![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
which valvular disease/es is associated with a "pressure overload"? |
aortic stenosis
|
|
|
which valvular disease/es is associated with a "volume overload"? |
aortic and mitral regurge
|
|
|
which valvular disease/es is associated with "volume and pressure underload"? |
mitral stenosis
|
|
|
name 6 compensatory mechanisms and secondary problems associated with valvular disease?
|
chamber enlargement, hypertrophy, changes in sympathetic activity, altered LV compliance, myocardial ischemia and chronic dysrhythmias
|
|
|
how does TEE work? The beam is adjusted so that it is _______to the cardiac structure of interest. The image displayed is based on ______ and _____ of reflected signals
|
transmits high-frequecy sound waves that are reflected from the cardiac structures encountred; perpendicular; amplitude, time delay
|
|
|
what are 6 contraindications to TEE?
|
esophageal stricture, esophageal masses, recent bleeding from esophageal varices, zencker diverticulum, s/p radiation to neck, recent gastric bypass surgery
|
|
|
which TEE view visualizes the left ventricle from the direction of stomach and evaluates ventricular performance?
|
transgastric short axis view
|
|
|
which TEE view would you use to evaluate calcification of the aorta?
|
ascending aorta short axis view
|
|
|
which TEE view is best for assessing clot formation?
|
left atrial appendage view
|
|
|
what TEE view is important to assess before cannulating the aorta?
|
ascending aorta short axis
|
|
|
which type of valve replacement is the best choice for an elderly person who cant take blood thinners? Which type is best for a young patient? |
bioprosthetic (porcin or bovine); mechanical (metal or carbon alloy) |
|
|
which type of valve has the lowest thrombogenic potential?
|
bioprosthetic
|
|
|
what is the most common cause of mitral stenosis?
|
rheumatic heart dz.
|
|
|
The onset of mitral stenosis typically occurs very _____. MItral stenosis is associated with what 3 complications?
|
slowly; CHF, pulmonary htn, RV failure
|
|
|
name 5 symptoms of MS. These symptoms are related to ______ left atrial pressures
|
DOE, Orthopnea, PND, Left atrial enlargement on CXR, Borad notched P-waves; high;
|
|
|
what is considered "critical" mitral stenosis?
|
MV area < 1.5 cm2 (normal = 4-6)
|
|
|
what is the goal in mgt of patients with MS?
|
prevent/treat pulmonary edema or decreases in CO (avoid tachycardia, prompt txt of arrhythmias, avoid trendelendburg position, avoid fluid overload); avoid tachycardia (anti-cholinergics, histamine releasing NMB, ketamine, and have esmolol handy); avoid hypoventilation/resp acidosis (care with anti-anxiety meds, avoid increases in PVR)
|
|
|
which valvular disease is really difficult on pregnant women?
|
MS
|
|
|
is it okay to use neuraxial anesthesia on a MS pt?
|
yes but only if they are not anti-coagulated
|
|
|
what is an absolute contraindication for IABP?
|
AI
|
|
|
what valvular disease process is associated with rheumatic fever?
|
MS
|
|
|
what type of murmur is associated with mitral stenosis? What type of filling abnormalities present with mitral stenosis?
|
mid diastolic murmur; decreased EDV and ESV
|
|
|
positioning for robotic procedures would be least tolerated by what valve dz?
|
mitral stenosis
|
|
|
Vasopressor of choice for MS?
|
Neo
|
|
|
what type of murmur is associated with MR/MI? What might be seen on the pulmonary artery waveform and ECG?
|
holosystolic murmur; increased v-wave and LVH on ECG
|
|
|
filling pattern associated with MR/MI?
|
increased LVEDV
|
|
|
name some of the causes associated with MR
|
endocarditis, MVP, LVH, papillary muscle dysfunction, SLE, Rheumatoid arthritis, Ankylosing spondylitis, Carcinoid syndrome
|
|
|
the left atria become more compliant, the left ventricle gradually enlarges, and there is an overall decreased forward left ventricular stroke volume in what type of valve dz?
|
mitral regurge
|
|
|
treatment of MR?
|
early replacement (before EF<30% or LVESD >55mmHg)
|
|
|
should treatment of symptomatic MR be considered an emergency if EF is normal?
|
yes
|
|
|
what is the ideal form of treatment for MR, replacement or repair of the valve?
|
repair preferred to maintain normal ejection anatomy
|
|
|
what are the anestheia goals for MR?
|
Forward, Fast, Full (forward pressure, fast HR, full volume) 1. prevent and treat decreased CO 2. improve forward LV stroke volume 3. Maintenance of normal to slightly high HR 4. afterload reduction
|
|
|
anesthetic choices for pt with MR?
|
avoid excessive narcotic-induced bradycardia, volatile agents are a GOOD CHOICE to decrease SVR, maintain adequate volume, neuraxial techniques are a GOOD CHOICE to decrease afterload
|
|
|
which valve dz is associated with increased age, htn, and hlp? Why would this disease occur if they are younger (30-50yrs)?
|
AS; if bicuspid
|
|
|
what is considered severe AS?
|
<0.8cm2 (normal 2.5-3.5)
|
|
|
which valve dz is associated with increased myocardial O2 demand and decreased supply?
|
AS
|
|
|
name 3 symptoms associated with AS; what is the 3-year mortality rate if they have all 3 symptoms?
|
angina, syncope, DOE; 75%
|
|
|
anesthesia goals for pt with AS?
|
maintain NSR, maintain normal systemic pressure, maintain fluid volume
|
|
|
induction/maintenance of anesthesia with the AS pt?
|
avoid neuraxial!; do not decrease SVR, treat hypotension with alpha agonists, prompt treatment of brady or tachy dysrhthymias, pulmonary artery catheters are useful
|
|
|
which type of arrhythmia is most likely to occur in AS? MS?
|
ventricular arrhythmias; atrial arrhythmias
|
|
|
what is your vasopressor of choice for treatment of hypotension in AS?
|
Neo
|
|
|
what is your vasopressor of choice for treatment of AR?
|
Ephedrine
|
|
|
what type of anesthetic agents would be ideal for induction with the AS pt? Which induction agent should be avoided?
|
benzos, narcotic, etomidate; avoid ketamine
|
|
|
name 6 possible causes of AR
|
endocarditis, Rheumatic fever, bicuspid aortic valve, aortic dissection, marfan's syndrome, anorexigenic drugs (wt loss drugs)
|
|
|
the amount of regurge that occurs in AR is dependent on the ____ and _____-
|
HR and SVR
|
|
|
what is the mortality associated with valve replacement for AR?
|
0.2% asymptomatic and 10% symptomatic
|
|
|
name 5 symptoms associated with the diagnosis of AR
|
widened pulse pressure; LV dysfunction (fatigue, dyspnea, orthopnea), coronary ischemia, LVH on ECG, abnormal echo
|
|
|
what are the 3 anesthesia goals for AR?
|
maintain forward, LV stroke volume (HR 80ish), prevent abrupt increases in SVR (vasodilator/inotropic support); maintain contractility
|
|
|
what type of induction/maintenance of anesthesia should be used for pt with AR
|
prevent extreme bradycardia (probably dont use high narcotics), volatile anesthetics are GOOD CHOICES, maintain fluid volume to support preload
|
|
|
Do we need to hold anticoagulants for minor surgery in a pt with mechanical valve? what is the process for major surgery? |
not for minor surgery; hold coumadin for 3-5 days and lovenox instituted with heparin post op until INR is therapeutic
|
|
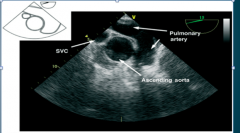
What TEE view is this? |
ascending aorta short axis view |
|
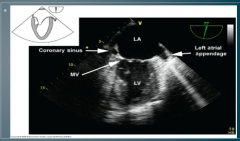
What TEE view is this? |
Left atrial appendage |
|
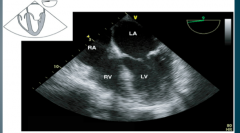
What TEE view is this? |
4 chamber view |
|
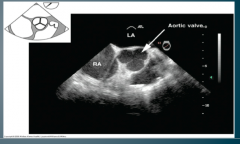
What TEE view is this? |
Aortic valve short axis view |
|
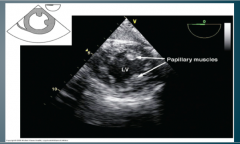
What TEE view is this? |
Transgastric short axis view |

