![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Example of Hypertonic solution |
50% dextrose |
50% |
|
|
Aminophyline |
Bronchial dilator |
Theophylline |
|
|
How many teeth a cat has |
30 |
30 or 42 |
|
|
How many teeth does a dog have |
42 I 3/3 C1/1 PM 4/4 M 2/3, X2 |
30 or 42 Dentistry |
|
|
Reticulocyte |
Identified by supravital stain/ new methylene blue dye |
Identified by what stain |
|
|
I.V. site in a mouse |
Tail vein |
Caudal |
|
|
Feline rhinotracheitis |
Caused by virus |
What's it caused by |
|
|
Rabies requirements are determined by |
County |
Sacramento county |
|
|
Greenstick fracture |
Often found in puppies |
|
|
|
Laws of rvt: legally cannot |
Diagnose, presribe, perform surgery |
|
|
|
Pulse rate in cow obtained by |
Coccygeal artery |
Caudal |
|
|
Hemoglobin is made up by |
Fe |
Card unfinished |
|
|
Urinary tract |
Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra |
Structures of the system |
|
|
Strongylus sp. |
Can cause colic in horses |
Unfinishes |
|
|
Dirofilaria immitis |
Transmitted by mosquitos |
Unfinished |
|
|
Flukes |
Can cause hepatic necrosis |
Unfinished |
|
|
Pseudoparasite |
Object resembles parasite |
Not a parasite |
|
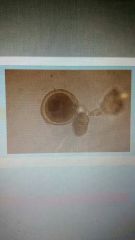
Identify this species. |
Toxocara sp. |
Roundworm |
|
|
Most non selective lab test media |
Blood agar |
|
|
|
Paired serum smaples, drawn several weeks apart, are essential in diagnosing serology to: |
Establish presence of current, active infection |
|
|
|
Microhematocrits measure |
Red blood cell volume |
|
|
|
Lymphocyte |
Highest percentage of wbc found in bovine differential count |
|
|
|
Microscopic examination of urine sediment looks for: |
Casts, erythrocytes, leukocytes, bacteria |
|
|
|
Gram stain |
Most commonly used in microbiology Identifies gram neg/pos |
|
|
|
Purpose of cover slip |
Prevent preparation from getting on lens Flatten surface so light enters at correct angle. |
|
|
|
Specific gravity : 1.050 |
Concentrated urine |
Type of sample |
|
|
ALT is specific to |
Liver |
What organ? |
|
|
Hemocytometer |
Counts blood cells |
Purpose |
|
|
Staphylococcus sp. |
Gram pos Occur in grape like clusters |
|
|
|
Erythrocytopenia |
Decrease in rbc |
|
|
|
MCV |
Mean corpuscular volume |
|
|
|
Hypersegmented neutrophill |
Segmented neutrophil of normal size but presenting more than normal number of nuclear lobes |
|
|
|
Relationship between hemoglobin and PCV |
hemoglobin is 1/3 of PCV |
|
|
|
Normal pH range of urine |
5 to 6 |
Acidic |
|
|
Macrocyte |
Larger than normal erythrocyte |
Big |
|
|
Spectrophotometer |
Measures chemical reactions of clinical chemistries |
|
|
|
Antihelintics |
Treat GI parasites |
|
|
|
Atropine |
Anticholinergic Dilates pupils Increases heart rate |
|
|
|
Schedule I drugs |
Most tightly controlled |
Unfinished |
|
|
Preanesthetics |
Decrease amount of anesthetic needed |
Benefit |
|
|
Pop off valve: high gas flow rates |
Should be open |
|
|
|
Tachycardia |
Fast heart rate |
|
|
|
Innovar-vet |
Classified as neuroleptanalgesic |
Unfinished |
|
|
Pop off valve: when using rebreathing bag as respirator |
Alternate open and closed |
|
|
|
Anesthetic uses |
Restraint |
Unfinished |
|
|
Reservoir bag |
Provides adequate fresh gases available to patient |
Purpose |
|
|
Hyperthermia |
High temperature Treated with cold water baths |
|
|
|
Halothane |
Anesthesia that causes less respiratory depression than isofurane |
Unfinished |
|
|
Isofurane |
Causes more respiratory depression than halothane |
Unfinished |
|
|
Coccidiosis: in rabbits |
Treated with sulfamethazine |
Treatment |
|
|
Major problems of goat anesthesia |
Regurgitation, salivation, difficult intubation, hypoventilation, bloat |
5 issues |
|
|
Dental fistula are caused by |
4th upper premolar |
Infection occurs beneath eye |
|
|
Stain used to identify Hemobartonella |
Gram stain |
Stain to identify |
|
|
Hemoglobinuria |
Increased hemoglobin in urine |
Define |
|
|
Modified Knott's test |
Detects microfilaria |
Identifies what? |
|
|
I grain = ___ mg |
65 mg |
|
|
|
Streptococcus |
Gram pos cocci occurs in chains |
|
|
|
I ml = ___ gtts |
15 gtts (drops) |
|
|
|
TB testing location in primates |
In the eyelid |
Easily observable |
|
|
Enzootic disease |
Constantly present in animal population and only usually effects a small percent of animals at a time |
|
|
|
Epizootic disease |
Epidemic outbreak of disease in animal population |
|
|
|
Mycosis |
Fungal infection |
What type of infection |
|
|
One ounce = ? CC's |
30 CC's |
|
|
|
Heifer |
Young cow |
|
|
|
How many teeth does a rat/mouse have |
16 teeth I 1/1, C0/0, PM 0/0, M 3/3 |
Include dental formula |
|
|
Guinea pig dentistry |
I 1/1, C 0/0, PM 1/1, M 3/3 |
|
|
|
Rabbit dentistry |
I 2/1, C 0/0, PM 3/2, M 3/3 28 teeth |
|
|
|
Animals susceptible to penicillin toxicity |
Hamsters and guinea pigs |
|
|
|
Macrominerals |
Minerals needed in larger amounts Calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, potassium, chloride |
|
|
|
Microminerals |
Trace minerals, minerals needed in smaller amounts Iron, copper, zinc, manganese, selenium, iodine |
|
|
|
Pineal body |
Pea sized structure in brain Function: secretes hormone that affects circadian rythm within 24 hrs. |
|
|
|
Hypophysis/ pituitary gland |
Peas sized below hypothalamus. 3 lobes. Master gland. |
|
|
|
Anterior lobe of pituitary gland |
HGH promoted growth. Hypo - dwarfism Hyper - giantism |
|
|
|
Thyroid stimulating hormone TSH |
stimulates thyroid glad to secrete thyroxine and tri-iodothyronine which acts to depress secretion of TSH. hyper - goiter |
|
|
|
Gram pos organisms |
Staphylococcus, streptococcus, closttridia, actinomyces |
|
|
|
Gram neg organisms |
E coli, klebsiella, proteus, salmonella, pasturella, psudomonas |
|
|
|
Cachexia |
Loss of lean body mass Seen with cancer and CHF |
|
|
|
Enterotoxemia |
Caused by toxins of clostridium perfringens Aka over eating disease |
|
|
|
Round worms |
Toxocara canis (dogs) Toxocara cati (feline ) Toxascaris leonina (cats and dogs) Baylisascaris procyonis (dogs and wildlife) |
|
|
|
Hookworm |
Ancylostoma canium (dog) Ancylostoma tubaeforme (cats) Ancylostoma braziliense, uncinaria stenocephala (both cats and dogs) |
|
|
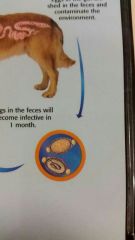
Whipworms |
Only in dogs Trichuris vulpis |
|
|
|
Tapeworms |
Dipylidiim canum, echinococcus multilocularis (dogs and cats) Echinococcus granulosus, taenia pisiformis (dog) Tania taenaeformis (cat) |
|
|
|
Organs of female reproduction system |
Hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, ovaries, ovaducts, uterus, vagina |
|
|
|
Ovulation |
Ejection of egg (ovum) from a follicle in the ovary |
|
|
|
Corpus hemorragicum |
Clot filled structure after ovulation. Nutritional matrix to support development of surrounding cells. Tissues develop into corpus luteum. |
|
|
|
Corpus luteum |
Develops after corpus hemorragicum. Produces progesterone (P4). Increases in size, increases level of progesterone. |
|
|
|
Progesterone |
Created by corpus luteum. Aids in preparation of pregnancy. |
|
|
|
Selenium deficiency |
Horse myopathy White muscle disease |
|
|
|
Superfecunidation |
Multiple sites of 2 or more offspring in one gestation |
|
|
|
Superfetation |
Multiple ovulation and conception while already pregnant. |
|
|
|
Anestrous |
Last month of cycle |
|
|
|
Estrous cycle stages |
Proestrous, estrous, diestrous, anestrous Lasts about 6 months |
|
|
|
Cardiac arrest symptoms |
No carotid pulse, dilated pupils, no respiration |
|
|
|
Tallest wave in electrocardiographic complex |
R |
|
|
|
In fertility can be caused by |
Abnormal estrous cycle, disease of uterus, poor breeding schedule, abortions |
|
|
|
4 basic body tissue |
Muscular, nervous, epithelial, connective |
|
|
|
Parasite in the hair follicle |
Demodex sp. |
|
|
|
Wright-Giemsa Stain |
Used for detection of anaplasma marginalie |
|
|
|
Normal blood urea nitrogen in dogs - ml per 100 ml |
10 to 20 |
|
|
|
Granulocytes |
Eosinophil and basophil |
|
|
|
Major function of erythrocytes |
Transport gases |
|

