![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
describe the arrangement of meningeal covering of the brain and spinal cord |
brain: (from superficial to deep) dura, arachnoid, pia maters
spinal cord: all three layers fuse to form denticulate ligament (@ every vertebral space) and filum terminale (caudal end of SC), which both keep SC suspended in fluid & protect it from injury |
|
|
describe the meningeal spaces in the brain and spinal cord |
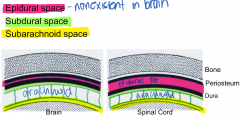
|
|
|
describe the anatomy of ventricular system and how CSF flows through the ventricles & around the brain & SC |
flow of CSF: lateral ventricles in the telencephalon > interventricular foramina > 3rd ventricle in diencephalon >mesenphalic aqueduct > 4th ventricle in rhomboencephalon > lateral apertures and central canal of medulla |
|
|
describe the development of the choroid plexus |
the CP are villous projections, composed of capillaries, pia mater, and cuboidal ependymal cells. The CP capillaries, in which the CSF is derived, proliferate from the roof plate of the ventricle. |
|
|
compare and contract capillaries in CNS w/ the capillaries in the rest of the body |
the capillaries in the vascular endothelium of the ventricle are fenestrated to allow for easy flow of plasma/serum |
|
|
describe how CSF is produced & absorbed in brain
|
Choroid plexus has tight junctions that regulates what comes through, modifying the ultrafiltrate from blood plasma, resulting in CSF. The production of CSF is driven by the blood pressure pulsations in the CP
CSF is absorbed 3-5 x/day and is absorbed via the arachnoid villi in brain, draining into the major sinuses |
|
|
what are the functions of CSF |
1. physical support 2. protection of CNS tissues 3. maintain ionic balance |

