![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
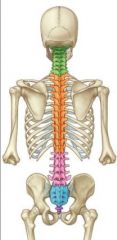
Name the green vertebral region
|
Cervical
|
|
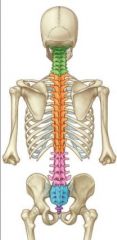
Name the orange vertebral region
|
Thoracic (12 vertebrae)
|
|
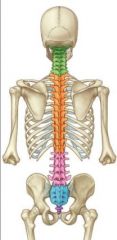
Name the pink vertebral region
|
Lumbar (5 vertebrae)
|
|
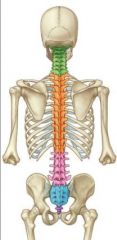
Name the blue bone
|
Sacrum
|
|
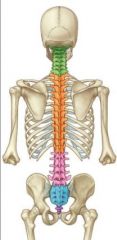
What's the purple thing?
|
The Coccyx!
|
|
|
Increase convexity of thoracic curvature (abnormality)
|
Kyphosis
|
|
|
Increase concavity of lumbar curvature (abnormality)
|
Lordosis
|
|
|
Contributing factors of Kyphosis
|
poor habit and aging
compression fracture of the thoracic vertebra from osteoporosis |
|
|
Contributing factors of Lordosis
|
poor habit
muscle imbalances abdominal weakness large abdomen pregnancy |
|
|
Lateral curvature of the spine coupled with rotation
|
Scoliosis
|
|
|
Causes of Scoliosis
|
Congenital (hemi vertebra)
Bone or Spinal cord Cancer Abnormal muscle tone due to disease(polio, cerebral palsey) disk protrusion Idiopathic Scoliosis (unknown causes) |
|
|
The membranous layer that encases the spinal cord within the vertebral canal
|
Dural (thecal) sac
|
|
|
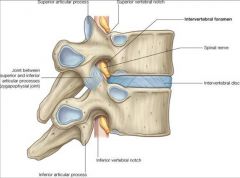
The narrowing of the foramen (in the vertebral column)
|
Foraminal Stenosis
|
|
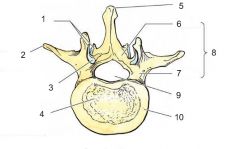
Q
|
A
|
|
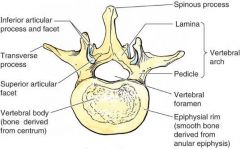
Q
|
A
|
|
|
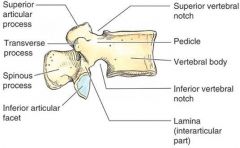
What are the functions of the spinous and transverse processes?
|
Muscle attachment and movement
|
|
|
What is the function of the articular process?
|
Restriction of movement
|
|
|
Function of the vertebral arch (Pedicles + Laminae)
|
Spinal Cord protection
|
|
|
Function of Vertebral Body
|
Weight baring
|
|
|
A disorder in which the 2 sides of vertebral arches, usually in lower vertebrae, fail to fuse during development resulting in an ‘open’ vertebral canal
|
Spina Bifida
|
|
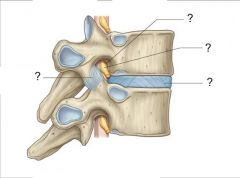
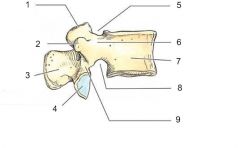
Q
|
A
|
|
|
In a ______ joint the bones are united by a joint capsule composed an outer fibrous layer and an inner synovial membrane
|
Synovial
|
|
|
A vascular connective tissue that produces synovial fluid, which lubricates and provides nutrients to articular cartilage
|
Synovial Membrane
|
|
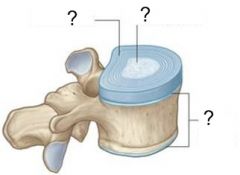
Q
|
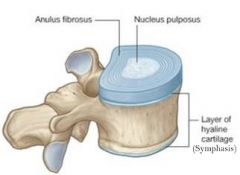
A
|
|
|
Degeneration of this could lead to herniation of the nucleus pulposus.
|
What is degeneration of the annuls fibrosis?
|
|
|
What is the imaging technique of choice when herniation of the vertebral disk is suspected?
|
MRI
|
|
|
Which nerves are compressed when herniaition occured between 2 vertebrae?
|
The nerve named after the lower vertebra.
|
|
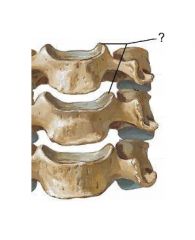
Found only in the cervical vertebrae. What are they called when articulated
|
Unicinate processes
Uncovertebral joints |
|
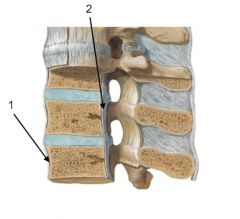
Q
|
1. Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
2. Posterior Longitudinal Ligament |
|
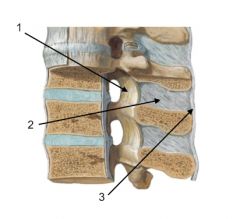
Q
|
1. Ligamentum Flavum
2. Interspinous Ligament 3. Supraspinous Ligament |
|
|
Which ligaments of the spine are stretched during full flexion of the spine?
|
Ligamentum Flavum, Interspinous Ligament, Supraspinous Ligament, Posterior Longitudinal Ligament and Facet Joint Capsule
|
|
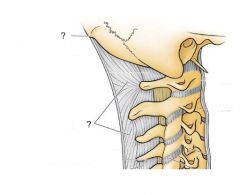
Q
|
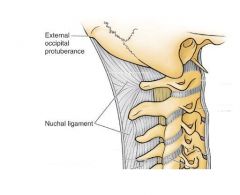
A
|
|
|
Which ligament limit back extension?
|
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of a zygophophyseal joint?
|
Synovial Joint
Guides/Limits movement in adjacent vertebrae |
|
|
Which region has the greatest region of mobility for the zygopophysial joints?
|
Cervical
|
|
|
Where is 50% of the cervical rotation located?
|
50% in the atlantoaxial joint (C1-C2)
50% in the rest (C2-C7) |
|
|
Where does nodding occur?
|
Atlantoccipital joint
|
|
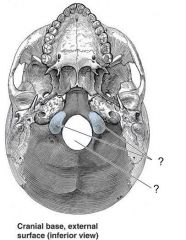
Q
|
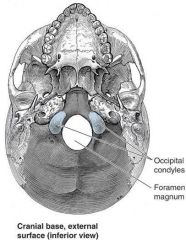
A
|

