![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a major sign of aortoiliac occlusive disease in males? |
Vasculogenic Impotence |
|
|
What may be a complication of vascular surgery if a bypass conduit reduces pelvic blood flow? |
Vasculogenic impotence |
|
|
Where is the blood supply to the penis derived from? (Two steps) |
Internal Iliac Artery via the Internal Pudendal Artery |
|
|
Where does the internal pudendal artery enter the male perineum? |
Through the lesser sciatic foramen |
|
|
How many branches is the internal pudendal artery divided into? Names? |
THREE 1. Cavernosal A 2. Bulbourethral A 3. Dorsal A |
|
|
What does the Cavernosal artery supply? |
Corpora cavernosa (main erectile tissue) |
|
|
What does the Bulbourethral artery supply? |
Corpus spongiosum |
|
|
Where does the Dorsal artery supply blood to? |
Skin and glans of the penis |
|
|
What occupies the distal 2/3 of the penis? |
TWO corpora cavernosa |
|
|
What occupies the ventral 1/3 of the penis? |
Corpus spongiosum |
|
|
What thick fascial layer surrounds the erectile tissues? |
Tunic Albuginea |
|
|
Where does the urethra pass through? |
Center of the corpus spongiosum |
|
|
What drains the corpora cavernosa? |
Emissary veins |
|
|
Bulge of smooth muscle cells, i.e. penile a's and v's, formerly thought to regulate blood flow |
Polster |
|
|
During what state are arterioles leading into the corpora cavernosa constricted? |
FLACID state |
|
|
What type of stimulation to the smooth muscle of sinusoids causes relaxation of these muscles? |
Parasympathetic |
|
|
During erection, what is there a decrease of while more blood flows into the sinusoids? |
Decrease in resistance |
|
|
T/F: As sinusoids become distended, inter-cavernosal pressure increase? |
TRUE |
|
|
What reduces venous outflow and promotes sinusoidal distension (maintaining penile rigidity)? |
Compression of emissary veins compressed against the wall of the tunic albuginea |
|
|
What is the condition of being swollen or tumid? |
Tumescence |
|
|
When do normal males have regular erections? |
During REM phase of sleep |
|
|
How are changes in penile circumference monitored? |
Using strain gauge plethysmography |
|
|
How large of cuff is used when taking penile pressures? |
2.5 cm wide |
|
|
How is a PBI calculated? |
Penile pressure/highest brachial pressure |
|
|
What are values for the following phases: Normal? Equivocal? Abnormal? |
Normal: >0.75 Equivocal: 0.65-0.74 Abnormal: <0.64 |
|
|
What is a normal diameter for the cavernosal arteries? |
0.5 mm |
|
|
What is the purpose of Intercavernosal injection of vasodilators? |
To test if the arterial, venous and sinusoidal mechanisms are intact |
|
|
What is considered the normal time where no disease is present w/ intracavernosal injection? |
Erection w/in 10 minutes, maintain for 30 |
|
|
If abnormal study presents what is the next step taken? |
Second dose of drug is administered |
|
|
At what time interval are serial measurements taken? |
5, 10, 15, 20 minutes post-injection |
|
|
What is the waveform appearance for a penis in the flaccid state? |
Low resistance, good systolic upstroke |
|
|
What is the waveform appearance for a penis in the tumescent/intermediate state? |
Same as flaccid state however slightly diminished |
|
|
What is the waveform appearance for a penis in the erect/rigid state? |
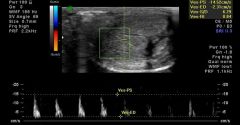
|
|
|
What increase in vessel diameter (%) is adequate to indicate normal arterial inflow? |
75% |
|
|
What peak systolic velocity is considered normal? |
40 cm/sec or greater |
|
|
What is a velocity indication of arterial insufficiency? |
Peak systolic velocity of less than 25 cm/sec |
|
|
What is the cause of veinogenic impotence? |
Unknown; COULD BE: Excessive leakage from corpora cavernosa Defect in tunic albuginea
|
|
|
What is an indicator of veinogenic problems? |
Prominent diastolic flow in the cavernosal arteries |
|
|
What is an erection that occurs spontaneously and the penis remains rigid for an extended period of time? |
Priapism erection |
|
|
What happens with the blood during a priapism erection? |
Viscosity rises (due to increased CO2 tension) Relative venous occlusion (no blood outflow) |
|
|
What is the process known as the twisting of testis around the axis of the spermatic cord within the scrotal sac? (at least once) |
Testicular torsion |
|
|
Testicular torsion results from abnormal mobility of what? |
Testis |
|
|
At what time is testicular tension the most common? |
Puberty |
|
|
After how many hours is testicular torsion classified as acute? What is the appearance? |
4-6 hours Hypoechoic, enlarged testes |
|
|
After how many days is testicular torsion considered early subacute? What is the appearance? |
1-4 days - Necrosis Hypoechoic, enlarged |
|
|
When is testicular torsion classified as late subactue? |
5-10 days Hyperechoic (decrease in findings) |
|
|
When is testicular torsion classified as chronic? Appearance? |
>10 days ATROPHIC testes Hyperechoic, enlarged dpididymis |
|
|
How is testicular torsion corrected? |
Surgically |
|
|
What are velocities present in testicular torsion? |
4-19 cm/sec Low resistance Diminished/absent flow |
|
|
What's the term for an enlargement of veins of the spermatic cord & dilatation of pampiniform plexus? |
Varicocele |
|
|
T/F: The reason behind varicocele is known? |
FALSE; it is unknown |
|
|
Which side of the body is varicocele more popular? |
LEFT side |
|
|
T/F: Varicocele are easily palpated? |
TRUE |

