![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Right atrium |
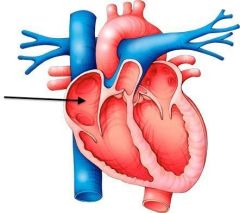
Seen from the right side of the heart, with the venae cavae entering it |
|
|
Left Atrium |
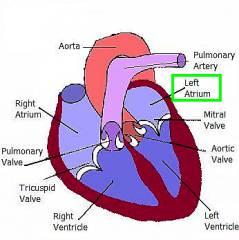
The chamber into which the pulmonary veins empty |
|
|
Right Ventricle |
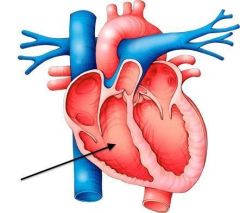
Makes up most of the heart on the right side, below the coronary groove. It "wraps" around the cranial side of the heart to continue as the pulmonary trunk |
|
|
Septum (interventricular septum) |
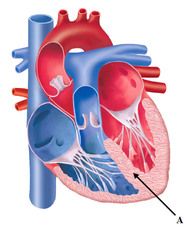
the wall separating the ventricles |
|
|
Auricles |
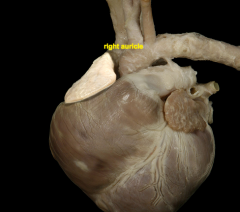
the ear-shaped appendage of either atrium of the heart. |
|
|
Coronary Arteries |
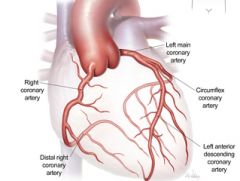
The arteries encircling the base of the heart like a crown. These are the first branches off the aorta. |
|
|
Pulmonary Valve (semilunar) |
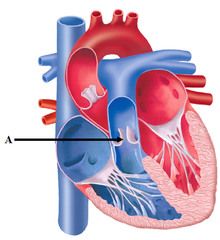
The valve between the conus of the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk. It is similar to the aortic valve, but of lighter construction. |
|
|
Aortic Valve (semilunar) |
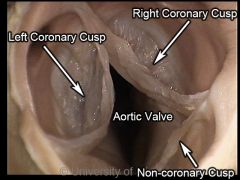
The three semilunar cusps attached to the aortic fibrous ring in the origin of the aorta. |
|
|
Pericardium |
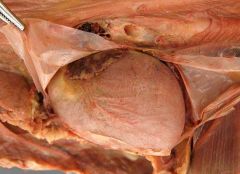
The fibroserous sac enclosing the heart; composed fo the fibrous and serous pericardium covered by mediastinal (pericardiac) pleura |
|
|
Pericardial Mediastinal Pleura |
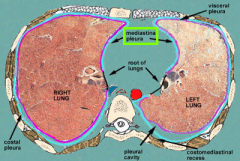
The serosa on the mediastinum; part of the mediastinal pleura on either side of the pericardium |
|
|
Right Atrioventricular (A-V) Valve |
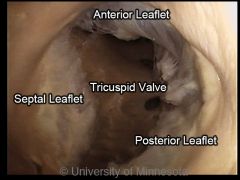
AKA tricuspid valve. Operates the right AV opening. Two major cusps (parietal and septal) in the dog, with intervening secondary cusps. |
|
|
Left Atrioventricular (A-V) Valve |
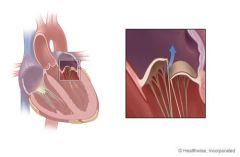
AKA mitral or bicuspid valve.Two major cusps (septal and lateral). Between L atrium and L ventricle. |
|
|
(tendinous cords) the though strands anchoring the free edges of the atrioventricular (AV) valves to the papillary muscles and preventing eversion of the valve leaflets into the atrium upon ventricular contraction (systole) |
chordae tendineae |
|
|
the muscular projections serving as attachments for the tendinous cords (chordae tendineae) of the atrioventricular (AV) valves.
|
papillary muscles
|
|
|
Linguofacial artery; branches of the external carotid artery. The facial artery winds around the ventral border of the mandible to supply the face. Also known as separate lingual and facial arteries
|
facial artery
|
|
|
Maxillary and linguofacial veins join to form the external jugular vein. The external jugular veins and subclavian veins join to form the brachiocephalic vein in carnivores and pigs. The brachiocephalic veins then join to form the cranial vena cava. In horses & ruminants the external jugular veins and subclavian veins join to form the cranial vena cava.
|
facial vein
|
|
|
The direct continuation of the external carotid artery to the space below the orbit (the pterygopalatine fossa). Its branches supply the orbit, teeth, chin nose, nasal cavity and palate.
|
maxillary artery
|
|
|
Maxillary and linguofacial veins join to form the external jugular vein. The external jugular veins and subclavian veins join to form the brachiocephalic vein in carnivores and pigs. The brachiocephalic veins then join to form the cranial vena cava. In horses & ruminants the external jugular veins and subclavian veins join to form the cranial vena cava.
|
maxillary vein
|
|
|
The great artery leaving the left ventricle and arching caudally. It sends oxygenated blood from the left heart to the heart itself and to the rest of the body through its systemic branches.
|
aorta
|
|
|
The continuation of the ascending aorta, it sends branches to the head, neck and thoracic limbs
|
aortic arch
|
|
|
the part of the aorta caudal to the aortic arch, divided into the thoracic aorta and the abdominal aorta by the diaphragm.
|
descending aorta
|
|
|
the initial part of the aorta, originating from the left ventricle at the center of the heart's base
|
ascending aorta
|
|
|
Ascend the neck to supply the head, face and brain.
Dogs-arise separately; ungulates (hooved animals) - arise by a short, common bicarotid trunk |
common cartoid artery - right and left
|
|
|
supply the neck, thoracic limb and the cranial portion of the thoracic wall. Each has many branches: Vertebral artery, Costocervical trunk, Cuperficial cervical artery, internal thoracic artery.
|
subclavian artery - right and left
|
|
|
a portion of the cervical fascia enclosing the carotid artery, the internal jugular vein, and the vagus nerve.
|
Carotid Artery (contained in carotid sheath) |
|
|
two branches of the pulmonary trunk carrying blood to the lungs; one to the right lung, one to the left lung
|
Pulmonary artery |
|
|
First branch of the arch of the aorta. As its name implies, it extends cranially to supply the right limb, neck and head. The brachiocephalic trunk gives off the left common carotid artery and then terminates in the right common carotid and right subclavian artery.
|
brachiocephalic artery (brachiocephalic truck)
|
|
|
are formed by the anastomoses of ventral intercostal artery of the internal thoracic and musculophrenic aa. and the dorsal intercostal a. of the costocervical trunk and aorta. They pass on the caudal border of the ribs in the intercostal spaces with like named veins and nerves.
|
Intercostal Arteries
|
|
|
The large vein in the neck returning blood from the head to the heart. Empties into the brachiocephalic vein in carnivores and pigs; directly into the cranial vena cava in ruminants and horses
|
External Jugular Vein
|
|
|
A single vein arising in the abdomen as a branch of the ascending lumbar vein. It passes upward through the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm into the thorax, then along the right side of the vertebral column to the level of the 4th thoracic vertebra, where it turns and enters the superior vena cava.
|
Azygos Vein
|
|
|
The major lymphatic vessel draining the entire body, except the right thoracic limb, right cranial thorax, and right side of the neck. It begins at the cisterna chyli, passes through the aortic hiatus cranally on the right side between the azygos vein and the aorta. Passing to the left side of the thorax in the cranial mediastinum, it empties near the thoracic inlet (venous angle) into the jugular vein or the cranial vena cava. |
Thoracic Duct
|
|
|
Great vessle emptying into the cranial or caudal part of the right atrium. Cranial returns blood from the head, neck thoracic limbs and cranial part of the wall of the thoracic cavity. The caudal part returns blood to the heart fromt he abdomen, pelvis and pelvic limbs
|
Vena Cava-cranial & caudal
|

