![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
difference between tendon and ligament |
tendon = muscle and bone
ligament = bone and bone |
|
|
functional difference between tendon and ligament |
tendon: 1. support (stance phase) 2. locomotion (flex/extend)
ligament: 1. support load 2. provide joint stability |
|
|
why are tendons and ligaments important? |
they're commonly injured (especially in horses) |
|
|
what are the implications of tendon/ligament injuries? |
1. prolonged disability 2. failure to restore normal morphology and function 3. potential for reinjury |
|
|
describe the cellular components of tendons and ligaments |
tendon 1. dense regular fibrous CT (in same direction) 2. fewer fibrocytes (produce ECM) 3. ECM (collagen mainly type I,less GAG, organized collagen cross-linking)
ligaments 1. dense regular fibrous CT (in same direction) 2. more fibrocytes (produce ECM) 3. ECM (collagen mainly type III, more GAG, less organized collagen cross-linking)
|
|
|
function of type I collagen in tendon/ligament? |
provide high tensile strength |
|
|
tendon structure from deep to superficial |
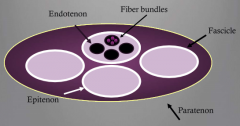
fiber bundle > endotenon > epitenon > fascicle > paratenon |
|
|
extrinsic vascular supply??? |
????? |
|
|
intrinsic vascular supply |
A comprehensive network of BV runs within tendon, formerly thought to be avascular |
|
|
the 4 tendon/ligaments on palmar surface of metacarpus/tarsus in horse |
from superficial to deep: 1. superficial digital flexor tendon 2. deep digital flexor tendon 3. inferior check ligament 4. suspensory ligament |
|
|
what are the 2 types of tendon synovial structures? what is their function |
bursae and tendon sheaths
function: preserve gliding function (reduce friction over joints and bony protuberance |
|
|
where would you expect to find bursae and tendon sheaths? |
bursa: over large bony protuberance and low motion of tendon over joint
sheath: over small bony protuberance and high motion of tendon over joint |
|
|
T/F: in horses, there's NO muscle below carpus/tarsus |
True |
|
|
responses to acute tendon/ligament injury
how about chronic injury? |
acute: 1. fiber disruption > hemorrhage, edema, fibrolysis 2. inflammation > further fibrolysis 3. compartment syndrome > fiber necrosis
chronic: 1. local soft tissue fibrosis 2. secondary joint disease 3. mineralization
|
|
|
how long could it take for a tendon/ligament injury to heal? does this healing result in full recovery? |
a long time 9-12 months!!
not really |
|
|
during early healing (1-6 months), what type of collagen fibers are laid down to repair injured tendon/ligament? |
type III (immature and weaker) |
|
|
T/F: after a tendon/ligament injury repair, remodeling can continue for years post injury |
true |
|
|
what are the goals of treatment used for tendon/ligament injury ? |
1. decrease inflammation (acute) 2. maintain tendon length & strength 3. decrease adhesion formation (fibrous band that limits gliding motion) |
|
|
how do we decrease tendon/ligament inflammation? |
1. hydrotheraphy 2. standing bandages 3. NSAIDs (1-2 week course) |
|
|
what factors does a tendon/ligament injury prognosis depend on? |
1. severity of injury 2. location of injury 3. adherence to controlled exercise program 4. desired use of animal 5. attitude and behavior of patient and owner |
|
|
how does a "controlled" exercise program rehabilitate a tendon/ligament injury? |
1. gradual increase loading 2. simulate maturation of granulation tissue 3. encourage longitudinal alignment of fibers 4. decrease adhesion formation |

