis D virus |
1- RNA delta virus 2- Sexual, Perinatal and parenteral transmission 3- Superinfection- short incubation (HDV after HBV) Coinfection - long incubation ( HDV and HBV) 4- Symptoms 1- Fever 2- Rash 3- Arthralgia 5- Prognosis superinfection- worst prognosis 6- Associated with HCC 7- Liver biopsy 1- Granular eosinophilic ground glass appearance 2- Cytotoxic T cell mediate damage 8- Defective require HBV HBsAg to enter into hepatocytes |
|
|
|
Hepatitis C virus |
1- RNA flavavirus 2- Blood transmission 3- Long incubation 4- Symptoms 1- Cirrhosis 2- Carcinoma 5- Prognosis majority develop stable chronic hepatitis C 6- Associated with HCC 7- Liver biopsy 1- lymphoid aggregated with focal area of macro vascular steatosis 8- Carrier state common |
|
|
|
Hepatitis D virus |
1- RNA delta virus 2- Sexual, Perinatal and parenteral transmission 3- Superinfection- short incubation (HDV after HBV) Coinfection - long incubation ( HDV and HBV) 4- Symptoms 1- Fever 2- Rash 3- Arthralgia 5- Prognosis superinfection- worst prognosis 6- Associated with HCC 7- Liver biopsy 1- Granular eosinophilic ground glass appearance 2- Cytotoxic T cell mediate damage 8- Defective require HBV HBsAg to enter into hepatocytes |
|
|
|
Hepatitis E virus |
1- RNA Hepevirus 2- Fecal oral 3- Short incubation 4- Symptoms - Fulminat hepatitis in pregnant women 5- Prognosis worst in pregnant women 6- Not associated with HCC 7- Liver biopsy- Patchy necrosis 8- No carrier state |
|
|
|
Why are the hepatitis B, C and D virus unable to spread via the Fecal oral sout |
Envelope viruses which are killed by gut |
|
|
|
What sign and symptoms are characteristic of all hepatitis viruses |
1- Fever 2- Jaundice 3- Increase AST and ALT |
|
|
|
In what part of the world is hepatitis E infection most common |
1- Asia 2- Africa 3- Middle East |
|
|
|
Extra-hepatic manifestation of hepatic B virus |
1- Aplastic anemia 2- Membranous GN > Membranoproliferativ GN 3- Polyarteritis nodosa |
|
|
|
Extra-hepatic manifestation of hepatic B virus |
1- Aplastic anemia 2- Membranous GN > Membranoproliferativ GN 3- Polyarteritis nodosa |
|
|
|
Extra hepatic manifestation of hepatic C virus |
1- Essential mixed cryoglobinemia 2- B cell NHL 3- ITP 4- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia 5- Membranoproliferative GN > membranous GN 6- Lymphocytoclastic vasculitis 7- Sporadic porphyria cutanea tarda 8- Lichen planus 9- Increase risk of diabetes mellitus 10- Autoimmune hypoparathyroidism |
|
|
|
Anti HAV IgM |
1- IgM antibodies to hepatitis A 2- Indicate acute hepatic A infection |
|
|
|
Anti HAV IgM |
1- IgM antibodies to hepatitis A 2- Indicate acute hepatic A infection |
|
|
|
Anti HAV IgG |
1- IgG antibodies to hepatitis A 2- Indicates prior infection or vaccination 3- Protects against reinfection |
|
|
|
Anti HAV IgM |
1- IgM antibodies to hepatitis A 2- Indicate acute hepatic A infection |
|
|
|
Anti HAV IgG |
1- IgG antibodies to hepatitis A 2- Indicates prior infection or vaccination 3- Protects against reinfection |
|
|
|
HBsAg |
1- Hepatitis B surface antigen 2- Indicated hepatitis infection |
|
|
|
Anti HBs |
1- Antibodies against HBsAg 2- Indicate immunization from vaccination or recovery from infection |
|
|
|
Anti HBs |
1- Antibodies against HBsAg 2- Indicate immunization from vaccination or recovery from infection |
|
|
|
HBcAg |
1- Hepatitis B core antigen |
|
|
|
Anti HBc |
1- Antibodies against HBcAg 2- IgM- acute/recent infection IgG- prior/chronic infection |
|
|
|
Anti HBc |
1- Antibodies against HBcAg 2- IgM- acute/recent infection IgG- prior/chronic infection |
|
|
|
HBeAg |
1- Release from infected hepatocytes into circulation 2- Not part of the mature HBV virion 3- Indicate acute viral replication 4- Highly transmissible and poor prognosis |
|
|
|
Anti HBc |
1- Antibodies against HBcAg 2- IgM- acute/recent infection IgG- prior/chronic infection |
|
|
|
HBeAg |
1- Release from infected hepatocytes into circulation 2- Not part of the mature HBV virion 3- Indicate acute viral replication 4- Highly transmissible and poor prognosis |
|
|
|
Anti HBe |
1- Antibodies against HBeAg 2- Low transmissibility 3- Window period |
|
|
|
HIV |
1- Diploid genome (2 molecules of RNA) 2- Reverse transcriptase synthesis dsDNA from genomic RNA, dsDNA is integrated into host genome 3- 3 Structural genes 1- Env (go120, gp41) 1- Formed from cleavage of go160 to form glycoproteins 2- gp120- attachment of CD4 to host cell 3- gp41- fusion and entry 2- gag (p24, p17) - capsid and matrix proteins respectively 3- pol - reverse transcriptase, integrase, protease 4- Receptors CD4 CCR5 on macrophages (early infection) CXCR4 on T cell (late infection) 5- Homozygous CCR5 mutation - immunity Heterozygous CCR5 mutation- slow course |
|
|
|
HIV diagnosis |
1- Presumed diagnosis with HIV1/2 Ag/Ab immunoassay 2- Immunoassay detects viral p24 capsid protein Ag and IgG Ab of HIV1/2- high sensitivity and specificity 3- Viral load is use to determine the amount of viral RNA in plasma and monitor effect of drug therapy 4- High viral load associated with poor prognosis 5- HIV viral load in babies with suspected HIV 6- AIDS diagnosis 1- CD4 count < 200 2- HIV + with AIDS defining conditions 3- CD 4 < 14% |
|
|
|
What test can be performed in the setting of an inconclusive HIV1/2 differentiate assay |
HIV-1 nucleic acid test |
|
|
|
Which test determines appropriate antiretroviral therapy in HIV positive patients |
HIV genotype testing |
|
|
|
What’s is the normal range of CD4 count |
500-1500 cells/mm3 |
|
|
|
Time course of untreated HIV |
1- Four phases of untreated HIV 1- Flu like symptoms (acute) 2- Felling fine (latency) 3- Falling count 4- Final crises 2- During clinical latency period, virus replicated in lymph nodes |
|
|
|
Moderately immunocompromised in HIV |
CD4 - 200-400 |
|
|
|
During which phase of HIV infection does the CD4 cell count drop most sharply |
Acute stage (first 1-2 months) |
|
|
|
What is the time frame for the development of anti-envelope antibodies following initial HIV infection |
Begin after first month |
|
|
|
Disease when CD4 < 500 |
1- Candida albican 1- Oral thrush 2- Scrapable white plaque on tongue 2- EBV- Oral hairy leukoplakia 2- Unscarpable white plaque on lateral tongue 3- HHV 8- 1- Kapossi sarcoma 2- Biopsy with lymphocytic inflammation 4- HPV- squamous cell carcinoma of anus or cervix
|
|
|
|
Disease when CD4 < 200 |
1- Histoplamsa capsulatum 1- Fever, weight loss, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspnea, fatigue 2- Oval yeast cell within macrophages 2- HIV- 1- Dementia 2- Cerebral atrophy on neuroimaging 3- JC virus - Progressive multi focal luekoencephalopathy 3- Non enhancing areas of demyelination on MRI 4- Pneumocystis jerovecii- 1- Pneumocystis pneumonia 2- Ground glass opacity on chest imaging |
|
|
|
Disease when CD4 < 100 |
1- Aspergillus fumigatus 1- Hemoptysis and pleuritic pain 2- Cavitation or infiltration on Chest imaging 2- Bartonella spp -1 Bacillary angiomatosis 2- Biopsy with neutrophilic infiltrate 3- Candida albican - 1- Esophagitis 2- White plaque on endoscopy 4- CMV- 1- colitis,retinitis, esophagitis, encephalitis and pneumonia 2- Linear ulcer on endoscopy, cotton wool spot on fundoscopy and intranuclear owl eye inclusions 5- Crytococcus neoforman- 1- Meningitis 2- Encapsulated yeast on India ink 6- Cryptosporidia spp- 1- Chronic watery diarrhea 2- Acid fast oocyts in stool 7- EBV- 1- B cell lymphoma (NHL, CNS lymphoma) 2- Single ring enhancing lesion 8- Mycobacterium avian- 1- Non- specific symptoms, focal lymphodenitis 2- Most common seen when CD4< 50 9- Toxoplasma Gondi 1- Brain abscess 3- Multiples ring enhancing lesion
|
|
|
|
Prion |
1- Prion disease is formed by the conversion of normal proteins (predominantly alpha helix) termed prion proteins to a beta plated form that is transmissible via CNS related tissue and Food contamination by BSE infected animal products 2- Resit protease degradation 3- Resist standard sterilization procedures 4- Accumulation of beta plated prion protein cause 1- Spongiform encephalopathy 2- Dementia 3- Ataxia 4- Death |
|
|
|
Creutzfeldt Jakob disease |
1- Rapidly progressive dementia 2- Usually sporadic (some familial form) |
|
|
|
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy |
Mad cow disease |
|
|
|
Kuru |
1- Acquired prion disease noted in tribal population that practice human cannabolism |
|

