![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
103 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nabothian Cyst |
benign, simple cyst found in cervical region of uterus |
|
|
Symptoms of Nabothian Cyst |
asymptomatic unless very large |
|
|
Nabothian Cysts are more common in.... |
women who have been pregnant |
|
|
Measurement of Nabothian Cyst |
< 2cm |
|
|
Sonographic Appearance of Nabothian Cyst |
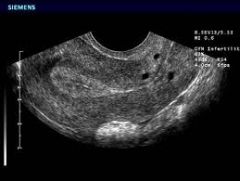
-simple -discrete -round -anechoic |
|
|
What is the most common finding on pelvic ultrasound? |
Nabothian Cyst |
|
|
Adenomyosis |
inner lining of uterus (endometrium) breaks through muscle wall of the uterus (myometrium) AKA endo migrates into myometrium |
|
|
Adenomyosis is seen in what percent of hysterectomies? |
70% (2/3) |
|
|
In Adenomyosis, the ectopic glands are typically seen how far below the endo-myometrium junction? (mmt) |
2-3mm |
|
|
2 Causes of Adenomyosis |
1. defect/absence of basement membrane at junction 2. endo migration by lymph of vascular channels |
|
|
Risk Factor of Adenomyosis |
uterine trauma (more common in mature reproductive age patients) |
|
|
Signs & Symptoms of Adenomyosis |
- uterine tenderness (dull, achy pain) - dysmenorrhea - dysfunctional menstrual bleeding - menorrhagia - uterine enlargement |
|
|
Dysfunctional Menstrual Bleeding |
irregular |
|
|
Menorrhagia |
heavy bleeding for several days |
|
|
Differential Diagnosis for Adenomyosis |
-fibroids -pelvic congestion syndrome -endometriosis -endometrial polyps -endometrial carcinoma |
|
|
Treatment for Adenomyosis (if patient doesn't want Hysterectomy) |
-GnRH inhibitors -Birth control pills -nSAIDS (steroids) -Endometrial Ablation -Uterine Artery Embolization |
|
|
The only sure Treatment of Adenomyosis is.. |
Hysterectomy |
|
|
Fibroids co-exist with Adenomyosis in what percent of cases? |
>60% |
|
|
Sonographic Appearance of Adenomyosis |
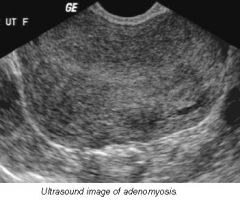
-rounded enlargement of uterus WITHOUT focal mass -abnormal heterogenous myometrium -poor definition of endomyometrial junction -Doppler: hypervascularity throughout uterus |
|
|
*Key Sonographic Finding of Adenomyosis |
Enlargement of uterus will be greater posterior to endometrium |
|
|
Sonographically, how can we differentiate Adenomyosis from Fibroids ? |
fibroids- will have focal, defined mass & peripheral vascularity adenomyosis- no focal mass & diffuse hypervascularity |
|
|
Which imaging modality is most sensitive to Adenomyosis? What are the disadvantages? |
MRI -cost -scheduling -insurance (pre-cert) |
|
|
Hystersalpingogram (HSG) |
radiology procedure that inserts contrast to look at uterus, fallopian tubes & surrounding area |
|
|
Disadvantages to HSG |
- not very specific - very uncomfortable for patients - does not always provide diagnosis |
|
|
Appearance of Focal Adenomyosis |
-poorly delineated margins -may appear as intracavitary polyp |
|
|
Diffuse Adenomyosis *most common form |
- entire uterus involved - often associated with endometrial hyperplasia & carcinoma |
|
|
Fibroids |
benign growth of uterus |
|
|
Fibroids AKA... |
leiomyomas myomas leiomas fibromyoma |
|
|
What is the most common tumor of the uterus & female pelvis? |
Fibroid |
|
|
What is a Fibroid composed of? |
smooth muscle connective tissue |
|
|
Incidence of Fibroids |
20-30% women over 30 more common in African Americans |
|
|
Cause of Fibroids |
idiopathic (unknown) |
|
|
What does Estrogen do to Fibroids? |
increases! |
|
|
Why do Fibroids tend to shrink after menopause? |
lack of Estrogen |
|
|
Do we typically see 1 Fibroid, or multiple? |
multiple |
|
|
What do Fibroids cause in the Uterus? |
- enlargement - surface lobularity (bumpy) |
|
|
What feature do Fibroids have that allow them to be removed with little disruption to surrounding myometrium? |
they are encapsulated |
|
|
Signs / Symptoms of Fibroids |
- palpable pelvic mass - uterine enlargement - pelvic pain - dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB) |
|
|
How do Fibroids in the Endometrium affect pregnancy? |
- increased risk of miscarriage |
|
|
How do Fibroids in the Cervix or Lower Uterine Segment affect pregnancy? |
can interfere with delivery -should be closely monitored |
|
|
3 Types of Fibroids & their locations in myometrium |
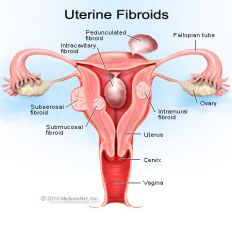
1. Submucosal - innermost 2. Intramural - center 3. Subserosal - outer |
|
|
2 Types of Subserosal Fibroids |
1. pedunculated 2. exophytic |
|
|
Submucosal Fibroid |
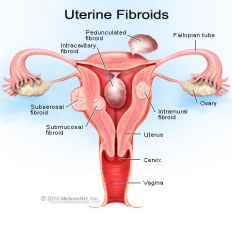
- innermost - will affect endometrium |
|
|
Which Fibroid is most likely to cause symptoms? What are they? |
Submucosal - irregular / heavy menses |
|
|
Intramural Fibroid |
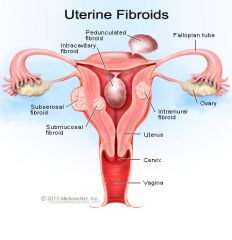
- center - do not effect endo unless large - usually will not have defined borders - usually multiple found = enlargement of uterus |
|
|
What are Intramural Fibroids sometimes defined as? |
"Heterogenous Echotexture" "Fibroid Uterus" "Diffuse Enlargement of Uterus" |
|
|
What is the most common type of Fibroid? |
Intramural |
|
|
Subserosal Fibroids |
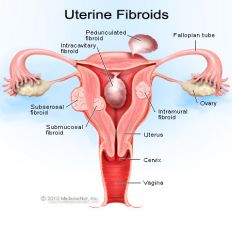
- outer - distorts outer contour of uterus (lumpy uterus - exophytic fibroids) - can become pedunculated |
|
|
Pedunculated Fibroid |
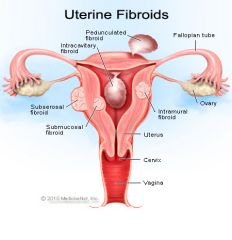
- grows outside of uterus with a stalk - can twist and undergo torsion |
|
|
Parasitic Leiomyoma |
exophytic fibroid in close contact with another adjacent pelvic structure and acts as a parasite on the structures blood supply - can become detached fromuterus completely |
|
|
Will vascularity be seen in Fibroids? If so, where? |
yes - along periphery (ring of fire) |
|
|
What happens if a Fibroid outgrows it's blood supply? |
degenerates |
|
|
Name the 4 types of Fibroid Degeneration |
1. Hyaline - fibrous tissue replaces smooth muscle 2. Cystic - necrosis 3. Calcific - after menopause 4. Red Degeneration - acute, common during pregnancy |
|
|
What do Fibroids look like on Ultrasound as degeneration, calcification, or growth occurs? |
- heterogenous - hypoechoic to myometrium |
|
|
Differential Diagnosis for Fibroids |
- adnexal mass - endometrial polyp |
|
|
How to tell Fibroid from Adnexal Mass |
fibroids will have shadowing throughout |
|
|
How to tell Fibroid from Endometrial Polyp |
fibroid -vascularity around periphery -shadowing polyp -1 single vessel |
|
|
What will ultimately differentiate Fibroids from Polyps? |
Sonohysterography |
|
|
Where will Fibroids be when visualized Sonographically? |
In the MYOMETRIUM |
|
|
What might Fibroids look like Sonographically? |
- variable - may be focal, hypoechoic mass with hypoechoic rim |
|
|
Complications of Fibroids |
- hydronephrosis - infertility - miscarriages - submucosal / cervical fibroids can obstruct delivery |
|
|
Treatments of Fibroid |
most common - no treatment If causing symptoms.. - hysterectomy - myomectomy (fibroid) - Lupron: shrinks fibroids - Uterine Artery Embolization |
|
|
Endometrial Polyp |
localized overgrowth of endo tissue - may be pedunculated, broad-based, thin stalk |
|
|
Signs and Symptoms of Endometrial Polyps |
- usually asymptomatic - infertility - PMB - AUB |
|
|
Sonographic Appearance of Endometrial Polyps |
- focal thickening of endo - discrete mass **possible feeder vessel **polyps DO NOT shadow |
|
|
Where are Endometrial Polyps located? |
In ENDOMETRIUM |
|
|
Endometrial Hyperplasia |
proliferation of endometrial glandular tissue |
|
|
What percent of Endo Hyperplasia will progress to Endo Carcinoma? |
25% |
|
|
What is the most common cause of AUB? |
Endometrial Hyperplasia |
|
|
Causes of Endometrial Hyperplasia |
- unopposed estrogen - persistent anovulatory cycles - PCOD - obesity - estrogen-producing tumors of ovary |
|
|
Diagnosis of Endometrial Hyperplasia |
- ultrasound @ beginning of hormone cycle - D&C with thorough path exam |
|
|
Sonographic Appearance of Endometrial Hyperplasia |
- smooth - homogenous - echogenic - maybe cystic changes |
|
|
Sonographic Measurements of Endometrial Hyperplasia |
pre-meno - >14mm postmeno estrogen - >5mm postmeno estrogen phase - up to 8mm postmeno prog phase - decreases |
|
|
Asherman's Syndrome |
adhesions of the endometrium that develop as a result of trauma (c-section, D&C, elective abortion, miscarriage) |
|
|
What can Asherman's Syndrome result in? |
- infertility - recurrent pregnancy loss (due to scar tissue) |
|
|
Which Uterine pathology requires SIS to diagnose? |
Asherman's Syndrome |
|
|
Treatment for Asherman's Syndrome |
remove adhesions under hysterscope |
|
|
Uterine Sarcoma |
aggressive, malignant tumor - poor prognosis if not detected early |
|
|
What is Uterine Sarcoma difficult to differentiate from? |
Degenerating Fibroid |
|
|
What are some Sonographic clues that would point towards Sarcomas instead of Fibroids? |
sarcomas - local invasion - distant mets - increase in size peri / postmeno |
|
|
What is the most common gynecological malignancy? |
Endometrial Carcinoma |
|
|
Risk Factors for Endometrial Carcinoma |
- obesity (2-3x more likely) - nulliparous (2-3x more likely) - late menopause - Hx of polyps - family Hx - unopposed estrogen - Hx of Tamoxifen |
|
|
If a patient has a History of Tamoxifen AND prior uterine abnormalities, what is their chance of developing Endometrial Carcinoma? |
18 fold increase |
|
|
What 2 things will DECREASE the risk of Endometrial Carcinoma? |
1. birth control pills - 10 year safety net 2. smoking - decreased obesity - go thru menopause 1-2 yrs earlier |
|
|
Statistics of Endometrial Carcinoma |
- usually diagnosed 6-7th decade (age 50-60) - higher prevalence in white women - higher mortality in black women |
|
|
Signs / Symptoms of Endometrial Carcinoma |
Uterine bleeding !!!! |
|
|
Treatments for Endometrial Carcinoma |
- total hysterectomy - bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy - peritoneal fluid aspiration & washing - lymphadenectomy |
|
|
Sonographic Appearance of Endometrial Carcinoma |
- heterogenous - irregular / poorly defined margins - cystic changes - hydrometra / hematometra - enlarge uterus - lobular contour - subendometrial halo: very distinct = probably localized. borders not distinct = metastatic spread |
|
|
Which Ultrasound exam is most helpful in diagnosing Endometrial Carcinoma? What is the clear evidence? |
Transvaginal - showing myometrial invasion = clear evidence of endo carcinoma |
|
|
What are the 2 Uterine Potpourri |
1. Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs) 2. IUD's |
|
|
Arteriovenous Malformations |
communication between vein / artery (can be congenital OR iatrogenic) |
|
|
Signs / Symptoms of Arteriovenous Malformation |
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding |
|
|
Why is it important to differentiate Arteriovenous Malformation from other causes of DUB? |
Treatment for AVMs is different, less invasive, and more effective |
|
|
What do IUD's look like on Ultrasound? |
brightly echogenic with beam attenuation |
|
|
Why do we use Transvaginal for IUD's? |
- rule out migration into myometrium - correct location (fundus / corpus) |
|
|
What may happen if IUD is not placed correctly? |
may exist with an intra-uterine pregnancy |
|
|
IUD's may increase risk of....
|
- ectopic pregnancy - PID |
|
|
First step when experiencing AUB |
rule out pregnancy |
|
|
What do we consider AUB in women over 40 until proven otherwise? |
Cancer |
|
|
How we take Endometrial Measurements |
- sagittal - 'basalis to basalis' / 'functional' to 'functional' - if fluid is present, measure halves seperate |
|
|
Saline-Infused Sonography AKA Sonohysterography |
insert fluid to view -MUST know uterine position PRIOR to exam -best to perform ASAP after bleeding |
|
|
Risks / Contraindications for SIS |
- infection - irregular menses (if irregular, will prompt menses with 10 day hormone regimen) |
|
|
Purpose of SIS |
1. distinguish who needs hormone therapy vs. invasive procedure to treat AUB 2. differentiate polyps & fibroids |

