![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four areas involved in blood pressure control in the body? |
Arterioles Postcapillary Venules Heart Kidneys |
|
|
What are the four types of Antihypertensives? |
Diuretics Sympathoplegic Agents Direct Vasodilators Agents that block Production or action of Angiotensin |
|
|
How do diuretics lower blood pressure? |
Lower blood pressure by depleting the body of sodium and thereby reducing blood pressure. Initially Blood volume and CO, SVR may initially increase, but after 6-8 wks CO returns to normal and SVR returns to normal |
|
|
How do Sympathoplegic Agents work? |
They lower blood pressure by decreasing SVR, inhibiting cardiac function, and increasing venous pooling. Divided by specific site of action, alpha and beta blockers. |
|
|
How do direct vasodilators work? |
Decrease blood pressure by relaxing vascular smooth muscle. |
|
|
How do agents that block production of action of angiotensin work? |
By blocking angiotensin there is a decrease in PVR. |
|
|
How does the sympathetic reflex work with antihypertensives? |
It prevents orthostatic hypotension or sexual dysfunction. |
|
|
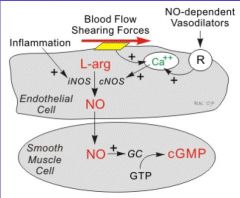
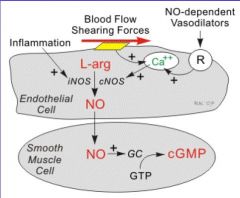
How does calcium influence blood pressure? |
Calcium decreases vascular resistance by dilating through three pathways: G-Protein cAMP Nitric Oxide cGMP Phospholipase C |
|
|
Nitric Oxide |
Causes smooth muscle relaxation Is Ca++ and Calmodulin dependent, flow dependent, and receptors can be increased by acetlycholine, substance P, Stress, Bradykinin, and thrombin. |
|
|
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Sodium Nitroprusside? |
Direct non-selective Vasodilator Relaxes arterial and venous vessels reducing SVR Interacts with oxyhemoglobin dissociating into methemoglobin, cyanide and Nitric Oxide. |
|
|
How is Sodium Nitroprusside Metabolized? |
Rapidly metabolized by uptake into RBCs releasing cyanide. Cyanide is metabolized by rhondase into Thiocyanate (active metabolite) and eliminated by kidneys. |
|
|
Why can patients on Nipride develop cyanide toxicity? |
The conversion of cyanide to thiocyanate is delayed with hypothermia. |
|
|
What is the dose and onset of Sodium Nitroprusside? |

|
|
|
What are the systemic effects of Sodium Nitroprusside? |
CV-Tachycardia, increased contractility, Coronary Steal Renal-Decreased renal function, renin release Hepatic-No change in hepatic blood flow Cerebral-Increased ICP Pulmonary-Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction Hematologic-Inhibits platelet aggregation |
|
|
What causes toxicity with Sodium Nitroprusside? |
Cyanide and Thiocyanate. S/S- Fatigue, N&V, CNS, Hypothyroid Treatment- Dialysis |
|
|
What classifies unstable angina? |
When there is a change in the frequency, character, duration, and precipitating factors in pts with stable angina. |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Nitroglycerine? |
Stimulates production of cGMP, needs specific enzyme to generate NO. Works primarily on venous capacitance and large coronary arteries. Needs special IV tubing (absorbed) SL no first pass metabolism |
|
|
Isosorbide Dinitrate |
Not subject to first pass metabolism Metabolite is more active Long duration of action Acute administration=orthostatic hypotension |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Fenoldopam? |
Dopamine type I receptor agonistcausing arterial dilitation throughsincreasing cAMP, will increase RBF Can be used like renal dose dopamine Rapid onset Adverse effects-IOP |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Hydralazine? |
Directly dilates arteries but not veins Well absorbed and rapidly metabolized (first Pass) Adverse effects- HA, Nausea, palpitations, seating, flushing, lupus with long term use Dose 10-20 mg Onset 20 minutes |

