![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
OSHA |
Occupational Safety and Health Administration |
|
|
What is OSHA's job? |
·Enforces federal laws that help ensure a safe workplace ·Require employers to have a safety program ·(PPE) Personal Protective equipment
"assure safe and healthful working conditions for working men and women." |
|
|
What does PASS stand for? |
Pull the pin Aim low Squeeze the handle Sweep from side to side |
|
|
Formalin |
Tissue preservation, diagnostic test and sterilization |
|
|
Microbe |
Microorganism that is pathogenic (can cause disease) |
|
|
Pathogenic |
Capable of causing disease |
|
|
-static |
A chemical agent that will inhibit or slow down the growth, but not destroy a microorganism |
|
|
-cidal |
To kill; chemical agents with this suffix will kill the assigned target |
|
|
Disinfectant |
Used on objects: Alcohol Quaternary ammonium compounds (inactivated by hard water and soaps) Chlorine compounds (skin and respiratory system) |
|
|
Antiseptic |
Used on living tissues Iodine (yellow and brown cleaner) Chlorhexadine Hydrogen Peroxide (do not use in surgery) |
|
|
What is an ideal disinfectant? |
·Broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity ·Nonirritating and nontoxic to animal or human tissues ·Easy to use on inanimate objects without causing corrosion or stains ·Stable and not easily inactivated after application ·Inexpensive |
|
|
Cleaning a cage How many side to a cage? What are they? |
7 sides to a cage. ·Ceiling ·Walls: left, right, back ·Floor ·Inside surface of the door ·Outside surface of the door |
|
|
What is the proper technique to recap a needle? |
Always recap needles using "one handed needle recapping" |
|
|
Ethology |
The study of animal behavior. Used to determine best way to maneuver and control animals. |
|
|
What is the most common reason for dogs and cats to be surrendered to animal shelters? |
Behavioral problems |
|
|
What are the behavior problems in dogs? |
Jumping Obsessive behavior Aggression Separation anxiety Fear, nervousness Excessive barking Excitability House soiling, marking Spinning/tail chasing Fear of thunder Chewing |
|
|
How can technician help decrease dog fear in the clinic? |
Avoid staring, reaching over, or bending over toward a fearful dog. Turn sideways, stand several feet back, squat, use sideways glance, offer slightly outstretched hand. Let the dog make the first approach. Use least restraint possible. Follow every procedure immediately with a treat. |
|
|
What are behavior problems in cats? |
Fear Aggression Repetitive behavior Spraying/Elimination problems Scratching/Destructive behavior |
|
|
Cats: High Tail |
Greeting, investigating or frustration |
|
|
Cats: Aggression |
Tiptoes; head down; rear higher than fore; piloerection in tail; swiveled ears |
|
|
Cats: Fear |
Crouched with flat ears and tucked tail; eyes dilated; spitting or hissing |
|
|
Cats: Predatory aggression |
Body carried low to ground; slow, silent movement forward; then pause, tail-twitch, and pounce |
|
|
Avoidance Behaviors... |
Aggression must be taken seriously because of the chances of physical injury Instinctive predator Meet the cat on its own terms Read body language: ·Vocalization ·Ears back ·Batting Use minimal restraint at all times |
|
|
Complications with Restraints |
·Trauma due to excessive force ·Hyperthermia ·Dyspnea, especially in brachycephalic breed ·Proptosis (eye pops out) ·Emotional stress |
|
|
Why do we restrain? |
1.To control an animal so that it can receive medical care 2.To protect the animal from harming itself 3.To protect personnel 4.To protect practice owners from liability 5.To protect the animal form injury for the procedure |
|
|
T or F: The veterinarian may be held legally responsible if a client is injured by his/her own animal during a veterinary procedure. |
True |
|
|
Tranquilizers |
to alleviate anxiety ·Injectable drugs such as Acepromazine and Diazepam |
|
|
Inhalant anesthesia |
Isoflurane |
|
|
Sedatives |
produce drowsiness and may have analgesia effects ·Domitor (medetomidine hydrochloride)
|
|
|
Obtaining an Accurate History for a patient |
1.Signalment 2.Chief complaint 3.History of the present illness 4.Medical and surgical history 5.Environmental history 6.Medication history 7.Dietary history 8.Body system review |
|
|
Signalment |
Age Breed (or dominant breeds if mixed) Sex Reproductive status |
|
|
PD |
Polydipsia Excessive drinking |
|
|
PU |
Polyuria Excessive urination |
|
|
BAR |
Bright, alert, and responsive |
|
|
QAR |
Quiet, alert, and responsive |
|
|
Depressed |
Animal is not active or abnormal response to stimuli |
|
|
Comatose |
Animals not responding to any stimuli, severe depression without consciousness |
|
|
CV |
Cardiovascular system |
|
|
Rep |
Respiratory system |
|
|
Abd |
Abdomen |
|
|
LN |
Lymph nodes |
|
|
MS |
Musculoskeletal system |
|
|
EENT |
Eyes Ears Nose and Throat |
|
|
Neuro |
Neurological system |
|
|
Int |
Integumentary system (skin) |
|
|
Uro |
Urogenital system (reproductive organs) |
|
|
Normal Ranges for body temp (°F) |
Dogs & Cats 100.0-102.2°F Horse 99.0-101.5°F Cow 101.5°F (range 100.4-103.1) |
|
|
Bell (stethoscope) |
Low pitch sounds |
|
|
Diaphragm (stethoscope) |
High pitch sounds |
|
|
Normal Ranges for Heart Rate |
Cats: 140-220 bpm Dogs: 60-160 bpm Horse: 28-44 bpm Cow: 40-80 bpm |
|
|
Normal Ranges for Respiratory Rate |
Cats: 20-42 bpm Dogs: 16-32 bpm Horse: 6-16 bpm (8-12 bpm) Cow: 10-30 bpm (20-30 bpm) |
|
|
Body Condition score on a 5 level system |
3/5 ideal 1/5 very thin 5/5 obese |
|
|
Body condition score 9 level system |
5/9 Ideal 1/9 extremely thin 9/9 overt obese |
|
|
Entropion |
Eyelid that rolled inward (eyelashes will touch eyeball) |
|
|
Ectropion |
Eyelids that rolled outward (hound dogs) |
|
|
Otoscope |

Used for ear exams |
|
|
Stridor |
High pitched breathing sound caused by a blockage in the throat or voice box (larynx) medical emergency |
|
|
Crackles (Rales) |
Sounds like bubble wrap Due to accumulation of fluid in the areolar and small bronchioles or inflammation/edema |
|
|
Rhonchi (wheezes) |
Airway obstruction in the large airway. Low-pitched whistling/snoring sound during breathing. It occurs when air moves through narrowed airway lumen. (Best heard on expiration) |
|
|
Pleural Friction Rub |
Inflamed lung that has lost its slippery surface, Painful Sounds like "Creaking Leather" and squeaks |
|
|
Wheel-barrowing |
Performed by holding the animal's rear legs in the air while slowly moving forward.
A normal animal will move the front legs forward and maintain an upright position. |
|
|
Tachypnea |
Very fast breathing Not panting |
|
|
Cyanosis |
A bluish color of the skin and the mucous membranes due to insufficient oxygen in the blood |
|
|
Apnea |
Cessation of breathing EMERGENCY! |
|
|
Dyspnea |
Increased difficulty or distress in breathing |
|
|
Depth of respiration |
Volume of air inspired with each breath. Increased depth = Greater demand for Oxygen |
|

What type of syringe is this? |
Luer Lock |
|

What type of syringe is this? |
Concentric tip |
|

What type of syringe is this? |
Eccentric tip |
|
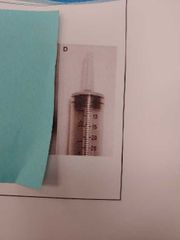
What type of syringe is this? |
Catheter tip |
|
|
How do you choose a needle? |
Size of vessel Quantity needed Intended use of sample |
|
|
PO |
Oral (by mouth) |
|
|
Complications with oral meds |
Aspiration of the medication Injury to Tech Inaccurate dosage (how much did they really get?) |

