![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Observational study
|
Study in which we observe and measure specific characteristics, but don't attempt to manipulate or modify the subjects being studied.
|
|
|
Experiment
|
Application of some treatment followed by obervation of its effects on the subjects.
|
|
|
Experimental Units
|
Subjects in an experiment.
|
|
|
Cross-sectional study
|
study in which data are observed, measured, and collected at one point in time.
|
|
|
Retrospective study
|
aka: case-control
Study in chich data are collected from the past by going back in time (through examination of records, interviews, and so on). |
|
|
Prospective Study
|
aka: longitudinal or cohort
Study of subjects in identified groups sharing common factors (called cohorts), with data collected in the future. |
|
|
Confounding
|
A situation that occurs when the effects from two or more variables cannot be distinguished from each other.
|
|
|
Random Sample
|
Sample selected in a way that allows every member of the poulation to have the same chance of being chosen.
|
|
|
Simple Random Sample
|
Sample of a particular size selected so that every possisble sample of the same size has the same chance of being chosen.
|
|
|
Probability Sample
|
Sampling involves selecting members from a population in such a way that each member has a known (but not necessarily the same) chance of being selected.
|
|
|
Systematic Sampling
|
Sampling in which every Kth eleent is selected.
|
|
|
Convenience Sampling
|
Sampling in which data are selected because they are readily available.
|
|
|
Stratified Sampling
|
Sampling in which samples are drawn from each stratum (class).
|
|
|
Cluster Sampling
|
Dividing the population area into sections (or clusters), then randomly selecting a few of those sections, and then choosing ALL the members fro those selected sections.
|
|
|
Sampling Error
|
Difference between a sample result and the true population result; results from chance sample fluctuations.
|
|
|
Nonsampling Error
|
Errors from external factors not related to sampling.
|
|
|
Frequency Distribution
|
aka: Frequency Table
Listing of data values (either individually or by groups of intervals), along with their corresponding frequencies (or counts). |
|
|
Lower class limits
|
Smallest numbers that can actually belong to the different classes in a frequency distribution.
|
|
|
Upper class limits
|
Largest numbers that can belong to the different classes in a frequency distribution.
|
|
|
Class boundaries
|
Values obtained from a frequency distribution by increasing the upper class limits and decreasing the lower class limits by the same amount so that there are no gaps between consecutive classes.
|
|
|
Class midpoints
|
In a class of a frequency distribution, the value midway between the lower class limit and the upper class limit.
|
|
|
Class width
|
The difference between two consecutive lower class limits in a frequency distribution.
|
|
|
CVDOT:
Center |
A representative or average value that indicates where the middle of the data set is located.
|
|
|
CVDOT:
Variation |
A measure of the amount that the data vlaues vary amoung themselves.
|
|
|
CVDOT:
Distribution |
The nature or shape of the distribution of the data (such as bell shaped, uniform, or skewed).
|
|
|
CVDOT:
Outliers |
Sample values that lie very far away from the vast majority of the other sample values.
|
|
|
CVDOT:
Time |
Changing characteristics of the data over time.
|
|
|
CVDOT
|
Center, Variation, Distribution, Outliers, Time
|
|
|
Relative Frequency Distribution
|
Variation of the basic frequency distribution in which the frequency for each class is divided by the total of all frequencies.
|
|
|
Cumulative Frequency Distribution
|
Frequency distribution in which each class and frequency represents cumulative data up to and including that class.
|
|
|
Normal distribution
|
Bell-shaped probability distribution.
|
|
|
Arithmetic mean
|
Sum of a set of values divided by the number of values; usually referred to as the mean.
|
|
|
measure of center
|
Value intended to indicate the center of the values in a collection of data.
|
|
|
mean
|
The sum of a set of values divided by the number of values.
|
|
|
median
|
Middle value of a set of values arranged in order of magnitude.
|
|
|
mode
|
Value that occurs most frequently.
|
|
|
midrange
|
One-half the sum of the highest and lowest values.
|
|
|
Rounding-Off Rule
|
Carry one more decimal place than is present in the original set of values.
|
|
|
skewed
|
Not symmetric and extending more to one side than the other.
|
|
|
symmetric
|
Property of data for which the distribution can be divided into two halves that are approximately mirror images by drawing a vertical line through the middle.
|
|
|
range
|
The measure of variation that is the difference between the highest and the lowest values.
|
|
|
standard deviation
|
Measure of variation equl to the square root of the variance.
|
|
|
variance
|
Measure of variation equal to the square of the stanard deviation.
|
|
|
empirical rule
|
Rule that uses standard deviation to provide information about data with a bell-shaped distribution.
|
|
|
coefficient of variation (CV)
|
The ratio of the standard deviation to the mean, expressed as a percent.
|
|
|
Range Rule of Thumb
|
Rule based on the principle that for typical data sets, the difference between the lowest typical value and the highest typical value is approximatley 4 standard deviations (4s)
|
|
|
s
|
SAMPLE standard deviation
|
|
|
POPULATION standard deviation
|
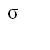
define
|
|
|
POPULATION variance
|

define
|
|
|
SAMPLE variance
|
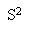
define
|
|
|
Exploritory data analysis
|
EDA
Branch of statistics emphasizing the investigation of data |
|
|
5-number summary
|
Minimum value, maximum value, median, and the first and third quartiles of a set of data
|
|
|
boxplot
|
aka: box-and-whisker diagram
Graphical representation of the spread of a set of data (5# summary). |
|
|
Relative Frequency Approxiation of Probability
|
P(A) = number of times A occurred / number of times the trial was repeated
|

