![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What advantage do retroviral vectors have over episomal virus vectors? |
integration of the recombinant gene into host genome, providing continuous expression for as long as the cell lives |
|
|
What is the role of the LTR? |
- it acts as a strong promoter - provides signals for packaging |
|
|
What is the purpose of Packaging Cell Lines? |
To produce a whole bunch of recombinant retrovirus particles (which are then used to infect target cells) |
|
|
What is the general process of making and utilizing retroviral vectors to deliver target gene into host cell? |
1. transfect packaging cell with retrovirus vector construct (including gene of interest, surrounded by two LTR) 2. packaging cell produces new virus particles with gene of interest, able to infect but not reproduce 3. infect target cell with virus. virus releases genome. 4. target gene integrates into host genome and is expressed as long as cell lives |
|
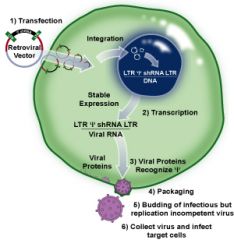
|
retrovirus construct with gene of interest (surrounded by two LTR) --> packagin cell --> recombinant retrovirus particle --> infects target cell --> integrates the gene |
|
|
What are advantages of using HIV vector? |
Larger genome than other retroviruses or Adeno-Associated Virus so it can accept large/multiple foreign genes gene-of-interest integrates leadingto stable expression of your gene over time |
|
|
What are disadvantages of using HIV vector? |
- Causes AIDS - Primarily infects CD4 T cells - Integration can cause cancer (LTR) (inability to express IL-2 due to LTR integration next to an oncogene - Unstable virion(enveloped virus - will not survive in the environment) |
|
|
Which modifications have been made to HIV vector |
- Delete most viral proteins from the genome - Create a "self-inactivating" genome - subclone individual genes into the vector, preventing reconstitution of infectious virus - Pseudotyping: env protein replaced with VSV-G, that is more stable and allows infection of more cell diverse types |
|
|
Explain Self-Inactivating (SIN) genome: |
5' LTR is replaced with CMV and 3' LTR is deleted (LTRs are the promoters of retroviruses) |
|
|
What is included in the HIV POL gene/protein? |
POL = RT, protease,helicase |
|
|
What is included in the HIV POL gene/protein? |
ENV = gp120 (external), gp41 (transmembrane) |
|
|
What are the following HIV regulatory proteins: vif tat rev nef |
vif - virion infectivity factor tat - transactivator protein - transcription reg rev - regulatory virion protein nef - negative regulatory factor |
|
|
3 Methods of titer analysis |
FACS: Dependent on promoter - predicts infection rate Real-Time PCR: for *integrated* viral DNA - predicts infection rate RTase Real-Time PCR: for presence of viral RNA - doesn't predict infection rate |

