![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
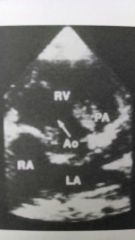
What type of vsd is this?
|
perimembraneous
|
|
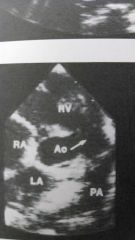
What type of vsd is this?
|
supracristal
|
|
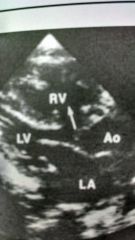
What type of vsd is this?
|
perimembraneous
|
|
|
Where does a perimembranesous show up on sax view?
|
10:00-11:00
|
|
|
where does supracristal show up on sax view?
|
1:00-2:00
|
|
|
What are the four types of vsd?
|
1. outlet (supracristal/infundibular)
2. inlet (subvalvular) 3. muscular (trabecular) 4. membraneous/perimembraneous |
|
|
Which is most common?
|
membraneous
|
|
|
What is the membraneous vsd bordered by?
|
av
tv muscle |
|
|
What is muscular bordered by?
|
muscle/myocardium
|
|
|
What is the inlet bordered by?
|
mv
tv muscle |
|
|
What is the outlet bordered by?
|
av
pv muscle |
|
|
What are symptoms?
|
depends on size but usually dyspnea and chf
|
|
|
What murmur is associated?
|
loud holosystolic LSB
|
|
|
What happens to chambers?
|
normal size with small vsd
rv hypertrophy with large dilated la with large |
|
|
What three doppler functions are used in evaluating vsd?
|
color to id location
cw to measure pressure diff between ventricles cw to measure vsd velocity |
|
|
What is the vsd velocity measure used for?
|
to estimate rvsp
|
|
|
What other element is required to measure RVSP?
|
systolic BP
|
|
|
What is the formula for calculating RVSP?
|
systolic BP minus vsd gradient
|
|
|
How do you calculate the VSD gradient?
|
4v squared
|
|
|
What would RVSP be in a patient with 5 m/sec VSD jet and BP of 130/80?
|
30 mmHg
|
|
|
What would it be with a VSD jet of 2 m/sec?
|
114 mmHg
|
|
|
Which jet, the 5 m/sec or the 2 m/sec, is more harmful and why?
|
The 2 m/sec, because it creates higher pressure which is more damaging to the lungs?
|
|
|
What happens if the lungs get damaged?
|
you might get PHTN, in which case the shunt might reverse, going right to left, which is Eisenmemger
|
|
|
What would protect the lungs from this happening?
|
PS
|

