![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
137 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
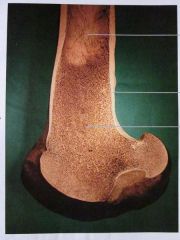
In order from top to bottom!
|
Medullary cavity
Compact bone Cancellous bone |
|
|
What are the two types of animal skeletons?
|
Exoskeleton (Arthropods)
and Endoskeleton (Vertebrates) |
|
|
Os and Osteo in medical words refer to?
|
Bone
|
|
|
Bone is the 2nd hardest substance in the body. What is the hardest?
|
Enamel
|
|
|
What are the three bone cell types?
|
Osteoblasts
Osteocytes Osteoclasts |
|
|
What does an Osteoblast do?
|
Create bone! (Ca and PO4)
They create the matrix and trap themselves. |
|
|
What are osteocytes?
|
They are the bone cell after it has stopped being an osteoblast and created it's matrix. It can revert to a blast cell for repair.
|
|
|
What do Osteoclasts do?
|
They are for remodeling of bone and break it down. They remove the Ca+
|
|
|
What are the functions of bone?
|
Support
Protection Leverage Storage - Mainly Ca+ Blood cell formation! |
|
|
Cancellous bone is considered to be?
|
Spongy bone
|
|
|
Compact bone is considered to be?
|
Heavy, dense and strong.
Shafts long bones. |
|
|
What constitutes most of the bone tissue of the axial skeleton?
|
Cancellous bone.
|
|
|
What is the outer fibrous tissue covering bone surfaces called?
|
Periosteum
|
|
|
What is the fibrous membrane lining the hollow interior of bones called?
|
Endosteum
|
|
|
What are the long bones?
|
Arms, legs, hands and feet.
|
|
|
What are the short bones?
|
wrist and ankle
|
|
|
What are the flat bones?
|
Ribs, shoulder blades, hip bones, cranial bones.
|
|
|
What are the irregular bones?
|
The vertebrae, sesamoid, and facial bones.
|
|
|
What is the surface called that has smooth areas of compact bone where bones come in contact with each other?
|
Articular surfaces.
|
|
|
What is the surface called that is a large round and found on distal ends of humerus and femur?
|
Condyle
|
|
|
What is the surface that is spherical and found on the proximal end of a long bone and typically unites the main shaft by a narrow region called the neck?
|
Head
|
|
|
What is a flat surface that is used for movement in a rocking motion?
|
Facet
|
|
|
What are all the lumps, bumps and other projections on a bone called?
|
Processes.
|
|
|
What is a depression on a bone called?
|
Fossa
|
|
|
What is a hole in the bone called?
|
Foramen
|
|
|
What are the bones of the axial skeleton?
|
Skull
Spinal column Ribs Sternum "Bones of the head and trunk." |
|
|
What are bones of the ear called?
|
Ossicles
|
|
|
What are the three types of joints?
|
Fibrous joints
Cartilaginous joints Synovial joints |
|
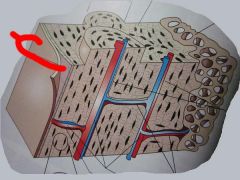
What is the name of these two layers?
|
Periosteum
|
|
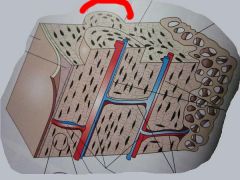
What system is this?
|
The Haversian Systems
|
|
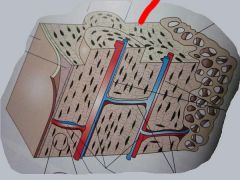
What type of bone is this?
|
Compact Bone
|
|
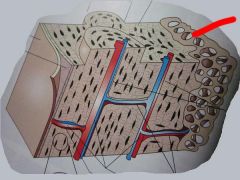
What type of bone is this?
|
Concellous (spongy) bone trabeculae.
|
|
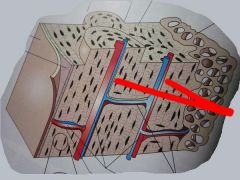
What are these vertical tubes called?
|
Harversian canals!
|
|
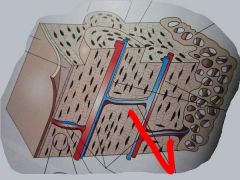
What are these horizontal tubes called?
|
Volkmann's canals!
|
|
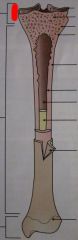
Label Red
|
Epiphysis
|
|
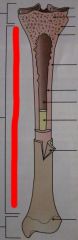
Label Red
|
Diaphysis
|
|
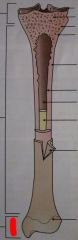
Label Red
|
Epiphysis
|
|
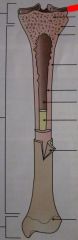
Top of bone area!
|
Articular cartilage
|
|
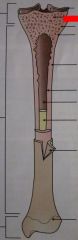
What type of bone is this?
|
Spongy bone
|
|
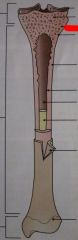
There is a grove through the spongy bone. What is it called?
|
Epiphyseal plate
|
|
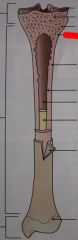
The holes in the spongy bone area are?
|
Red marrow cavities
|
|
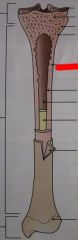
What type of bone is this?
|
Compact bone
|
|
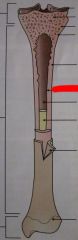
What is the lining between the compact bone and medullary cavity called?
|
Endosteum
|
|
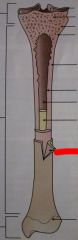
What is this skin over the bone called?
|
Periosteum
|
|
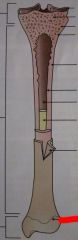
What is this line formation on the bottom of the bone called?
|
Epiphyseal plate
|
|
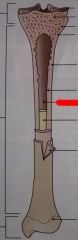
What is this opening in the bone called?
|
The Medullary Cavity!
|
|
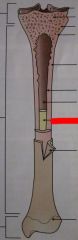
What is this colored substance within the center of the bone called?
|
Yellow marrow
|
|
|
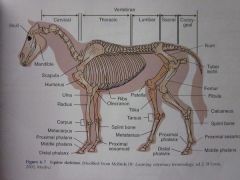
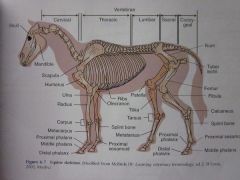
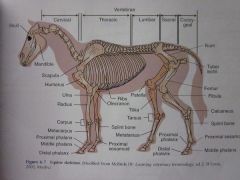
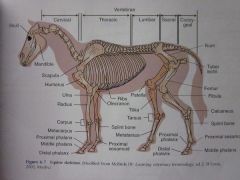
Skull
|
|
|
Cervical Vertebrae
|
|
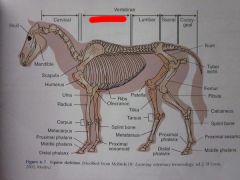
|
Thoracic Vertebrae
|
|
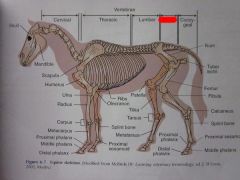
|
Sacral Vertebrae
|
|
|
Ilium
|
|
|
Femur
|
|
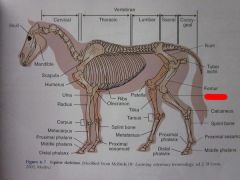
|
Fibula
|
|
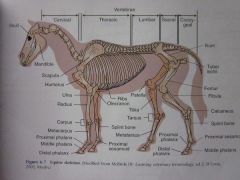
|
Calcaneus
|
|
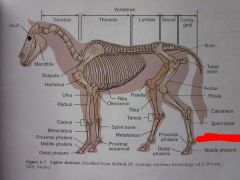
|

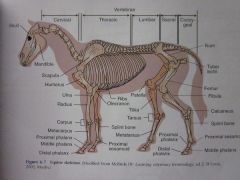
Proximal sesamoid
|
|
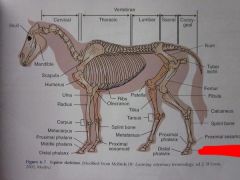
|
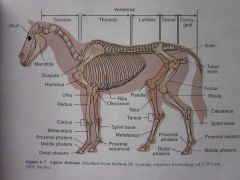
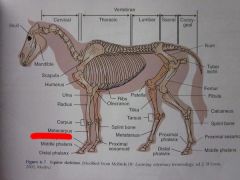
Middle phalanx
|
|
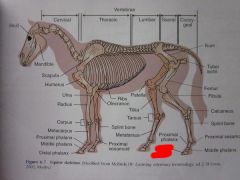
|
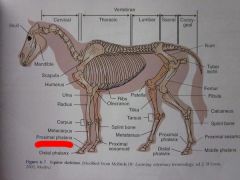
Distal phalanx
|
|
|
Proximal phalanx
|
|
|
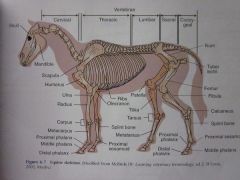
Metatarsus
|
|
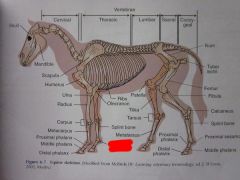
|
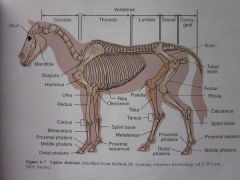
Proximal sesamoid
|
|
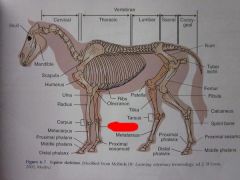
|
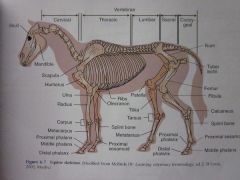
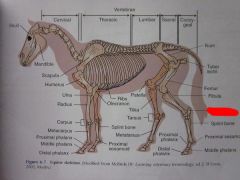
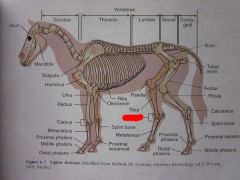
Splint bone
|
|
|
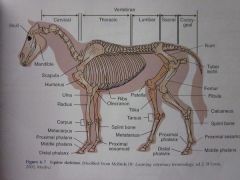
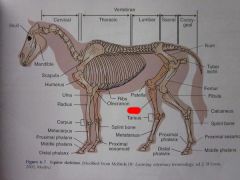
Tarsus
|
|
|
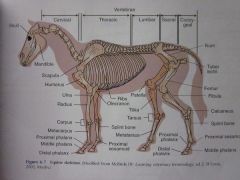
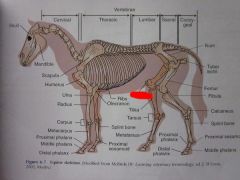
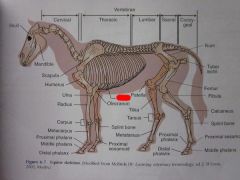
Tibia
|
|
|
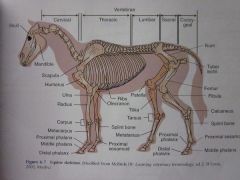
Patella
|
|
|
Ribs
|
|
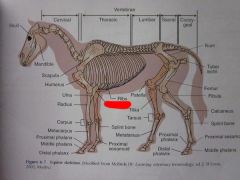
|
Olecranon
|
|
|
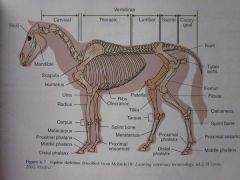
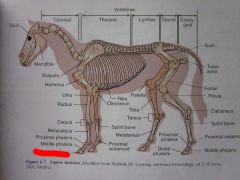
Distal phalanx
|
|
|
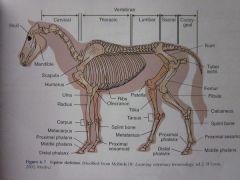
Middle phalanx
|
|
|
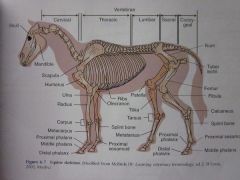
Proximal phalanx
|
|
|
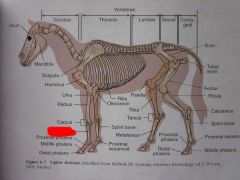
Metacarpus
|
|
|
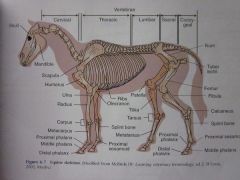
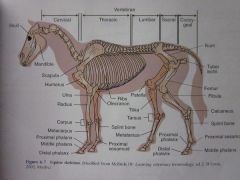
Carpus
|
|
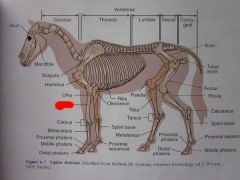
|
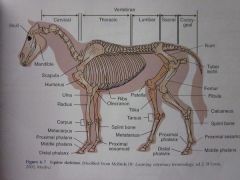
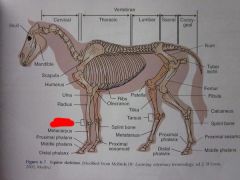
Radius
|
|
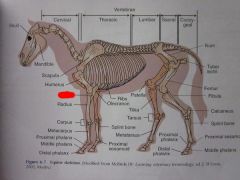
|
Ulna
|
|
|
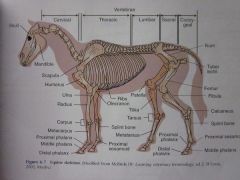
Humerus
|
|
|
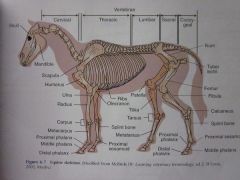
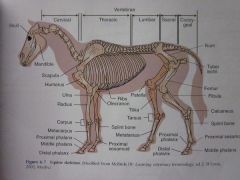
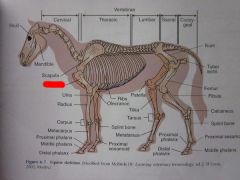
Scapula
|
|
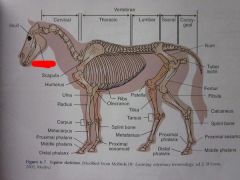
|
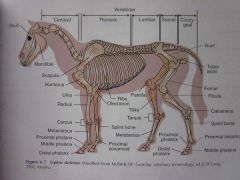
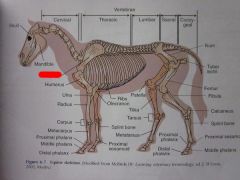
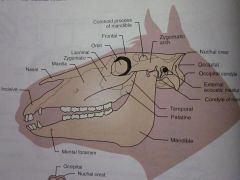
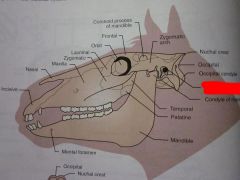
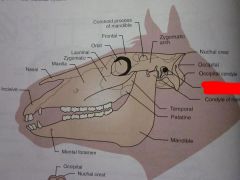
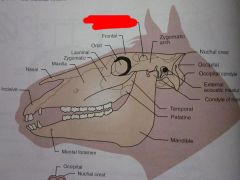
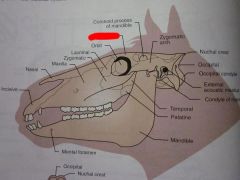
Mandible
|
|
|
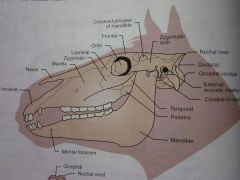
Mental foramen
|
|
|
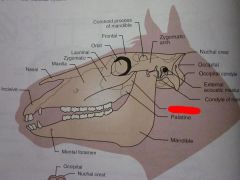
Mandible
|
|
|
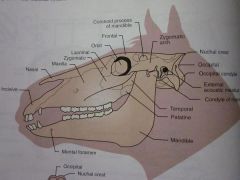
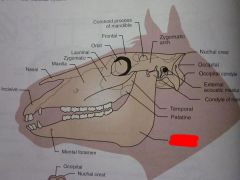
Palatine
|
|
|
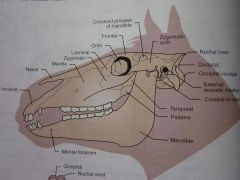
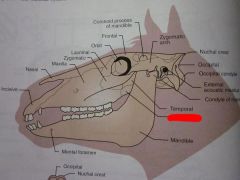
Temporal
|
|
|
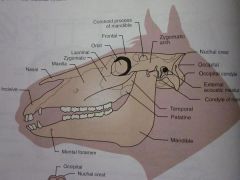
Condyle of mandible
|
|
|
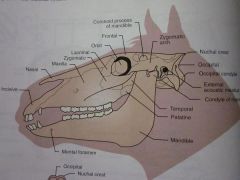
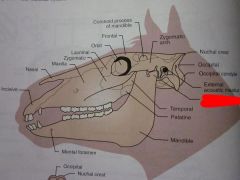
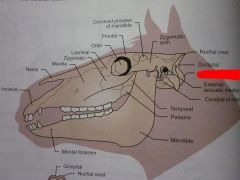
External acoustic meatus
|
|
|
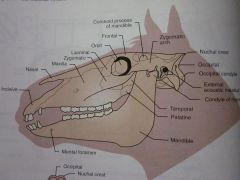
External acoustic meatus
|
|
|
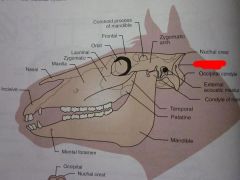
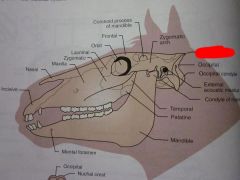
Occipital condyle
|
|
|
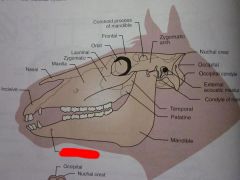
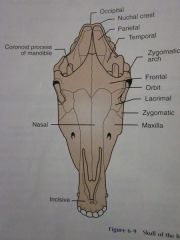
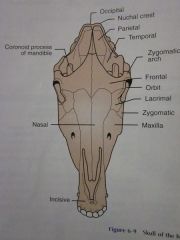
Occipital
|
|
|
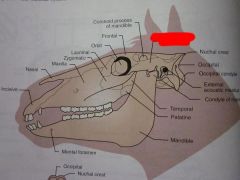
Nuchal crest
|
|
|
Zygomatic arch
|
|
|
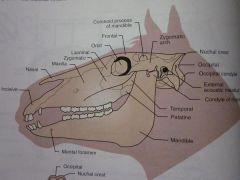
Coronoid process of mandible
|
|
|
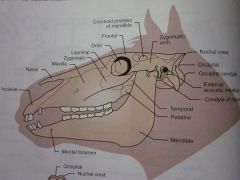
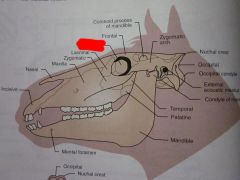
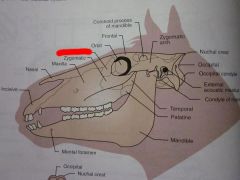
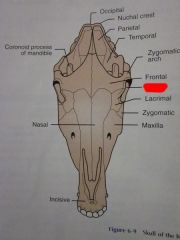
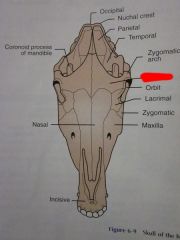
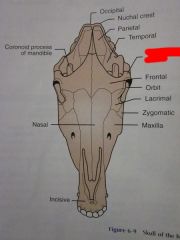
Frontal
|
|
|
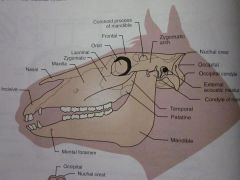
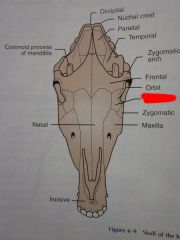
Orbit
|
|
|
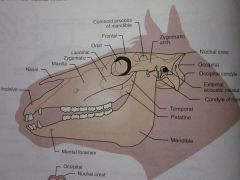
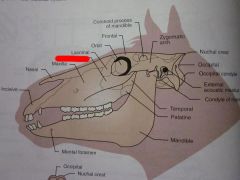
Lacrimal
|
|
|
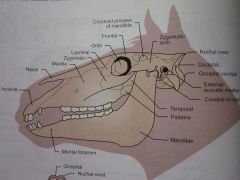
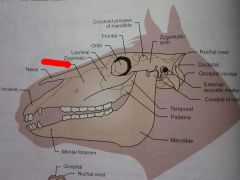
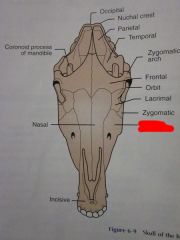
Zygomatic
|
|
|
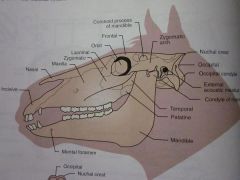
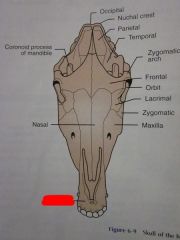
Maxilla
|
|
|
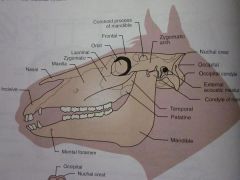
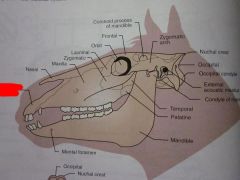
Nasal
|
|
|
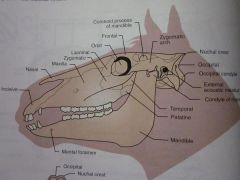
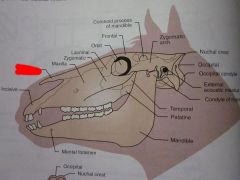
Incisive
|
|
|
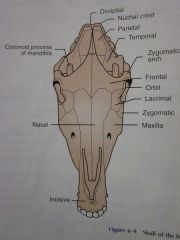
Incisive
|
|
|
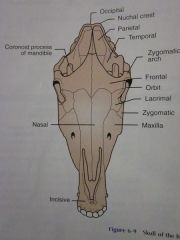
Maxilla
|
|
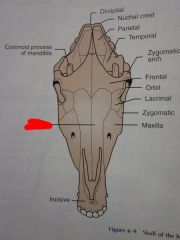
|
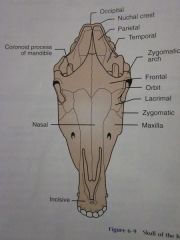
Nasal
|
|
|
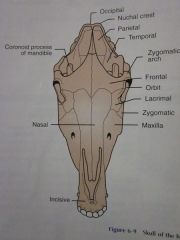
Zygomatic
|
|
|
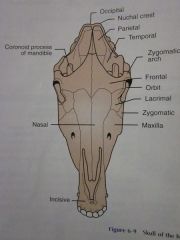
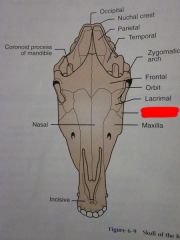
Lacrimal
|
|
|
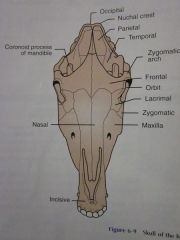
Orbit
|
|
|
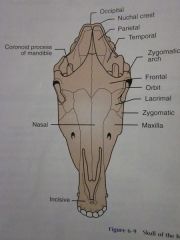
Frontal
|
|
|
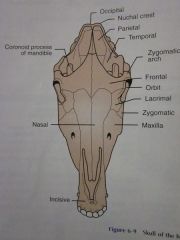
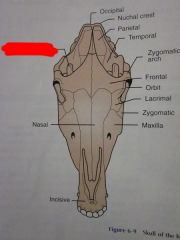
Zygomatic arch
|
|
|
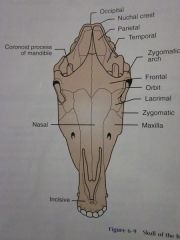
Coronoid process of mandible
|
|
|
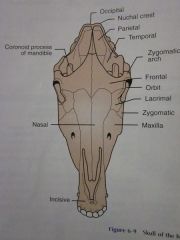
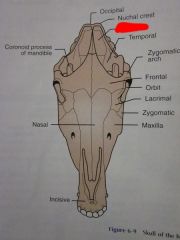
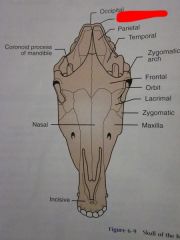
Temporal
|
|
|
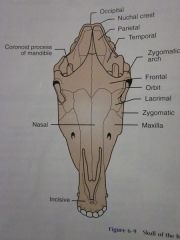
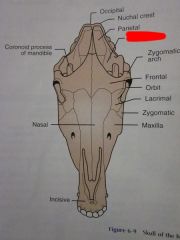
Parietal
|
|
|
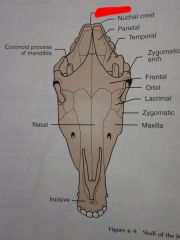
Nuchal crest
|
|
|
Occipital
|
|
|
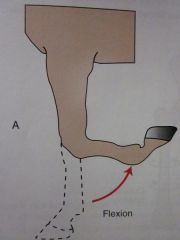
Flexion
|
|
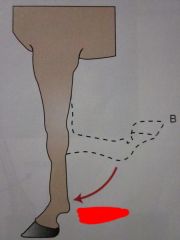
|
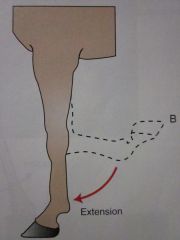
Extension
|
|
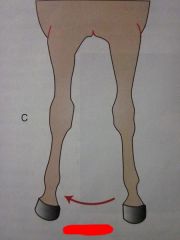
|
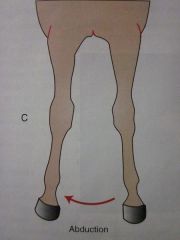
Abduction
|
|
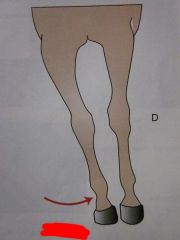
|
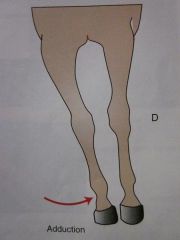
Adduction
|
|
|
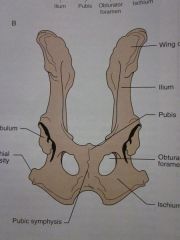
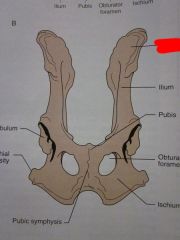
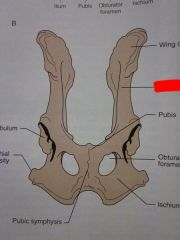
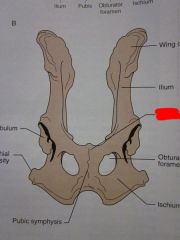
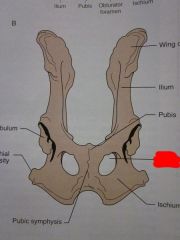
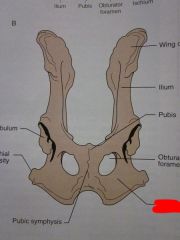
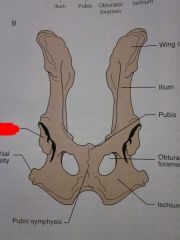
Wing of ilium
|
|
|
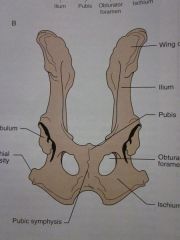
Ilium
|
|
|
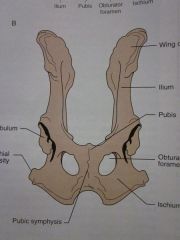
Pubis
|
|
|

Obturator foramen
|
|
|
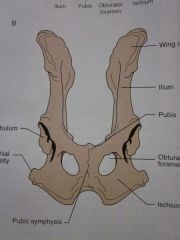
Ischium
|
|
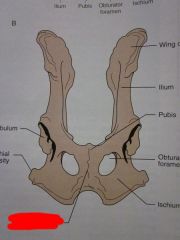
|
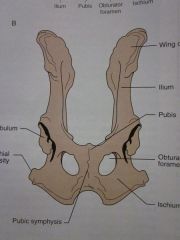
Pubic symphysis
|
|
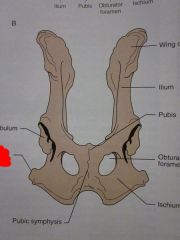
|
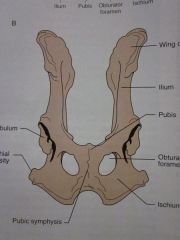
Ischial tuberosity
|
|
|
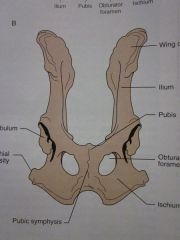
Acetabulum
|
|
|
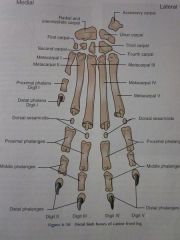
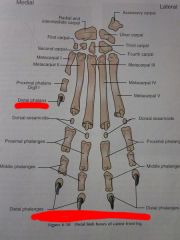
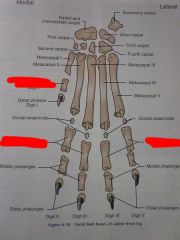
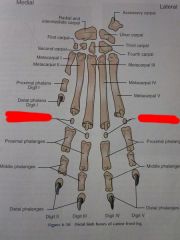
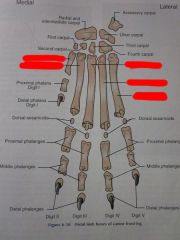
Digits I through V
|
|
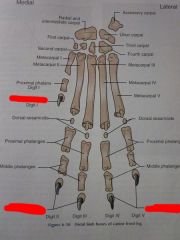
|
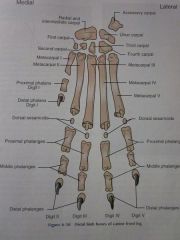
Distal phalanges
|
|
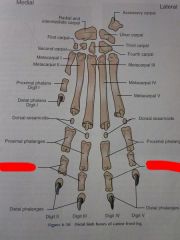
|
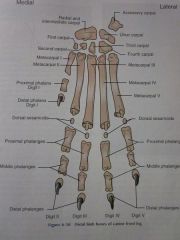
Middle phalanges
|
|
|
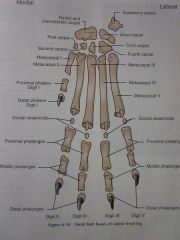
Proximal phalanges
|
|
|
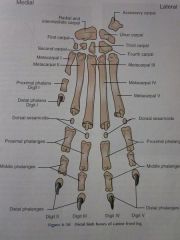
Dorsal sesamoids
|
|
|
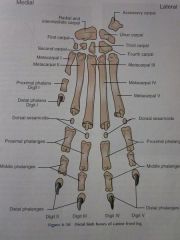
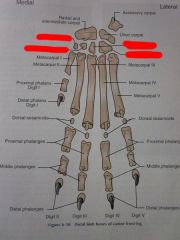
Metacarpals I through V
|
|
|
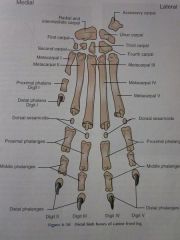
Carpals First through Fourth
|
|
|
What are the large blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves visible on radiographs called?
|
Nutrient Foramina
|
|
|
What is?:
Found in spongy bone. Produces red blood cells. |
Red bone marrow
|
|
|
What is?:
Primarily fills the shafts of long bones in adults? Serves as an energy reserve? |
Yellow bone marrow!
|
|
|
What number of cervical vertebra are in all mammals?
|
Seven
|
|
|
In the Sternum what is the 1st sternebrae called?
|
Manubrium
|
|
|
In the Sternum what is the last sternebrae called?
|
Xiphoid
|
|
|
Arthro- is a terminology for what?
|
Articular joints!
|
|
|
What joint type has a fluid filled joint capsule?
|
Synovial joint!
|
|
|
What fibrous connective tissue connects bone to bone?
|
Ligaments
|

