![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
210 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many diastolic peaks are shown across the mitral valve and what are they called?
|
2 Peaks
E & A Wave |
|
|
What does an E wave represent in the MV?
|
Passive early diastolic filling
|
|
|
What does an A wave represent in the MV?
|
Late diastolic filling due to atrial contraction
|
|
|
Where is the sample volume placed in LV inflow for diastolic function?
|
At the MV leaflet tips
|
|
|
What are two views where you can view LV inflow for diastolic function?
|
1. Apical 4 chamber
2. Apical 3 chamber |
|
|
True or False
The sample volume for LV inflow for diastolic function should be small and parallel to flow |
True
|
|
|
What is the MV E/A ratio dependent upon?
|
Placement of the PW Doppler at leaflet tips
E & A peak velocities |
|
|
What is the MV E/A ratio mainly used for?
|
Evaluation of LV diastolic function
|
|
|
What is the normal range of MV E/A ratio?
|
1.0-1.5
|
|
|
For the LV inflow for SV measurements where is the PW sample volume placed and from what views?
|
Placed at the Annulus of MV
Viewed from Apical 4 or 3 chamber views |
|
|
True or False
The flow for LV inflow for SV measurements should be perpendicular |
False
Should be parallel to flow |
|
|
What are the normal velocities for MV?
|
Less than 1.3 m/s
|
|
|
What is the normal velocity range for an E wave?
|
0.7 - 1.2 m/s
|
|
|
What is the normal velocity range for an A wave?
|
0.4 - 0.7 m/s
|
|
|
Where should the sample volume of a PW be placed for deceleration time in the MV?
|
MV leaflet tips
|
|
|
What view should be used to visualize the MV deceleration time?
|
Apical 4 chamber
|
|
|
What is the normal range of MV for deceleration time?
|
160 - 240 msec
|
|
|
From what two views should the LV outflow be obtained from?
|
1. Apical 3 chamber
2. Apical 5 chamber |
|
|
True or False
Doppler angle for LV outflow should be 60 degrees |
False
Doppler angle for LV outflow should be 0 degrees |
|
|
Where should the PW sample volume be placed in the LV outfow?
|
In LVOT
|
|
|
What are the 3 characteristics of LV ejection velocity?
|
1. Steep acceleration slope
2. Sharply peaked early systolic maximum velocity 3. Less steep deceleration slope |
|
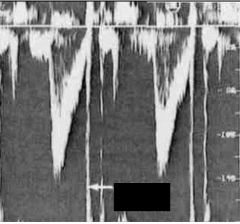
What is the arrow pointing to in this image?
|
Closing click of LV outflow
|
|
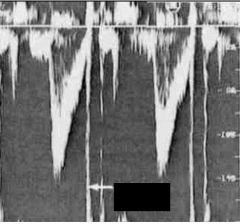
What is the arrow pointing to in this image?
|
Opening click of LV outflow
|
|
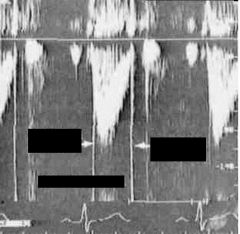
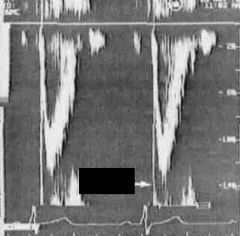
Is this CW or PW Dopler? What is the arrow to the right and left pointing too?
|
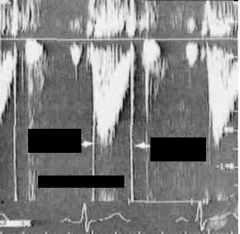
CW Doppler
Right Arrow: Closing click Left Arrow: Opening click |
|
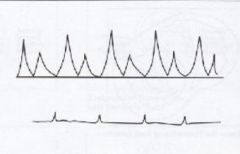
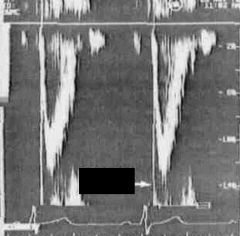
What valve makes this type of waveform?
|
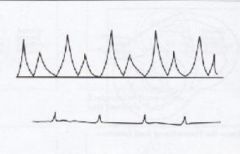
Mitral Valve
|
|
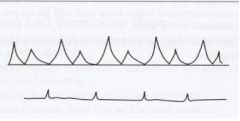
What valve makes this type of waveform?
|
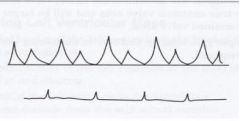
Tricuspid valve
|
|
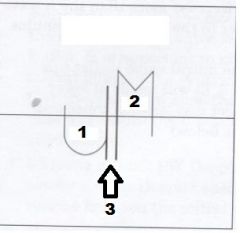
Label Numbers 1, 2 and 3
|
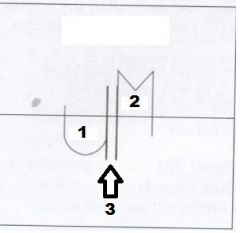
1. Aortic Valve
2. Mitral Valve 3. IVRT |
|
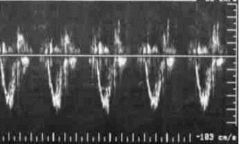
What PW Doppler signal is this?
|
RV outflow
|
|
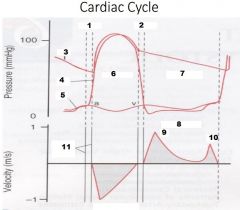
Label Numbers 1-6
|
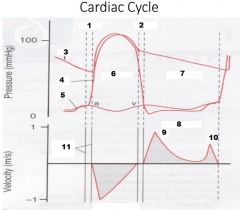
1. IVCT
2. IVRT 3. Aorta Pressure 4. LV Pressure 5. LA Pressure 6. Systole |
|
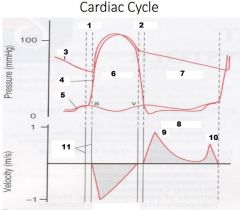
Label Numbers 7-11
|
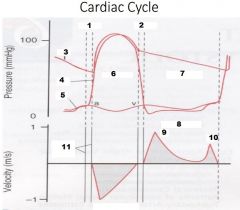
7. Diastole
8. LV Inflow 9. E Wave 10. A Wave 11. Valve clicks |
|
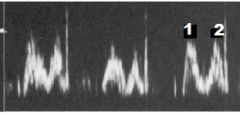
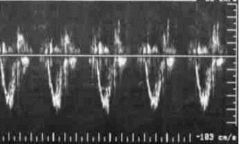
What PW Doppler signal is this? Label numbers 1 & 2
|
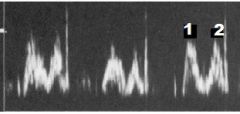
RV Inflow
1. E wave 2. A wave |
|
|
What is the normal LVOT VTI?
|
0.7 - 1.1 m/s
|
|
|
What is the average velocity of AV?
|
Less than 2.0 m/s
|
|
|
What are 2 views that can be used to visualize the RV inflow?
|
1. Parasternal
2. Apical 4 chamber |
|
|
True or False
TV flow is similar to MV flow except that TV peak velocities are less than MV peak velocities |
True
|
|
|
True or False
TV velocities will not show respiratory variation |
False
TV velocities will show respiratory variation |
|
|
What 2 views can be used to visualize the RV outflow?
|
1. Parasternal
2. Subcostal short axis |
|
|
True or False
RV ejection curve is similar to LV ejection curve |
True
|
|
|
Ture or False
RVOT will have a greater peak velocity with a pointed curve |
False
RVOT peak velocity will be lower and the curve will be rounded |
|
|
What is IVRT?
|
From AV closure to MV opening
|
|
|
What two places will you place the CW Doppler between to obtain IVRT?
|
Between AV and MV
|
|
|
Where will you place a PW Doppler sample volume to obtain IVRT?
|
In LVOT and increase sample volume
|
|
|
True or False
CW Doppler is preferred over PW Doppler when obtaining IVRT |
True
|
|
|
What is normal IVRT?
|
70-90 msec
|
|
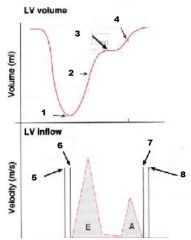
Diastole of LV
Label numbers 1 - 8 |
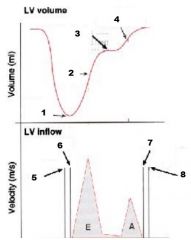
1. End Systole
2. Rapid filling 3. Diastasis 4. Atrial Contraction 5. Ao-valve closing click 6. MV opening click 7. MV closing click 8. Ao-valve opening click |
|
|
What is the best view for the aortic arch?
|
Suprasternal notch LAX
|
|
|
What are two locations you would place the PW in the aortic arch?
|
1. Ascending aorta
2. Descending aorta |
|
|
Where would you place CW Doppler in the aortic arch?
|
Descending aorta
|
|
|
What are the normal velocities of the aortic arch?
|
Less than 2.0 m/s
|
|
|
What are 3 purposes of Color Doppler?
|
1. Evaluation of overall intracardiac flow patterns
2. Aliasing may indicate a turbulent/stenotic jet 3. Regurgitant flow may be detected |
|
|
In PLAX what color should be seen through the Aortic valve? Is it going away from or towards the trandsducer
|
Red; towards the trandsducer
|
|
|
In Apical views what is the color of aortic flow? Is it towards or away from the transducer?
|
Blue; away from the transducer
|
|
|
What type of flow is seen with the LV in the Apical view?
|
Vortex of colors
|
|
|
True or False
The normal color flow in the LV is Blue flows along the lateral LV wall and red flows along the septum in the apical views |
False
Red flows along the lateral LV wall and blue flows along the septum |
|
|
True or False
Physiologic regurgitation may detect regurgitation, with color and PW, CW Doppler |
True
|
|
|
How many valves of the heart have physiologic regurgitation?
|
3
|
|
|
What is the percentage of mild pulmonary insufficiency (PI) detected in normal people?
|
70-80%
|
|
|
What is the percentage of tricuspid and mitral regurgitation detected in normal people?
|
70-80%
|
|
|
True or False
Small amounts of physiologic valvular regurg is not clinically significant |
True
|
|
|
What are 3 systolic functions of cardiac hemodynamics?
|
1. Doppler Stroke Volume - SV
2. Cardiac Output - CO 3. Cardiac Index - CI |
|
|
Define Doppler stroke volume
|
Amount of blood ejected with each heart beat
|
|
|
What is the equation for Doppler SV?
|
SV = CSA x VTI
|
|
|
How do you calculate cross sectional area (CSA)?
|
CSA (cm^2) = 3.14 x (diameter/2)^2
Or CSA (cm^2) = 0.785 x diameter^2 |
|
|
From what view do you obtain a CSA of the Aortic valve?
|
PLAX of AV in systole
|
|
|
What do you measure to obtain the CSA of AV?
|
LVOT
|
|
|
True or False
LVOT measurement is made from the septal endocardium to the leading edge of the anterior MV leaflet |
True
|
|
|
What is the normal range of the LVOT diameter?
|
1.8 - 2.4 cm
|
|
|
What is Time velocity integral (VTI)?
|
The distance the blood travels with each stroke
|
|
|
From what 2 views can VTI of LVOT be measured with PW Doppler?
|
1. Apical 3
2. Apical 5 |
|
|
True or False
VTI of LVOT PW sample volume should be perpendicular to flow |
False
Sample volume should be parallel to flow |
|
|
What is the equation for Doppler SV using AV?
|
SV = LVOT diameter^2 x 0.785 x VTI of LVOT
|
|
|
What is the equation for SV using MV?
|
SV = CSA of MV x VTI of LVIT
|
|
|
What 2 reasons are why SV of MV is not used?
|
1. Inconsistency measuring true MV annulus - assumed to be circular but is actually more elliptical
2. VTI is affected by diastolic dysfunction |
|
|
What is cardiac output?
|
The amount of blood that is ejected out of the LV per minute
|
|
|
What is the unit of CO?
|
liters per minute or L/min
|
|
|
True or False
CO LV = CO RV |
True
|
|
|
What is the equation for CO?
|
CO = SV x HR
|
|
|
What is cardiac Index (CI)?
|
Reflects cardiac output for body surface area (BSA)
|
|
|
What are 2 equations for BSA?
|
BSA (m^2) = ([Height (cm) x Weight (kg)] / 3600) ^1/2
or BSA (m^2) = ([Height (in) x Weight (lbs)] / 3131) ^1/2 |
|
|
What is the equation for CI?
|
CI = CO/BSA
Or CI (L/min/m^2) = CO (L/min) / BSA (m^2) |
|
|
What is normal CI?
|
2.5 - 4.5 L/min/m^2
|
|
|
True or False
You can calculate SV, CO, and CI from any valve where both CSA and VTI can be measured |
True
|
|
|
True or False
SV, CO and CI can only be calculated accurately in the absence of regurgitaiton |
True
|
|
|
What are two reasons the LVOT/AV sites are most commonly used to represent systemic circulation?
|
1. Easily duplicated in every patient
2. Can be used even in instances of aortic stenosis because flow remains laminar proximal to the stenosis |
|
|
What is the continuity equation?
|
A1 x V1 = A2 x V2
|
|
|
What is the continuity equation based on?
|
The assumption that the flow through various cardiac chambers is constant
|
|
|
True or False
Continuity equation is commonly used to calculate valve areas |
True
|
|
|
How is the continuity equation used for stenotic valves?
|
By using valve annulus and velocities, the stenotic valve area can be measured
|
|
|
What are the 3 measurement requirements for Aortic valve area?
|
1. LVOT diameter with 2D
2. LVOT velocity VTI with PW 3. Peak AV velocity VTI with CW |
|
|
From what view should LVOT diameter be measured?
|
PLAX
|
|
|
What views should be used for Doppler assessment of LVOT?
|
Apical 3 or 5
|
|
|
True or False
PW Doppler sample volume of LVOT should be 0 degrees and parallel to flow |
True
|
|
|
What should be viewed in the AV of Doppler assessment of LVOT to ensure proper sample site?
|
Valve click
|
|
|
What views should the Doppler assessment of the AV be used?
|
Apical 3 or 5 chamber
|
|
|
True or False
The suprasternal notch can be used as well for Aortic stenosis with Doppler assessment. |
True
|
|
|
Where should the CW Doppler be placed to obtain the peak velocity?
|
Through the Aortic valve and parallel to flow
|
|
|
True or False
Ascending, descending aorta should be used during assessment of aortic valve to obtain true stroke volume |
False
Ascending, descending aorta should not be used because of the branches there is no true stroke volume |
|
|
What is the equation for Aortic Valve Area (AVA)?
|
AVA (cm^2) = CSA of LVOT x VTI of LVOT / VTI of AV
or AVA (cm^2) = 0.785 x LVOT diameter |
|
|
What is the normal aortic valve area?
|
Greater than 2.0cm^2
|
|
|
What is the normal annulus diameter of the aortic valve?
|
1.8 - 2.4 cm
|
|
|
What is the normal LVOT VTI?
|
18 - 22cm
|
|
|
What are the normal AV velocities?
|
Less than 2.0 m/s
|
|
|
What is the normal mitral valve area?
|
4 - 6 cm^2
|
|
|
What is the normal annulus diameter of the mitral valve?
|
2.7 - 3.5 cm
|
|
|
What is the normal MV inflow VTI?
|
7 - 13 cm
|
|
|
What is the normal MV velocities?
|
Less than 1.3 m/s
|
|
|
What are the 5 useful identifying factors of M-Mode?
|
1. Rapid motion of cardiac structures
2. Cardiac dimensions 3. Evaluation of effusions 4. Evaluation of vegetation's 5. Evaluation of wall thickness |
|
|
What is M-Mode?
|
Depicts the motions of structures along a single scan line or plane with a function of time
|
|
|
From what orientation is standard M-Mode imaged?
|
PLAX
|
|
|
True or False
2D imaging is used to place M-Mode scan line along the structures of interest |
True
|
|
|
What are the 4 standard scan lines used in PLAX?
|
1. Aortic Valve
2. Mitral valve Annulus 3. Mitral Valve 4. LV at Papillary Muscles |
|
|
What 5 structures are viewed for Aortic valve of M-Mode?
|
1. RV (Most Anterior)
2. Aortic Root 3. R. coronary cusp 4. Non-coronary cusp 5. LA (Most Posterior) |
|
|
The Aortic root motion reflects the dimension changes of what heart structure?
|
LA
|
|
|
What is responsible for the anterior displacement of the aortic root?
|
LA filling
|
|
|
True or False
LA emptying is not responsible for the posterior displacement of aortic root |
False
LA emptying is responsible for the posterior displacement of aortic root |
|
|
In diastole what the the aortic leaflet coaptation appear as?
|
A thin line
|
|
|
True or False
During systole, the aortic leaflets separate rapidly and completely |
True
|
|
|
What is the normal diameter for the RV?
|
Less than 35mm
|
|
|
What is the normal diameter of the Aortic root?
|
Less than 38mm
|
|
|
What is the normal diameter of the AV cusp separation?
|
Less than 26mm
|
|
|
What is the normal size of the LA?
|
Less than 42mm
|
|
|
What are 6 structures that the MV scan line passes through for M-Mode?
|
1. Anterior wall of RV
2. RV Chamber 3. IVS 4. Anterior mitral valve leaflet (AML) 5. Posterior mitral valve leaflet (PML) 6. Posterior LV wall |
|
|
During MV Diastole, What happens during the E point?
|
1. Maximum early diastolic motion of AML
2. PML also moves away but not as far |
|
|
During MV diastole, What happens during the E point septal separation (EPSS)?
|
The distance between the E point and the maximum posterior motion of the ventricle septum
|
|
|
During MV diastole, What happens during the F point?
|
Most posterior position of the AML immediately following E point
|
|
|
True or False
Diastasis is when the leaflets move together again in mid-diastole |
True
|
|
|
During MV Diastole, What happens during the A point?
|
Late diastole separation due to atrial systole
|
|
|
During MV Systole, What happens during the C point?
|
Closure point of leaflets in ventricle systole
|
|
|
During MV Systole, What happens during the D point?
|
Valve leaflets separate at the end of systole, this marks the beginning of diastole
|
|
|
What is E-F slope?
|
Rate of max opening of AML to end of rapid filling (mm/sec)
|
|
|
What does excursion mean?
|
Distance from D point to max anterior motion of AML (E Point). (mm)
|
|
|
What is EPSS?
|
Distance between the E point and maximum posterior motion of ventricular septum. (mm)
|
|
|
What is the normal E-F Slope?
|
Less than 150 mm/sec
|
|
|
What is the normal excursion?
|
Less than 28 mm
|
|
|
What is the normal EPSS?
|
Less than 7 mm
|
|
|
What 5 structures does the LV scan line pass through?
|
1. RV anterior wall
2. RV chamber 3. IVS 4. LV chamber 5. LV posterior wall |
|
|
What are 3 useful measurements of the LV M-mode?
|
1. Systolic wall thickness
2. Diastolic wall thickness 3. Chamber dimensions |
|
|
What systolic and diastolic measurements are made in LV M-Mode?
|
1. End systolic dimension (ESD)
2. End diastolic dimension (EDD) |
|
|
True or False
LV Dimensions can also be obtained from PSAX at papillary level |
True
|
|
|
True or False
Traditional M-Mode technique can be document every wall segment because the M-Mode cursor isn't being anchored to the apex of the scanning sector |
False
Traditional M-Mode cannot document every wall segment because of M-Mode cursor being anchored to the apex of the scanning sector |
|
|
What are 4 measurements of LV M-Mode?
|
1. LV Diastole
2. LV Systole 3. IVS wall thickness 4. Posterior wall of LV |
|
|
What is the normal LV Diastole?
|
Less than 56 mm
|
|
|
What is the normal LV systole?
|
Less than 38 mm
|
|
|
What is the normal IVS diastolic wall thickness?
|
Less than 11 mm
|
|
|
What is the normal thickness of the Posterior wall of LV?
|
Less than 11 mm
|
|
|
What views can the Tricuspid valve be visualized in M-Mode?
|
PLAX RVIT or PSAX at AV level
|
|
|
True or False
The TV exhibits motion patterns similar to anterior mitral valve leaflets |
True
|
|
|
True or False
usually only the anterior leaflet is visualized and never the posterior leaflet |
False
Usually only the anterior leaflet is visualized and sometimes the posterior leaflet |
|
|
What views can you obtain the pulmonic valve in M-Mode?
|
PLAX RVOT or PSAX at AV level
|
|
|
What does the A wave stand for in M-Mode of the Pulmonic valve?
|
Atrial contraction
|
|
|
What does the B point stand for in M-Mode of the Pulmonic vavle?
|
Onset of RV ejection
|
|
|
What does the C point stand for in M-Mode of the Pulmonic valve?
|
Maximum opening
|
|
|
What does the D point stand for in M-Mode of the Pulmonic valve?
|
End ejection
|
|
|
What does the F point stand for in M-Mode of the Pulmonic valve?
|
Precedes atrial contraction
|
|
|
What are 4 M-Mode pitfalls?
|
1. Technologist
2. Breathing 3. Patient position 4. Transducer position |
|
|
What method is being used to derive volumes and EF of M-Mode?
|
Teicholz method
|
|
|
True or False
An assumption is made that LV dilates along its mnior axis |
True
|
|
|
What is the formula for LV volume of M-Mode?
|
LV volume (LVV) = 7.0 / (2.4 + D) x D^3
D = diameter at end-diastole or at end-systole (cm) |
|
|
True or False
EF can be estimated using a single minor axis dimension of the LV |
True
|
|
|
What is the formula for Systolic function of SV?
|
SV = EDV - ESV
|
|
|
What is the formula for Systolic function of EF?
|
EF% = SV / EDV x 100
|
|
|
What is normal resting EF?
|
Greater than 55 - 70%
|
|
|
What is myocardial contractility?
|
Ability of the myocardium to contract
|
|
|
What 4 things affect systolic function?
|
1. HR
2. Pharmacologic agents 3. Preload 4. Afterload |
|
|
What are 4 characteristics of Preload?
|
1. LV volume at end-diastole
2. Determines force of contraction 3. Frank-Starling curve 4. Length-tension relationship |
|
|
True or False
With increased volume in ventricle it increases contractility |
True
|
|
|
Define Frank-Starling law
|
The more the muscles are stretched in diastole, the more forcefully the ventricles contract in systole
|
|
|
What is afterload?
|
Resistance to ejection of blood from the ventricle during systole
Determines the tension the myocardium must generate increased resistance equals decreased stroke volume |
|
|
True or False
Afterload refers to the pressure needed form the LV to overcome higher pressure in the aorta |
True
|
|
|
What are 4 types of methods used for LV dimensions for volume and function?
|
1. Teicholz Method
2. Cubed Method 3. Single Plane Area-Length 4. Modified Simpson's Biplane Rule |
|
|
What is the Teicholz method?
|
An assumption is made that LV dilates along its minor axis; LV becomes more spherical as it dilates so the relationship between major and minor axes change
|
|
|
What is the cubed method?
|
Permits volume to be calculated from a single linear dimension;
Allows for M-Mode measurements to calculate volume |
|
|
What is the formula for cubed method?
|
V = 1.047 x D^3
|
|
|
What are the 4 pitfalls of M-Mode/2D?
|
1. Dimension does not depict major axis of ventricle
2. Wall motion abnormalities, non-symmetric LV shape may not be reflected from single scan line evaluation 3. Over/under estimation may occur if M-line is not centered in the ventricular chamber 4. Cardiologists prefer direct volume measurements |
|
|
What is the Single Plane Area-Length method?
|
Useful when only one apical view can be assessed and when ventricle is considered symmetrical
|
|
|
What is the formula for Single Plane Area-Length Method?
|
Volume = 0.85 x A^2 / L
A = area of ventricle from Apical 2 or 4 L = long axis length of ventricle |
|
|
What is the Modified Simpson's Biplane Rule?
|
Volume of large figure can be calculated from sum of volumes of smaller, similar figures
Divides chamber into slices of known thickness |
|
|
True or False
Volume of the chamber = sum of volume of slices |
True
|
|
|
What views are used for the modified simpson's biplane rule?
|
Apical 4 or 2 chamber
|
|
|
What is traced in the modified simpson's biplane rule?
|
Endocardial boarders
|
|
|
What are 8 pitfalls of modified simpson's biplane rule?
|
1. Limited acoustic windows
2. If difference in length of LV in AP 2 and 4 is greater than 20%, the volume analysis may not be accurate 3. Algorithm is complex and not easy to perform manually 4. Difficulty visualizing endocardium due to body habitus and respiration 5. Bed/patient limitations 6. Ultrasound equipment 7. Technologist 8. ECG rhythm patterns |
|
|
What is Fractional shortening?
|
Instead of measuring blood volumes, the FS measures and ratios change in diameter of LV during systole and diastole
% of change in LV cavity dimension with systole |
|
|
What is the formula for Fractional shortening?
|
FS% = LVIDd - LVIDs / LVIDd x 100
|
|
|
What is the normal range of Fractional shortening?
|
25 - 45%
|
|
|
What are 3 visual assessment pitfalls?
|
1. observer dependent
2. Subjective 3. Echo report should mention whether EF is based on visual assessment or planimetry |
|
|
True or False
LV all walls and base move somewhat equally toward the center |
True
|
|
|
What 4 structures of the RV are evaluated by echo?
|
1. Thickness
2. Size 3. Shape 4. Contractility |
|
|
What is the normal RV wall thickness?
|
3-4 mm
|
|
|
Hypertrophy of the RV wall occurs when?
|
The RV wall is greater than 5 mm
|
|
|
True or False
Multiple views of the RV should be visualized |
True
|
|
|
What are the pitfalls of the RV shape and contractility?
|
1. Limited qualification of shape and function
2. No single view adequately images the entire RV 3. Other techniques can be used such as RV strain/strain but those are outside the scope of this course |
|
|
True or False
The 4 phases of diastole include the isovolumic contraction time, early rapid filling, diastasis, and atrial contraction |
False
Isovolumetric relaxation time, early rapid filling, diastasis and atrial contraction |
|
|
When assessing the LV diastolic function, sample volume is place at the ___________. When assessing LV SV, the sample volume is placed at the ____________.
|
MV leaflet tips and MV annulus
|
|
|
Which echocardiographic window is best for evaluating left ventricular inflow color patterns and spectral Doppler?
|
Apical
|
|
|
True or False
It is normal to have a trivial degree of physiological pulmonic regurgitation. |
True
|
|
|
What color is the pulmonic regurgitation if seen from parasternal short axis?
|
Red
|
|
|
True or False
Short duration early diastolic flow reversal in the aorta as seen from SSN is normal |
True
|
|
|
Hepatic venous flow will normally appear ___________ the baseline.
|
Below
|
|
|
Color Doppler analysis of the LVOT is best evaluated form which views?
|
AP 5
|
|
|
In PLAX if the probe is angled anteriorly, color flow through the LVOT and aortic root will be what color?
|
Red
|
|
|
During the MMode examination, motion or time is displayed on the ______________ axis, while distance or depth is displayed on the ______________ axis.
|
Horizontal and Vertical
|
|
|
The optimum window selection for MMode interrogation is the view in which the ultrasound beam is____________ to the structure (s) of interest
|
Orthogonal
|
|
|
MMode is far superior ______________ resolution in comparison to other methods.
|
Temporal
|
|
|
True or False
Lack of spatial information is a predominant limitation of MMode |
True
|
|
|
True or False
Because there are minor limitations to using MMode, it can be solely utilized in assessment and diagnosis of pathological findings |
False
Due to major limitations |
|
|
What echocardiographic window is primarily used for MMode applications?
|
Parasternal
|
|
|
True or False
Atrial contraction on the MMode trace will precede or occur at the same time as the P wave on the ECG |
False
The atrial contraction will follow the P wave |
|
|
True or False
Tricuspid and pulmonic MMode are routinely used in the echo labs today |
False
They are not routinely used |
|
|
True or False
MACS is the vertical distance between the left coronary cusp and the non-coronary cusp. |
False
Distance between the right coronary cusp and the non-coronary cusp |
|
|
The ASE recommended method for measuring structures by MMode is the _____________________ technique.
|
Most continuous echo line
|

