![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The horizontal plate of the ______________ contributes to the roof of the orbital cavities and nasal cavities.
|
frontal bone
|
|
|
The ________________ forms the lower and back portion of the cranium.
|
occipital bone
|
|
|
The ________________ form most of the rounded roof of the cranium.
|
parietal bones
|
|
|
The bony septum of the nasal cavity is formed, in part by the perpendicular plate of the ___________________ articulated with the midline crest of the sphenoid bone.
|
ethmoid bone
|
|
|
The __________________ form the lateral base and sides of the cranium.
|
temporal bone
|
|
|
The ___________________ is located at the base of the skull between the ethmoid and occipital bones.
|
sphenoid bone
|
|
|
The cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone contributes to the roof of the _______ cavity and separates it from the cranial cavity.
|
nasal
|
|
|
The parietal and frontal bones are joined by the ___________ suture.
|
coronal
|
|
|
The vertical plate or squamous portion of the frontal bone forms the ___________.
|
forehead
|
|
|
The two scroll-like extensions of the ethmoid bone form the _______________________ and superior nasal concha.
|
middle nasal concha
|
|
|
The two parietal bones are joined together by the ___________ suture.
|
sagittal
|
|
|
The parietal and occipital bones are joined by the ______________ suture.
|
lambdoid
|
|
|
In the occipital bone, the demarcation between the brain and the spinal cord occurs at the ___________________.
|
foramen magnum
|
|
|
The parietal and temporal bones are joined by the _____________ suture.
|
squamosal
|
|
|
The mandible is joined to the temporal bones by the ____________________ joint.
|
temporomandibular
|
|
|
The organs of hearing and equilibrium are located in the _____________ portion of the temporal bones.
|
petrous
|
|
|
Which is not a sinus cavity? Frontal
Maxillary Nasal Sphenoid |
Nasal
|
|
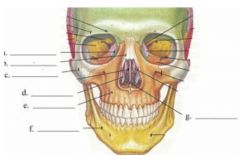
Identify the indicated cranial bones in the floor of the cranial cavity
|
a. ethmoid bone
b. temporal bone c. parietal bone d. frontal bone e. sphenoid bone f. occipital bone |
|
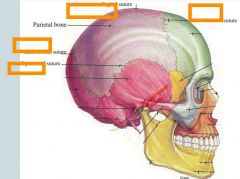
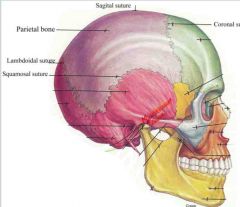
Identify the four sutures that go with the parietal bone
|
|
|
|
What part of the temporal bone houses the organs of equilibrium and hearing?
|
Petrous portion
|
|
|
Name of the hole that allows sound to go into the auditory bones
|
External auditory meatus/ear canal
|
|
|
Name the only joint of the skull that can move.
|
Temporalmandibularjoint
|
|
|
Where is the sphenoid located?
|
Base of skull and articulates with all the bones of the cranium
|
|
|
What bone has two greater wings and two lesser wings?
|
Sphenoid bone
|
|
|
What houses the pituitary gland??
|
Sella turcica (on sphenoid bone)
|
|
|
Where do optic nerves and
ophthalmic arteries enter the sphenoid bone? |
Optic canals
|
|
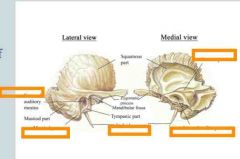
Identify the Styloid process, Mastoid Process, External auditory
meatus, Internal auditory meatus, and Petrous portion |
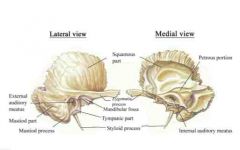
|
|
|
Where is the Foramen
rotundum and what does it contain? |
:
Sphenoid bone; contains the maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve. |
|
|
Where is the Foramen ovale and what does it contain?
|
transmits the
Sphenoid bone; mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve and meningeal arteries |
|
|
How many bones total are their in the head?
|
29
|
|
|
Name the four sinuses
|
Frontal
Maxillary Ethmoid Sphenoid |
|
|
What are sinuses?
|
Air filled spaces lined by mucoperiosteum
|

