![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
190 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adenoma sebaceum is assoc w/?
|
in about 90% of patients with tuberous sclerosis.
loc: malar eminences of the face between 2 and 5 years of age and may evolve into difficult-to-treat angiofibromas of the skin. |
|
|
Imperforate anus: eventual continence is greater with high or low endings?
|
may be broadly classified into high or low, depending on whether the rectum ends above or below the level of the levator ani complex. increased likelihood of continence when the rectum has descended to below the levator ani muscles
|
|
|
Imperforate anus tx
|
For the low cases, only a perineal operation may be required, and these children will be expected to be continent. A pull-through procedure will be required for the high imperforate anus, and the likelihood of continence is smaller. If there is doubt about the level or location of the termination of the rectum, it is better to perform a temporary colostomy than to compromise the ultimate chances of continence by an injudicious perineal approach.
|
|
|
Intussusception preceded by usually?
|
viral gastroenteritis
|
|
|
Intussusception tx W/O bloody mucus, peritonitis, or systemic toxicity?
|
hydrostatic reduction by barium enema is the appropriate initial treatment.
|
|
|
laboring mother given intravenous meperidine (Demerol) for pain -> lethargic limp infant after birth. Tx?
|
neonatal depression is maternal analgesic narcotic drug administration. While controlling the pain of the delivery in the mother, use of narcotics can result in depression of the newborn via crossing of the placenta.
TX: naloxone |
|
|
Na and K+ in G6PD pt?
|
HYPO
Patients with a deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase (von Gierke disease) are, as a rule, hyperlipidemic. Increased triglyceride concentration in the serum decreases the volume of the aqueous compartment. Because electrolytes are present only in the aqueous compartment of the serum but are expressed in milliequivalents per liter of serum as a whole, the concentrations of sodium and potassium can be factitiously low in these patients. |
|
|
infant who appears normal w/ sudden onset of high fever with pronounced elevation and shift to the left of the WBC count, suggests?
|
pneumococcal bacteremia.
Viral infections such as roseola occasionally can present in a similar fashion but without such profound shifts in the blood leukocyte count. |
|
|
Renal cause frequently between 6 and 12 months of age w/ failure to thrive with constipation, weakness, vomiting, polyuria, and polydipsia and hypokalemia, hypercalciuria, alkalosis, hyperaldosteronism, and hyperreninemia
|
Bartter syndrome (also known as juxtaglomerular hyperplasia) is an autosomal recessive condition that causes hypokalemia, hypercalciuria, alkalosis, hyperaldosteronism, and hyperreninemia; blood pressure is usually normal.
Treatment is aimed at preventing dehydration, providing nutritional support, and returning the potassium level to normal. |
|
|
recurrent gross hematuria, persistent microscopic hematuria, and complaints of dysuria or abdominal pain without initial stone formation. Dx? tx?
|
Idiopathic hypercalciuria
Over time, however, stones may form in 15% of cases. +/- hypercalcemia 24-hr urinary calcium excretion >4 mg/kg |
|
|
dark, cola-colored urine. Think?
|
acute glomerulonephritis,
oliguria frequently occurs as a direct consequence of the disease process itself; on occasion, it can be profound, with virtual anuria for several days. During this period of time, it is vital to monitor and restrict fluid intake lest massive edema, hypervolemia, and even pulmonary edema and death occur. |
|
|
Elevated cholesterol and triglycerides, hypoalbuminemia, Periorbital edema in the morning and scrotal edema
|
nephrotic syndrome
Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides are common in nephrotic syndrome because of increased generalized protein synthesis in the liver (including lipoproteins) and because of a decrease in lipid metabolism due to reduced plasma lipoprotein lipase levels. In the nephrotic syndrome, albumin is lost in the urine and, despite increased hepatic synthesis, serum levels drop. The upper limit of protein excretion in healthy children is 0.15 g/24 h; in nephrotic syndrome, proteinuria can exceed 2.0 g/24 h. When the serum protein level drops low enough, the oncotic pressure of the plasma becomes too low to balance the hydrostatic pressure. Plasma volume, therefore, decreases as edema occurs. Periorbital edema in the morning and scrotal edema in boys during the day is commonly reported. Endocrine and renal mechanisms then partially compensate by retaining water and salt. Overzealous monitoring and restriction of water and salt intake are usually not required. |
|
|
purpuric rash, arthritis, and abdominal pain, and w/ gross or microscopic hematuria.
|
Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis w/ associated glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
the most common chronic glomerulonephritis.
|
IgA (Berger) nephropathy
|
|
|
hematuria; episodic gross hematuria is frequently associated with a febrile illness. Most likely?
|
IgA (Berger) nephropathy
Initially thought to be benign, it is now known to progress over decades to chronic renal failure in many afflicted patients. IgA is found in the mesangium, but this occurs with other disease processes as well. The most common clinical finding is hematuria; episodic gross hematuria is frequently associated with a febrile illness. |
|
|
a coagulation disorder resulting from a deficiency or abnormality of factor VIII.
|
Hemophilia A deficiency?
|
|
|
a synthetic analogue of antidiuretic hormone that increases levels of factor VIII and von Willebrand factor.
|
Desmopressin (DDAVP)
|
|
|
severe hemophilia A: What is used for preventing or treating a bleeding complication?
|
DDAVP (a synthetic analogue of antidiuretic hormone that increases levels of factor VIII and von Willebrand factor.)
is given in combination with an inhibitor of fibrinolysis such as -aminocaproic acid (AMICAR). |
|
|
What phase and at what age does the child spends a good part of his or her day asleep and has little interest in interpersonal relationships.
|
autistic phase occurs during the first 2 months of life,
|
|
|
What phase and at what age does the child enter a psychological fusion or lack of differentiation between mother and child.
|
2 to 6 months, the child enters symbiosis
|
|
|
What phase and at what age does the child develop a concept of self as different and separated from the mother. During the same period, the infant gradually develops an internal, stable representation (introjection) of the mother, which includes both her positive and her negative aspects.
|
separation-individuation - third phase between 6 and 36 months
|
|
|
What phase and at what age is characterized by the integration of the good and bad aspects of the internalized images of both the mother and the child's self.
|
object constancy,
takes place during the third year of life |
|
|
What phase and at what age is characterized by a need to know where the mother is and frequent "refueling," triggered by the child's new awareness that independence also makes him or her vulnerable;
|
rapprochement, between 16 and 24 months
|
|
|
What phase and at what age is characterized by the child's enthusiastic exploration of the environment as a result of his or her newly acquired mobility;
|
; practicing, between 10 and 16 months,
|
|
|
What subphase and at what age does the child's initial awareness that the mother is a separate person
|
differentiation,
between 6 and 10 months, |
|
|
depressed fontanelle, tachycardia, sunken eyes, and the loss of skin elasticity. Which of the following is the correct percentage of dehydration?
|
5% to 9%
|
|
|
cardiac cause: syncopal episodes in late childhood or adolescence and associated w/ deafness
|
During the syncope episode arrhythmias may be noted, including ventricular fibrillation. These episodes may result in death.
An autosomal recessive form associated with deafness (Jervell-Lange-Nielsen syndrome) and an autosomal dominant form (Romano-Ward syndrome) has been described. |
|
|
newborn, blacks>whites w/ lesions 1- to 2-mm pustules that result in a hyperpigmented lesion upon rupture of the pustule.
|
Pustular melanosis
benign rash of the newborn period |
|
|
Analgesia for circumcision?
|
Topical lidocaine cream, dorsal penile nerve block, or subcutaneous ring block should always be provided to a newborn undergoing a circumcision procedure
|
|
|
hydramnios (polyhydramnios) is associated w/ what organ developmental abnormality?
|
reabsorption of swallowed amniotic fluid is impaired.
duodenal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Hydramnios is also associated with approximately 80% of infants who have trisomy 18. Approximately 50% of women with anencephalic fetuses have polyhydramnios. |
|
|
Oligohydramnios occurs in association with congenital abnormalities of the?
|
creation of amniotic fluid is impaired.
fetal kidneys or other parts of the genitourinary tract, such as renal agenesis or obstruction |
|
|
Tx for ingestion of drain cleaner? Milk and water? Endoscopic examination within the first 12 to 24 hours
|
Endoscopic examination of the esophagus and stomach is a diagnostic method of determining the extent of the mucosal injury.
Vomiting is to be avoided since it would expose the mucosal surfaces to the caustic agent a second time. The child can be given SMALL amounts of milk or water, but large amounts, which might cause vomiting, are unwise. |
|
|
poor growth, diabetes insipidus, and papilledema. Think?
|
craniopharyngioma - supratentorial tumors in children
|
|
|
craniopharyngioma is assoc w/ what eye finding and endocrine finding?
|
1. Bitemporal hemianopsia and papilidema
Upward growth of a craniopharyngioma results in compression of the optic chiasm. Particularly affected are the fibers derived from the NASAL portions of both retinas (ie, from those parts of the eyes receiving stimulation from the temporal visual field). 2. growth failure through disruption of pituitary excretions such as growth hormone. |
|
|
treatment of external otitis media
|
protection from additional moisture and avoidance of further mechanical injury from scratching. Otic drops containing antibiotics and corticosteroids are very effective.
|
|
|
Hypoglycemia with hyperinsulinemia but without evidence of C-peptide? Dx?
|
Factitious hypoglycemia - lack of C-peptide suggests that the insulin is exogenous; these findings occurring while the patient is in the hospital would suggest that the current caretaker is injecting insulin into the baby causing hypoglycemia. The caretaker (more commonly the mother) may be suffering from Munchausen by proxy (MPB) syndrome, a disorder in which a parent induces illness in the child or reports symptoms repeatedly to represent the child as ill.
|
|
|
parasites x2? gas, diarrhea, and bloating as common findings, but not fever and eosinophilia.
|
Giardia and Cryptosporidium
|
|
|
parasite? localized infestation resulting in perianal pruritus. No eosinophilia.
|
Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm)
|
|
|
parasite? abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and malaise. During the second week, muscle invasion occurs, which causes edema eyelids, myalgia, weakness, fever, and eosinophilia.
|
Trichinella spiralis
|
|
|
diffuse maculopapular rash that lasts for 3 days, marked enlargement of the posterior cervical and occipital lymph nodes, low-grade fever, mild sore throat, and, occasionally, conjunctivitis, arthralgia, or arthritis. Dx?
|
rubella (German measles)
NOTE: rubeola (measles) develop a severe cough, coryza, photophobia, conjunctivitis, and a high fever that reaches its peak at the height of the generalized macular rash, which typically lasts for 5 days. Koplik spots on the buccal mucosa are diagnostic; |
|
|
bright erythema on the cheeks , followed by a red maculopapular rash on the trunk and extremities, which fades centrally at first.
|
Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease) ("slapped cheek" sign)
|
|
|
age when differentiates parents from others?
|
6months
|
|
|
separation anxiety
|
6 months
|
|
|
age: plays in interactive games
|
9 months
|
|
|
age: dresses self w/ help
|
2 yrs
|
|
|
age: magical thinking
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: plays w/ others
|
4 yrs
|
|
|
age: able to distinguish fantasy from reality
|
6 yrs
|
|
|
age: crawls
|
9 mo
|
|
|
age: transfer object,
|
6 mo
|
|
|
age: holds 2 cubes,
|
6 mo
|
|
|
age: shakes rattle
|
6 mo
|
|
|
age: supports weight while standing
|
6 mo
|
|
|
age: babbles consonant sounds;
|
6 mo
|
|
|
age: imitates speech sounds
|
6 mo
|
|
|
age: mama, dada (nonspecific)
|
9 mo
|
|
|
age: understands own name
|
9 mo
|
|
|
age: peek a boo
|
9 mo
|
|
|
age: cruises,
|
12 mo
|
|
|
age: stands alone,
|
12 mo
|
|
|
age: walks with one hand held
|
12 mo
|
|
|
age: 3-6 specific words,
|
15 mo
|
|
|
age: follows simple commands,
|
15 mo
|
|
|
age: scribbles,
|
15 mo
|
|
|
age: drinks from cup
|
15 mo
|
|
|
age: walks independently,
|
15 mo
|
|
|
age:: stoops and recovers,
|
15 mo
|
|
|
age: plays ball
|
15 mo
|
|
|
age: Offers and empty dish;
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: partially feeds self with spills;
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: pulls a toy;
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: carries or hugs a doll
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: 10 words;
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: names pictures;
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: identifies at least one body part
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: Builds 3-4 cube tower
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: turns 2-3 pages of book at a time
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: Walks fast;
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: runs stiffly;
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: walks up stairs with hand held;
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: seats self in small chair;
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: climbs onto adult chair;
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: throws ball
|
18 mo
|
|
|
age: Interest in toilet training,
|
2 yrs
|
|
|
age: obstinate behavior
|
2 yrs
|
|
|
age: 50% intelligible words
|
2yrs
|
|
|
age: 2-3 word phrases,
|
2 yrs
|
|
|
age: “I,” “me,” “you,”
|
2yrs
|
|
|
age: begins to name pictures/objects
|
2 yrs
|
|
|
age: Runs,
|
2yrs
|
|
|
age: climbs,
|
2 yrs
|
|
|
age: throws,
|
2yrs
|
|
|
age: walks up/down stairs alone
|
2 yrs
|
|
|
age: 6-7 cube tower,
|
2 yrs
|
|
|
age: copies vertical strokes,
|
2 yrsa
|
|
|
age: begins circular strokes;
|
2 yrs
|
|
|
age: turns 1 page at a time
|
2 yrs
|
|
|
age: Tricycle,
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: hops 2-3 times,
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: jumps from step, alternating feet up stairs;
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: walks well on toes
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: 10 cube tower,
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: copies circle,
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: uses scissors,
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: buttons,
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: strings beads,
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: draws head
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: Imitates adults and playmates
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: Spontaneously shows affection for familiar playmates
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: Can take turns in games
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: Understands concept of "mine" and "his/hers"
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: laungage Understandable,
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: repeats 3 digits,
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: nursery rhymes,
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: Uses pronouns (I, you, me...), some plurals (cars, dogs)
|
3 yrs
|
|
|
age: alternating feet down stairs,
|
4yrs
|
|
|
age: hops 5 times,
|
4 yrs
|
|
|
age: balances on 1 foot, throws ball overhand
|
4 yrs
|
|
|
age: copies squares,
|
4yrs
|
|
|
age: laces shoes,
|
4 yrs
|
|
|
age: dresses self,
|
4 yrs
|
|
|
age: imaginary friends
|
4 yrs
|
|
|
age: asks “why, when and how”
|
4 yrs
|
|
|
age: Skips;
|
5 yrs
|
|
|
age: broad jumps;
and hops 10 x |
5 yrs
|
|
|
age: Copies triangle;
|
5 yrs
|
|
|
age: print letters;
|
5 yrs
|
|
|
age: draws person, including arms/legs;
|
5 yrs
|
|
|
age: ties a knot;
|
5 yrs
|
|
|
age: grasps pencil maturely
|
5 yrs
|
|
|
age: Defines words
|
5 yrsa
|
|
|
age: Plays cooperatively;
|
5 yrs
|
|
|
age: understands rules
|
5 yrs
|
|
|
age: writes name
|
6 yrs
|
|
|
age: Counts 10 objects;
|
6 yrs
|
|
|
age: knows right from left
|
6 yrs
|
|
|
loud first heart sound with a fixed and widely split second heart sound at the upper left sternal border that does not change with respirations. Heart defect?
|
ASD
pulses are normal, a right ventricular systolic lift at the left sternal border is palpable, and a fixed splitting of the second heart sound is audible due to excess blood in the right atrium causing delay in closure of pulmonary valve. Ventricular hypertrophy causes loud first heart sound |
|
|
a harsh or blowing holosystolic murmur best heard along the left lower sternum, often with radiation throughout the precordium.
|
vsd
|
|
|
middiastolic rumble at the lower left sternal border
|
Tricuspid regurgitation
|
|
|
infants with anorectal anomalies assoc w/ what congenital anomalies? VACTERL
|
Congenital anorectal anomalies are frequently associated with other congenital anomalies including
1. heart disease, 2. esophageal atresia (EA), 3. abnormalities of the lumbosacral spine, 4. double urinary collecting systems, 5. hydronephrosis, and 5. communication between the rectum and the urinary tract, vagina, or perineum. VACTERL syndrome: Vertebral anomalies, Anal atresia, Cardiac defect (eg, ventricular septal defect [VSD]), TracheoEsophageal fistula, Renal anomalies, and Limb defects (eg, radial dysplasia). |
|
|
Infant w/ HIV + mom. PPX? Which polio vaccine?
|
1. Prophylaxis against PCP - While awaiting final determination of this infant's HIV status, which can take several months, prophylaxis with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole starting at 6 weeks is usually appropriate.
2. Inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) is recommended. NO ORAL POLIO vaccine (OPV) for all patients now (not just immunosuppressed patients) because of the theoretical risk of paralytic polio. |
|
|
tx for obstruction secondary to an annular pancreas?
|
Duodenoduodenostomy is a bypass procedure is much more physiologic than gastrojejunostomy and does not require a vagotomy to prevent marginal ulceration; it is therefore the procedure of choice.
|
|
|
5-month-old infant is admitted with severe varicella infection. The lesions cover the infant's entire body, and the infant is beginning to show symptoms of respiratory distress. Past medical history is significant for a history of atopic dermatitis. The family also notes frequent epistaxis; the last episode required nasal packing in the ED. What is the most appropriate diagnostic laboratory test?
|
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome must be considered in a patient with severe eczema, thrombocytopenia, and unusual infections.
|
|
|
immobilized following the fracture of a weight-bearing bone gets, anorexia, occasional vomiting, polyuria, and lethargy. Worry about what? Dx test?
|
Hypercalcemia -> nephropathy, nephrocalcinosis, hypertensive encephalopathy, and convulsions.
Dx test: Collect urine for measurement of the calcium to creatinine ratio A ratio of greater than 0.2 establishes a diagnosis of hypercalciuria. TX: if symptomatic hypercalcemia, short-term therapy with calcitonin is highly effective in reducing the concentration of serum calcium by increasing bone resorption. |
|
|
age 5, a child is noted to have the loss of ankle jerks. At age 10, limb ataxia develops, followed by a peripheral neuropathy. During adolescence, retinitis pigmentosa develops. Acanthocytosis is present. Syndrome?
|
Abetalipoproteinemia (Bassen-Kornzweig syndrome) usually becomes symptomatic during early childhood.
- very low cholesterol and triglyceride content. - Acanthocytes are spiked or crenated RBCs. - CNS path: in patients with abetalipoproteinemia reveals posterior column and spinocerebellar tract degeneration. 1. spinocerebellar signs (similar to Friedreich disease): Position sense is lost and extensor plantar responses develop as the disease progresses. 2. NO DEMENTIA: As is true for Friedreich disease, dementia is not an obvious part of the syndrome. tx: Vitamin E supplementation may retard the disease's progression. |
|
|
scaphoid abdomen and respiratory disease. dx? tx?
|
congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
Path: These defects are posterolateral and occur due to failure of the embryologic iaphragm to fuse between the eighth and twelfth weeks of intrauterine life. - Any abdominal organ—pancreas, kidney, small and large intestine, stomach, liver, or spleen—can herniate into the chest. - The abdominal organ acts as a space-occupying lesion and retards growth of the lung, which results in pulmonary hypoplasia. Respiratory problems at birth stem from primary pulmonary hypertension, the consequence of hypoplasia, rather than from compression of the lung by abdominal contents. - Tx: Most experts recommend stabilizing the pulmonary hypertensive crisis medically or with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) prior to attempting repair. |
|
|
The best antibiotics to eliminate group A streptococcal carriage from oropharyngeal secretions are?
|
an oral respiratory quinolone or oral clindamycin.
|
|
|
How is acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) distinguishable from multiple sclerosis (MS)? MRI? multiphasic?
|
ADEM PATH: demyelinating disease of the brain, brainstem, and spinal cord that is indistinguishable from MS on MRI.
- monophasic, meaning that it occurs acutely on a single occasion and not in a recurrent fashion like MS. - It usually develops within days or weeks of a viral illness or an immunization. Childhood exanthems are especially likely to precipitate ADEM, as are smallpox and rabies immunizations. |
|
|
tx of head lice (Pediculosis capitis).
|
head lice (Pediculosis capitis).
AVOID: All the treatments outlined for this patient are appropriate for the treatment of lice except for use of 1% lindane in the 2-month-old family member, because of the potential of neurotoxicity from transdermal absorption. TX: 1. permethrin 1% cream rinse (Nix). 2. Use of 1:1 vinegar-water rinse for hair for nit removal 3. Washing clothing and bedding in very hot water 4. Replacement brushes 5. repeat in 7 to 10 days |
|
|
undescended testis, or cryptorchidism after 6 months. at risk for and px tx?
|
By 6 months of life, 0.8% of boys born at term still have cryptorchidism.
Risk: 1. higher risk testicular malignancy 2. Torsion of the testis is a potential risk because of the excessive mobility of the undescended testis. Orchiopexy helps to eliminate this problem. |
|
|
Disorders x 3 w/ retinal cherry-red spot
|
Path: represents the center of a normal retinal macula that is surrounded by ganglion cells in which an abnormal accumulation of lipid has occurred, thus altering the surrounding retinal color so that it is yellowish or grayish white;
Disorders as 1. GM1 generalized gangliosidosis type 1, 2. Sandhoff disease, and 3. Niemann-Pick disease type A |
|
|
newborne develops over weeks severe progressive central nervous system (CNS) degeneration, an enlarged liver and spleen, macroglossia, coarse facial features, and a cherry-red spot in the eye. Dx? complete lack of or deficiency of what enzyme?
|
Generalized gangliosidosis type 1 (type 1 GM1 gangliosidosis)
- complete lack of acid beta-galactosidase activity. causing a lysosomal storage disorder also: gingival hyperplasia, hernias, joint stiffness, dorsal kyphosis, and edema of the extremities. |
|
|
psychomotor retardation and hypotonia beginning at about 6 to 12 months of age; the children are usually normal at birth. A pronounced startle reflex and severe hyperacusis (over-sensitivity to certain frequency ranges of sound), seizures, loss of vision (with cherry-red macular spots), and macrocephaly are seen. Disease? complete lack of or deficiency of what enzyme?
|
beta -Hexosaminidase A deficiency (GM2 gangliosidosis, type 1, or Tay-Sachs disease)
|
|
|
presents in older children as acroparesthesia (numbness or tingling in one or more extremities), intermittent painful crises of the extremities or the abdomen, frequently low-grade fevers, and sometimes cataracts. Dx? complete lack of or deficiency of what enzyme?
|
Reduced activity of -alpha - galactosidase (Fabry disease)
|
|
|
onset between 1 and 2 years of age and is notable for progressive ataxia, weakness, and peripheral neuropathy. In this disorder, gray macular lesions can be seen that look somewhat similar to cherry-red spots. complete lack of or deficiency of what enzyme?
|
Metachromatic leukodystrophy (deficient activity of galactosyl-3-sulfate-ceramide sulfatase)
|
|
|
bilious emesis. Plain films of the abdomen show evidence of an intestinal obstruction. An upper gastrointestinal (UGI) contrast series reveals a midgut volvulus with the site of obstruction at the third portion of the duodenum. Cause?
|
Path: anomalies of intestinal rotation and fixation (aka malrotation).
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), Hirschsprung disease, hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, and intussusception are not associated with a midgut volvulus. |
|
|
What do the + mean on urine dipstick (e.g. 1+ protein)?
|
100 mg/dL per +
|
|
|
How is nephrotic syndrome diagnosed?
|
albuminuria = 3.5 g per 24 hours or greater.
|
|
|
albuminuria = 3.5 g per 24 hours or greater. Most common cause? Next step?
|
Nephrotic syndrome. Kidney biopsy is usually carried out in adults, but in children and adolescents, where minimal change disease is the commonest cause, a trial of corticosteroids usually precedes renal biopsy.
|
|
|
small, sharply edged lesions that occur most commonly on the head and neck of infants. These lesions are yellow-orange in color and are slightly elevated. They usually are hairless. dx?
|
Sebaceous nevi (nevus of Jadassohn)
|
|
|
rash is greasy, scaly, and erythematous and in smaller children involves the face, neck, axilla, and diaper area. In older children, the rash can be localized to the scalp and intertriginous areas. Pruritus can be marked
|
.Seborrheic dermatitis (aka cradle cap )
|
|
|
flat vascular lesions that appear more prominent during crying. The lesions on the face fade over the first weeks of life. Lesions found over the nuchal and occipital areas often persist. No therapy is indicated.
|
Salmon patches (aka nevus simplex or flameus)
|
|
|
Kid born w/ a inguinal hernia. Path?
|
congenital indirect inguinal hernia is the result of a patent processus vaginalis.
- Inguinal hernias are commonly seen in premature infants (16%-25%). - Incarceration is common; elective repair is often considered prior to hospital discharge. |
|
|
newborn w/ respiratory distress, trouble feeding, decreased fetal movement in pregnancy, and very hypotonic w/o movements, Deep tendon reflexes are absent. Spinal fluid is normal.Dx?
|
spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) type I (AKA Werdnig-Hoffman disease, or infantile progressive spinal muscular atrophy.
PATH: The defect is found in the survivor motor neuron (SMN) gene that stops apoptosis of motor neuroblasts. During development, an excess of motor neuroblasts is noted, and through apoptosis only about half survive in the normal newborn; the SMN gene regulates this natural destruction. A defect in the SMN gene results in a continuation of apoptosis, resulting in progressive destruction of motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord. |
|
|
prolongation of PT, aPTT, and TT and a decrease in factor VIII level and platelet count. In addition, the titer of fibrin split production is usually increased. Dx?
|
In disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), there is consumption of fibrinogen; factors II, V, and VIII; and platelets. D-dimer is a fibrin breakdown product and may also be elevated in DIC.
|
|
|
PT and aPTT are prolonged but thrombin time and platelet count normal. Dx?
|
vitamin K deficiency - decrease in the production of factors II, VII, IX, and X
thrombin time, which tests for conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, however, should be normal, and the platelet count should also be normal. |
|
|
a young, well-attached child is separated from a parent then the parent reappears the child acts ambivalent. Name this phenomenon
|
protest phase of a separation, ambivalence is anger
|
|
|
Tx for gasoline ingestion or aspiration ? emesis? Charcoal? nasogastric tube?
|
Hydrocarbons with low viscosity and high volatility are the most likely agents to cause respiratory symptoms. . Hydrocarbon aspiration can produce dyspnea, cyanosis, and respiratory failure.
Treatment is symptomatic, sometimes requiring intubation and mechanical ventilation. NO: 1. emesis is contraindicated, as this may cause further aspiration. Placement of a nasogastric tube is used only in high-volume ingestions or when the hydrocarbon is mixed with another toxin. Charcoal is not useful, and no intravenous binding agent is available. |
|
|
Most common bug for impetigo?
|
S pyogenes (group A -hemolytic Streptococcus).
|
|
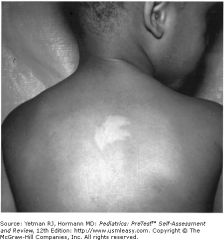
this and infantile spasms. dx?
|
achromic skin patches, especially in association with infantile spasms, are characteristic of tuberous sclerosis, an autosomal dominantly acquired condition. Other dermal abnormalities (adenoma sebaceum and subungual fibromata) associated with this disorder appear later in childhood. Children with this condition may present with infantile spasms, and a Wood lamp evaluation of their skin may assist in the identification of the hypopigmented, "ash-leaf" lesions. CT scan of the brain may demonstrate calcified tubers, but these may not be evident until 3 to 4 years of age.
|
|
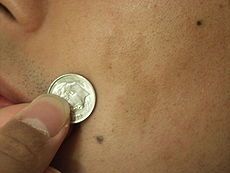
dx?
|
neurofibromatosis may have a few achromic patches, the identifying dermal lesions are café au lait spots
|
|
|
A 15-year-old sexually active girl with a single non-tender lesion on her labia and regional nontender lymphadenopathy. Dx?
|
syphillis
|
|
|
A healthy, LOW-birth-weight infant on breast milk only needs what supplement?
|
Calcium - requires a daily intake of calcium of about 200 mg/kg. Breast milk has much less calcium (and phosphorus) than do commercial formulas. The breast milk can be directly supplemented with calcium, or it can be supplemented with commercial fortifiers. Alternatively, it can be mixed with formulas designed for the premature infant. Breast milk promotes gut maturation and prevents intestinal atrophy induced by lack of enteral feeding; however, it is likely to have insufficient calcium and phosphorus for catch-up growth.
|
|
|
Homeless children experience a higher incidence of what?
|
1. acute illness symptoms, including fever, ear infections, diarrhea, and asthma exacerbations.
|
|
|
Heart defect in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome?
|
Mitral valve prolapse
|
|
|
Heart defect in Noonan syndrome?
|
pulmonic stenosis
|
|
|
erythema infectiosum or Fifth disease. Pregnant lady complication?
|
Pregnant women should avoid exposure to this virus, since it may cause fetal hydrops in 10% of cases.
|
|
|
erythematous malar blush followed by an erythematous maculopapular eruption on the extensor surfaces of extremities that evolves into a reticulated, lacy, mottled appearance. Dx? Complication in pt w/ chronic hemolytic anemias like sickle-cell disease?
|
erythema infectiosum or Fifth disease. Infection by parvovirus B19 produces this pattern of a "slapped cheek" appearance.
aplastic anemia is a serious complication. |
|
|
jejunoileal atresia. Path? Tx?
|
Path: probably a mesenteric vascular accident during intrauterine growth.
Tx: Resection and primary anastomosis |
|
|
After a generalized tonic-clonic seizure what increases in the blood and can be found on a lab? partial complex seizures? status epilepticus? simple partial seizures?
|
prolactin levels increase dramatically - Blood samples must be drawn within 20 minutes of the episode. This test is less reliable with partial complex seizures, and it is not useful in status epilepticus and simple partial seizures.
|
|
|
nocturnal abdominal pain and GI bleeding in a patient with a family member w/ similar issues. Dx?
|
peptic ulcer disease (PUD).
DX: endoscopy; stains and cultures obtained during endoscopy can diagnose PUD caused by Helicobacter pylori. treatment is acid blockade. Antibiotic treatment for H pylori can cure this disease in infected patients, although the optimal combination of medications is still unclear. |
|
|
frequent headaches and early papilledema. Dx: pseudotumor cerebri. tx?
|
removal of some of the CSF produces a protracted lowering of the intracranial pressure. This pressure reduction is desirable because persistent pressure elevations will damage the optic nerve
|
|
|
When can Duchenne dystrophy happen in girls?
|
Females if they have Turner syndrome if the inherited X chromosome carries the defective dystrophin gene. In the absence of a normal X chromosome, only the defective dystrophin will be produced. The person with Turner syndrome has only one X chromosome but is phenotypically female. Duchenne dystrophy may occur in girls with two X chromosomes, if translocations of material from the normal X chromosome inactivate or eliminate the normal dystrophin gene.
|
|
|
Na and K+ in diabetes insipidus
|
diabetes insipidus - the renal collecting tubules are impermeable to water, resulting in the excretion of hypotonic urine. Patients with diabetes insipidus present with polyuria and polydipsia. Net loss of water leads to dehydration and hemoconcentration and, therefore, to relatively high serum concentrations of sodium and potassium.
|
|
|
when is activated charcoal useful?
|
For drugs with an enterohepatic circulation (eg, phenobarbital and tricyclic antidepressants), or those with prolonged absorption (eg, sustained-release theophylline),
|
|
|
Premature infants w/ wheezing, hypoxia, and respiratory distress in winter; often an older sibling has milder, upper respiratory symptoms. Dx?
|
Bronchiolitis is a very common viral infection most often caused by respiratory syncytial virus. It is most often seen in the winter months
|
|
|
how should you explain an operation to a 4 y/o?
|
Act it out w/ a doll. preoperational stage of development according to Piaget. Such children do not understand concepts and are unable to abstract, thus they benefit from role-playing what will occur in the hospital more than any kind of verbal descriptions.
|
|
|
The parasitic brain lesion most likely to have a large cyst containing numerous daughter cysts is that associated with what bug?
|
Echinococcosis is usually acquired by ingesting material contaminated with fecal matter from sheep or dogs. Children are more likely to develop cerebral lesions than adults, but people at any age may develop this encephalic hydatidosis, which entails the development of a major cyst with multiple compartments in which smaller cysts are evident. This hydatid cyst of the brain behaves like a tumor and may become massive enough to cause focal deficits.
|
|
|
kid has S. Aeureus pneumo w/ upper lobe consolidation -> then a acutely worsened over the previous few minutes, with markedly increased work in breathing, increasing oxygen requirement, and hypotension. Dx? Tx?
|
Tension pneumothorax, a recognized complication of staphylococcal (and other) pneumonia is caused by toxin production by the bacteria leading to rupture of the alveoli into the pleural space. Tension pneumothorax can be quickly lethal if not recognized and treated; this makes a high index of suspicion and prompt diagnosis mandatory. The other complications can also occur but do not require so prompt a response. Immediate action to relieve the tension is mandatory, usually accomplished by inserting a needle or catheter into the second or third intercostal spaces in the midclavicular line, with the patient supine.
|
|
|
back pain, frequency, and dysuria and sexually active. when are urine cultures indicated?
|
Urine culture is indicated when acute bacterial cystitis is suspected, but the urinalysis (dipstick) leaves the diagnosis in question. Therefore, in the setting of classic symptoms but a negative dipstick or microscopic evaluation, a culture will confirm the diagnosis. In the other cases, either the urine dipstick or microscopic evaluation confirms the clinical suspicion and culture is not indicated.
|

