![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
201 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Half-moon shaped nucleus, I phagocytose, what am I?
|
Monocyte :)
|
|
|
|
Renal transplant patient, and see stuff in vessel intima, smooth mm cells and C.T. + arteriosclerosis. What type of rejection is this?
|
Chronic Rejection; ( Acute Rejection - days/weeks) due to T cell activation); ( Hyperacute- w/in minutes, it's an antibody reaction against the donor's antibodies)
|
|
|
|
spinal stiffness, LBP, limited motion of lumbar spine, see fusion of SI joints, which HLA- association?
|
Dx: Ankylosing Spondylarthritis
HLA-B27 association KNOW: 1. Post-gonococcal arthritis 2. Anterior Uveitis!! |
|
|
|
What are the other HLA associations?
|
1. HLA-DR3: Sjogren's, Hepatitis, DM Type I
2. HLA-DR4: RA, and Type I DM |
|
|
|
Ashkenazi Jew, + HSM, pancytopenia, skeletal deformities, What's seen in bone marrow biopsy?
|
Gaucher disease Type I; ( Lysosomal Storage Disease)
- see distended lysosomes.Gaucher is #1 MCC of Lysosomal storage disease worldwide; Accumalated thing: GLUCOCEREBROSIDE; Autosomal Recessive! |
|
|
|
Boy w/ classic CF symptoms, what are culture findings in sputum?
|
#1 MCC = Pseudomonas; Tx: CEFTRIAXONE? Answer: Gram Negative, Oxidase NEGATIVE!! What else could this be? Neisseria is also Gram Neg and Oxidase +, but it's a diplococci and grows on chocolate agar. What if Gram Neg + Factor X and V dependent? ( Haemophilus!!! I need my factors!)
|
|
|
|
3 yr old boy has repeated infections but Ig's normal ( B cells ok) and T cells normal, What protein is most likely missing?
|
Not SCID, so CGD! Loss of NAPDH oxidase. If it was SCID ( adenosine deaminase would be missing, also l/o common gamma chain IL receptors??)
Btk Tyrosine Kinase ( missing in Bruton's Agammaglobinemia) |
|
|
|
What the hell is a nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) test? What does it mean if it's negative?
|
NBT- is used to screen for CGD. If NADPH oxidase it present, it should turn blue (normal), if negative ( doesn't turn blue) indicate enzyme deficiency and CGD is most likely problem.
|
|
|
|
Cyclobenzaprine? used for muscle spasm can cause what SE?
|
Eye problems, blurred vision and ocular pain.
|
|
|
|
+ whiff test, smelly fishy vagina with KOH mount. what am I?
|
Bacterial vaginosis due to Gardnerella vaginalis ( normal flora).
|
|
|
|
Man got painful red areas on arms, chest, thighs. 5 days prior. he had CV incident. What is MOA of the drug that caused this?
|
He has painful, necrotic, ulcerations from WARFARIN or Coumarin anti-coagulants. Answer: Blocks Clotting factors 2,7,9,10
|
|
|
|
Man has severe pain @ hands, feet, especially during cold winter months, tingling of hands. No Hx of DM, Has ulcers that are painful on tips of fingers. What is this condition related to? ( list of substances)
|
DX: Thromboangitis Obliterans aka Buerger Disease.
|
|
|
|
What is the second messenger for ANP?
|
cGMP related to guanylyl cyclase
|
|
|
|
DiGeorge Dz: truncus arteriosis, hypocalcemia. Lab's would show L/O which CD antigen?
|
CD3!! due to Thymic aplasia, CD19/20 = B cells
|
|
|
|
PCR, where are primers bound to?
|
DNA polymerase synthesizes a new strand of DNA by extending the 3' end of an existing nucleotide chain, so 3' end of both coding and template
|
|
|
|
Boy had anexoria post chemotherapy for his ALL. He has staggering gait, disoriented speech. He recieved glucose therapy, but his sx get worse: LOC, irregular breaths, and opthalmoplegia.
|
Dx: Wernicke's encephalopathy
Secondary: What is the enzyme responsible? Wernicke's encephalopathy is a thiamine deficiency ( can also be due to alcoholism). Have to know that Thiamine is a cofactor for 3 enzymes: 1. TRANSKETOLASE 2. Alpha-KETOGLUTARATE DEHYDROGENASE 3. PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE |
|
|

NEED TO ADD IMAGE:
Young boy, mass on femur, see small round cells with scant cytoplasm, Genetics reveal t(11:22) translocation. Secondary: What is the gene product |
FA 381:
Know ( 11--> 22 translocation) New ONION appearance of bone gene product = transcription factor ( that is constitutively on!) |
|
|
|
What are gene products and resultant tumor associations?
|
Growth factors = astrocytoma, osteosarcoma, stomach/bladder cancer, thyroid cancer; Growth Factor Receptors: Breast CA, Ovarian, MEN2, Leukemia; Cyclin dependent Kinases: Glioblastoma, Melanoma, Sarcomas; Signal Transducing Proteins: Hematologic malignancies, Kidney Tumors
|
GOOD SUMMARY!
|
|
|
When do you us Indirect vs. Direct Coombs test for Rh antigens in pregnant mom+fetus?
|
There are two forms of the Coombs' test: direct and indirect. The direct Coombs' test is used to detect antibodies that are already bound to the surface of red blood cells. Many diseases and drugs (quinidine, methyldopa, and procainamide) can lead to production of these antibodies. These antibodies sometimes destroy red blood cells and cause anemia. This test is sometimes performed to diagnose the cause of anemia or jaundice. The indirect Coombs' test looks for unbound circulating antibodies against a series of standardized red blood cells. The indirect Coombs' test is only rarely used to diagnose a medical condition. More often, it is used to determine whether a person might have a reaction to a blood transfusion.
An abnormal (positive) indirect Coombs' test means you have antibodies that will act against red blood cells your body views as foreign. This may suggest: Autoimmune or drug-induced hemolytic anemia Erythroblastosis fetalis hemolytic disease Incompatible blood match (when used in blood banks) Basically ( DIRECT = bound IgG's), INDIRECT = circulating, unbound |
|
|
|
6 year old, with hx of severe recurrent bacteria/viral infxn. Hypopigmented skin and eyes, see giant intracellular granules in peripheral leukocytes. What cells are mostly affected
|
Dx: CHEDIAK-HIGASHI ( problem with microtubles, l/o motility, so no phagocytosis) FA 78
|
|
|
|
So HIV+ man has rash, and red spots/ nodules on skin. They bleed a lot if he pokes them. What's his CD4 count most likely?
|
Dx: Bacillary Angiomatosis ( suspect if you see skin papules on HIV person) Low CD4 ( 0-200) is the greatest risk Secondary: What's the bug that causes this vascular mass?
BARTONELLA HENSELAE FA 279 |
|
|
|
What are the hunger neuropeptides/hormones?
|
AGP- agouti related peptide; Ghrelin; Melanin-concentrating hormone; Neuropeptide Y
|
|
|
|
Which is the better beta blocker to use for STEMI + hx of emphysema?
Propranolol Acebutolol Metoprolol Timolol Sotalol |
Metoprolol (since B1- selective), won't exacerbate; ( generally for cardio use Metoprolol/ Atenolol) beta 1 selective. Sotalol : non-selective, but also a class III anti-arrythmic ( K+ channel blocker)
|
|
|
|
What factors are chemoattractant to neutrophils?
|
C5a- anaphylatoxin ( FA 207) also IL-8 " clean up on aisle 8"
|
|
|
|
27 yr old pregnant lady, has flu symptoms, red rash on ankles, wrists that spreads centrally** Associated with hiking trip. What is the best treatment?
|
Dx: rash on hands/feet that spreads centrally. This is Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever; Secondary: What bug causes this?
RICKETTSIA RICKETSII; What is the treatment for this tick infection? DOC is Doxycycline, but she's pregnant, so 2nd line for her is 3rd generation cephalosporin or Chloramphenicol. |
|
|
|
What are drugs that block cytochrome P450?
|
cimetidine, erythromycin, ketoconazole
|
|
|
|
What sugars are transported in small intestine?
|
glucose/galactose
|
|
|
|
What are some indications for splenectomy?
|
HS ( hereditary spherocytosis)- loss of spectrin/ankrin; Thalassemia major; ITP - immune thromocytic purpura; Hodgkin disease
|
|
|
|
Urea is a treatment for?
|
Sicke Dell Disease!
|
|
|
|
EDTA is a tx for disease showing what histological finding?
|
basophilic stippling, lead poisoning, causing sideroblastic anemia
|
|
|
|
Swimmer* ear pair, + yellow exudate, crusty. What are culture findings?
|
Dx: Otitis Externa ; Bug: Psuedomonas; Culture Findings: Oxidase +, Gram Negative; FA 151
|
|
|
|
Treatment for anaphylactic food reaction?
|
EPI - stimulate adrenergic receptors
|
|
|
|
Child has sx of Type I DM, what is he a risk of acquiring?
|
Key Point: Type I DM is autoimmune, concept is that autoimmune dz. are linked, he is at risk of developing: CELIAC disease, also ankylosing spondylitis, Graves dz, RA, SLE
|
|
|
|
What is the only DNA virus that can replicate outside of nucleus, in the cytoplasm of host only?
|
Molloscum contagiosum virus ( pox virus).
see dimples + moles ( YOU MOLE, YOU SCUM!!) Musculosum! |
|
|
|
What's DOC for angina?
|
beta blocker ( atenolol)
|
|
|
|
Family has bunch of Boys, lots of infections, low B cells markers, low IgM, and IgG. What is the defective protein?
|
Dx: Bruton's agammglobinemia ( BOYS! B-CELLS BRUTONS!) Lack of B cell precursors to differentiate into B cells; Lack of TYROSINE KINASE!!
|
|
|
|
What are lab findings in someone who hadn't slept in 3 nights, studying cram mode?
|
elevated cortisol ( stress)
increased DA increased TSH, T4 due to SNS response low lymphocytes, ( stress suppresses immune system) |
|
|
|
Patient presents with chronic tinnitus, b/l hearing loss, and mass on CN VIII, what gene is effed up?
|
NF2 @ Chromosome 22, and b/l Acoustic schwannomas!; Neurofibromatosis 2; Bening acoustic Neuromas; If it's in the eyes, it's NF-1!! aka Von-Reckinghausen! @ 17!! just 5 blocks down!! ( see cafe au lait spots)
|
|
|
|
Where in the hypothalamus is GnRH made?
|
arcuate nucleus
|
|
|
|
Between ovulation and formation of the corpus luteum, what cellular events happen?
|
This is the luteal phase. LH surge has taken place, and now we need to make the corpus luteum to secrete progesterone to maintain the thick uterine lining so implantation can happen in the event of fertilization. To make Progesterone, LH needs to bind to LH -R's at the granulosa cells!! ( this was the answer!).
Have to know where the receptors are on the cells, and what actions they do. |
|
|
|
Hot flashes, irregular menstruation, suspect menopause, what would be hormonal findings?
|
low estrogen
high FSH, LH, GnRH due to loss of negative feedback |
|
|
|
processus vaginalis ( evagination of peritoneum) fails to fuse, you'd get?
|
Hydrocele; Fusion of epididymis + tunica vaginalis = Spermatocele; Complete failure to form, you'd get a patent tunica vaginalis = Congenital hernia
|
|
|
|
What is the only negligence statute that Last Clear Chance applies to?
|
Contributory Negligence.
|
|
|

What cells are interconnected by the line?
|
Sertoli Cells- see tight junctions
|
|
|
|
What causes the second rise of estrogen?
|
Corpus luteum; The first rise is due to the follicle it self secreting estrogen. Remember the two cell type hypothesis? Theca cells and Graffian cells of the mature "graffian" follicle. Granulosa cells ( have the aromatase) to convert the androgens that the Theca cells made into estradiol.
|
|
|
|
what hormone is responsible for the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle?
|
Progesterone
|
|
|
|
What hormone would be expected to peak during the late stage of gestation?
|
CRH= corticotropin releasing hormone. CRH stimulates ACTH to make cortisol. THis steroid helps lung maturation!! to secrete surfactant!
|
|
|
|
What hormone maintains the corpus luteum and prevents it from degenerating?
|
hCG from the syncytiotrophoblast
|
|
|
|
What is teh zona pellucida made of?
|
rich in polysaccharides/glycoproteins, and stains really red w/ PAS
|
|
|
|
Which cells secrete inhibin, and what does inhibin block?
|
Remember, inhibin, acts to block the thing that secreted it. It autoregulates. So if Inhibin blocks FSH, ( FISH!!), then it must be secreted by ( Sertolie cells) since Sertoli cells have teh FSH receptors ( S for FSH in Sertoli) but ( L, for LH in Leydig cells!).
|
|
|
|
If you see kid with CAH symptoms, but he has major tan skin, then what enzyme defect would you suspect?
|
StAR or 3 Betahydoxylase. These enzymes would block synthesis of all hormones at adrenal gland ( aldosterone, cortisol, testosterone). Since cortisol is low, ACTH would be jacked up, ACTH gets metabolized to alpha- MSH ( melanocyte stimulating hormone) --> tan pigmented skin.
Answer was StaR ( steroidgenic acute regulatory protein) StaR mutations cause complete steroid hormone deficiency in adrenal and adrenal hyperplasia since ACTH is jacked up. |
|
|
|
What is the only female structure that has cilia?
|
Fallopian tubes
|
|
|
|
DM drug that works as a DNA enhancer by binding to PPAR's ( peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors)
|
PIOGLITAZONE ( P's!!)
|
|
|
|
If you have a hypokalemic CHF patient on many drugs (including digoxin), and they ask what's the best diuretic to treat edema, think?
|
TRIAMTERINE
because hypokalemia can increase digitoxicity. So you need a K+ sparing diuretic. It blocks the ENaC channels!. |
|
|
|
So you have a disease ( 1/2500) incidence. what is the carrier frequency ?
|
= 2pq or just 2p
|
|
|
|
What is the MCC of neonatal meningitis in the US? What test would you do?
|
strep agalactiae!
others are E.Coli and listeria ( Gram +/-) organisms. so You'd do a GRAM STAIN OF CSF !!! |
|
|
|
What are ACEI's used for?
|
Heart Failure, HTN, DM; Angioedema, facial swelling + Dry, hacking, bradykinin cough
|
|
|
|
white caucasian man, fatty cast, nephrotic syndrome, + edema Dx?
|
Membranous glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
|
What is the MCC of neonatal meningitis in the US? What test would you do?
|
strep agalactiae!
others are E.Coli and listeria ( Gram +/-) organisms. so You'd do a GRAM STAIN OF CSF !!! |
|
|
|
Girl is weird, has no friends, plays alone with barbie dolls, thinks everything's ok if she rubs her charm. What's her dx?
|
Schizotypal
|
|
|
|
What are ACEI's used for?
|
Heart Failure, HTN, DM
Angioedema, facial swelling + Dry, hacking, bradykinin cough |
|
|
|
white caucasian man, fatty cast, nephrotic syndrome, + edema Dx?
|
Membranous glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
|
What is pathophysiology behind malar rash in SLE?
|
C' activation and accum of IC deposits in vasculature
|
|
|
|
Girl is weird, has no friends, plays alone with barbie dolls, thinks everything's ok if she rubs her charm. What's her dx?
|
Schizotypal
|
|
|
|
What is pathophysiology behind malar rash in SLE?
|
C' activation and accum of IC deposits in vasculature
|
|
|
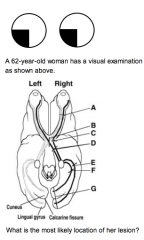
|
F
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 intrinsic muscles of thumb innervated by median nerve?
|
Abductor pollicus brevis, Flexor pollicus brevis, opponens ( OAF) pollicus. There's no longus for thumb!! in thenar eminence!
|
|
|
|
Patient has weakness, fatigue, and orthostatic hypotension. What else would be present?
Differential Dx? |
Hypotension, orthostatic changes
She was also PPD +, infection that can cause something to degenerate after attack? What could it be? It's TB attacking adrenal cortex --> Addison's Disease --> loss cortisol, jacks up ACTH so you see a-MSH increase and tanned skin. WOW, 5th order! |
|
|
|
Boy went swimming, got fever, frontal headaches, bug was found to be in CSF ~ 10-15 un diamter. What is it?
|
Naegleria Fowleri = the lake elsinore killer. Has cholesterol as cell membrane ( this was the secondary)
|
|
|
|
patient was prescribed a skeletal muscle relaxant but then developed ECG abnormalities, what drug is this?
|
Succinyl choline --> hyperkalemia + ventricular dsyrhhtymias
|
|
|
|
ALS treated w/ Clinda for aspiration pneumonia. Then he gets diarrhea, which is a following attribute of the pathogen that caused this diarrhea?
|
Think ClindA--> Diarrhea. Probably has pseudomembranous colitis. Must be Clostridium difficile. Answer: Spore formation!!! 4th order!
|
|
|
|
How can you treat CGD?
|
IFN-gamma
|
|
|
|
Man had drug induced SLE, w/ HTN, what was the drug?
|
hydralazine- vasodilator
|
|
|
|
What drug caused the Tea colored urine in a man with muscle pain?
|
Dx: rhabdomyolysis
STATINS cause rhabo also Drugs of abuse, cocaine, methamphetabmines. |
|
|
|
Should a primagravid term mother who has PKU be able to eat stuff with aspartame?
|
No, If she has PKU, phenylalanine will accumulate and cross placenta and act as a teratogen --> harms the fetus, risk of mental retardation, microcephaly, low birth weight
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of glycogen storage diseases?
|
1. Von Gierke's Disease ( I) - G-6- Phosphatase
2. Pompe's Disease (II) - Lysosomal, a-1,4 glucosidase (acid maltase) 3. Cori's disease (III)- Debranching enzyme ( a-1,6- glucosidase) 4. McArdle's syndrome (IV)-skeletal msucle phosphorylase |
|
|
|
Patient, 3 yrs old presents with hypotonia, on exam +cardiomeg, rales lower lung fieds, + liver edge. What enzyme is most likely defective?
|
Dx: Pompe's Disease = Pump!!
Only one of the 4 glycogen storage diseases that affects the heart |
|
|
|
Which conditions can overestimate Hg levels, which conditions can underestimate Hg levels?
|
Hemolytic anemia - underestimates ( since more Hg)
B12/folate deficiency- overestimate since ( less RBC's) |
|
|
|
Child ate some fruit, fructose, then started crying, swelling, and having shaking chills. What enzyme is deficient?
|
Aldolase deficiency
Fructose 1 phosphate aldolase. Dx: hereditary fructose intolerance. If no symptoms but just fructosuria, then most likely fructokinase deficiency |
|
|
|
2 yr. old with neurologic deterioration, + HSM, + cherry red macula,Dx?
|
only 2 lysosomal storage diseases present with cherry red macula = 1. Niemann pick dz 2. Tay sachs,
Answer: Niemann pick dz. No HSM in Tay Sachs Niemann Pick is classically in Askenazi Jews 2ndary: Which enzyme is deficient? Sphinomyelinase |
|
|
|
Labs how hyperammonemia, high orotic acid, sx: vomit, CNS problems, DX?
|
OTC deficiency
ornithine carboxylase deficiency |
|
|

What is use to stain this leukemia ?
|
Dx: Hairy Cell Leukemia; Stain: FA 359 - TRAP ( Tartrate resistant acid phosphatase)
|
|
|
|
If a patient comes in for pain but no inflammation, then the best drug is?
|
Acetominophen - analgesic, anti-pryetic, but not an anti-inflammatory. Aspirin/NSAIDS --> GI bleeds. Celecoxib/COX-2 Blocker --> CV risk and Sulf allergy CI
|
|
|
|
In which diseases are target cells seen?
|
1. Thalassemias 2. Liver disease 3. Asplenia 4. HbC disease
|
|
|
|
Patient has recurrent infection with malaria. + Schuffner dots, what is the most likely type of malaria?
|
The only type of malaria with dormant stages is Plasmodium vivax or ovale.
Vivax = Latin Hemisphere Tx: Primaquine - hemolytic ( check g6pd status) FA 161 |
|
|
|
Man comes in with swelling of lymph nodes in inguinal region " buboes" What is infectious etiology?
|
Dx: lymphogranuloma inguinale
Cause: chlamydia ( L1-L3) Types Tx: Azithromycin or Doxycycline FA 156 |
|
|
|
Pt. has hx of DIC, see rods in blood, dx ( AML) acute promyelocytic leukemia. What is chromosomal translocation?
|
t 15:17
Goljan 233 FA 359 |
|
|
|
Where do the babesia like to live inside?
|
1. ixodes tick
2. Borrelia burgdorfi ( Lyme disease) see maltese cross asplenia ( target cells) HALT!! Do a giemsa stain |
|
|
|
See Auer Rods in cells, if it leaks, what would manifest?
|
+ Auer Rods (M3) type
In AML ( > 60 years old) High risk of DIC!!!! t( 15:17) translocation pg 233 Goljan |
|
|
|
How would ESR be expected to change in Polycythemia?
|
ESR would decrease
Condiitons where RBC's settle slower would decrease ESR, since too many RBC's, they all settle slower, also the case in Sickle Cell, it's due to abnormal shape though. |
|
|
|
Why does teh 10 year boy undergoing a tooth extraction have a prolonged PTT time and also increased bleeding time?
|
Increased PTT time - intrinsic pathway ( TENET)
Increased bleeding time - Platelets Must be vWF: defect in vWF receptors also cause low factor VIII, since it's carried on vWF receptors. If gp1b receptors on platelets are messed up , it's called Bernard Soulier |
|
|
|
See eosinophil, what's inside it?
|
MBP--> causes asthmatic reactiosn
|
|
|
|
Infectious Mono infects what types of cells?
|
Caused by EBV, infects the B cells, so the circulating lymphocytes would most likely be CD8+, T cells.
|
|
|
|
See stellate granuloma
|
Dx: Bartonella Henselae!
|
|
|

See empty spaces, +RS cells, what is Dx?
|
Nodular Sclerosing, Hodgkin's Lymphoma
|
|
|
|
Patient has red granules inside RBC"s ( Shuffer bodies) indicating malaria but also has a reactant psoriasis, what meds would you use?
|
Chloraquine is first line for malaria but since he has psoriasis, can't give chloraquine since that exacerbates the psoriasis.
Answer: Give Atovaquone + Proguanil. |
|
|
|
Heparin, you monitor?
Coumarin, you monitor? |
Heparin--activates ATIII, so measure ( activated partial thromboplastin time)
- Measures the intrinsic pathway and common pathway Coumarin- measure INR or Prothrombin Time!!! |
|
|
|
Man is normal, but has decreased sperm count after taking drugs for his acid reflux. Increase in what could cause his impotence and infertility?
|
Prolactin,
Hyperprolactinemia n males can compete with GnRH and decrease pulsatile release of LH and FSH This can be caused by protom pump inhibitor ( Cimetidine) |
|
|
|
Pt. presents with PID. What drug is used to treat its most common cause of infection?
|
MCC = Chlamydia
Drug = Doxycycline or Azithromycin (DOC) MOA= macrolide, binds the 50s |
|
|
|
Tzank test tests for?
|
HSV. Know Latency! hallmark, Retrograde. Vesicular lesions
|
|
|
|
#1 MCC bacterial STD in world?
|
Chlamydia trachomatis
Know! they can't synthesize ATP!!! Obligate intracellular |
|
|
|
How do you dx chlamydia?
|
+ Cytoplasmic inclusions in epithelial cells on pap smear
|
|
|
|
Female @ 28 weeks gestation eats soft cheese, brie, then has spontaneous abortion. What bacteria caused this?
|
Listeria Monocytogenes
|
|
|
|
4 WAYS SUPERVISORS PREVENT DISCIPLINE PROBLEMS
|
COMMUNICATE STANDARDS AND BEHAVIORS
BE DIRECTLY INVOLVED BE A ROLE MODEL, LEAD BY EXAMPLE |
|
|
|
What genetic translocation is associated with nodular lymphoma?
|
t(14,18) bcl-2 activation
|
|
|
|
What genetic translocation is associated with CML?
|
bcr-c-abl ( t9:22)
|
|
|
|
What genetic translocation is associated with Burkitt lymphoma?
|
c-myc activation ( t8,14)
|
|
|
|
If patient is on anti-coag, following cardiac procedure and develops rash, it's because of?
|
Warfarin related skin necrosis. See erythematous indurated, purpuric lesions
|
|
|
|
If you see russell bodies, filled with Ig's in the cytoplasm of cells from a bone biopsy, think of?
|
Multiply Myeloma, a plasma cell dyscrasia
|
|
|
|
What's the differential for iron deficieny anemia?
|
Low iron, malnutrition, *uterine leiomyomas can cause chronic blood loss due to menorrhagia
|
|
|
|
What are lab findings of ferritin, transferrin, and iron in iron deficiency anemia?
|
Low iron, low ferritin, high transferrin
|
|
|
|
What are lab findings of ferritin, transferrin, and iron in beta thalassemia?
|
normal or high iron, high ferritin, and low transferrin
|
|
|
|
What drugs can cause aplastic anemia?
|
Chloramphenicol, benzene, alkylating agents
|
|
|
|
Would chronic autoimmune gastritis cause micro or megaloblastic anemia?
|
megaloblastic, because B12 deficiency
|
|
|
|
How is anemia of chronic disease such as from rheumatoid arthritis different from iron deficiency anemia?
|
it's due to defective iron utilization. Iron is plentiful so high iron, high ferritin, but low transferrin. Smear is almost same tho.
|
|
|
|
What's the difference between idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura?
|
ITP = no fragmented cells, IgG's against gp IIb/IIIa, while TTP is due to impaired cleavage of vWF via metalloproteinases ( see fragmented cell, see hemolytic anemia)
|
|
|
|
What are two causes of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia?
|
this form of anemia causes shistocytes or helmet cells due to DIC or prosthetic valves
|
|
|
|
What bug causes cat scratch fever?
|
bartonella henselae
|
|
|
|
What are symptoms of bartonella henselae?
|
regional lymphadenopathy, fever, see granulomas w/ necrotic debris
|
|
|
|
How do you treat bartonella henselae infection?
|
Azithromycine or Doxy, it's a gram neg bacillus
|
|
|
|
What's the MOA of ticlopidine?
|
irreversibly blocks ADP from binding platelets. bone marrow toxic!
|
|
|
|
Pancytopenia, + tartrate-resistant acid phoshphatase stain (TRAP). What's the dx?
|
Hairy Cell Leukemia
|
|
|
|
Philadelphia chromosome is seen in which leukemia?
|
CML and ALL
|
|
|
|
see old man with leukemia, indolent course (~ 2 mo hx) weight loss fatigue. Dx?
|
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
|
|
|
|
In cases of Heparin induced Thrombocytopenia, the drug of choice to use is?
|
not protamine sulfate, this is used for Heparin overdose. In cases of thrombocytopenia, use LMWH, such as lepirudin.
|
|
|
|
What's the differential for microcytic anemias?
|
#1 MCC Iron deficiency, anemia of chronic disease, thalassemia a/b, sideroblastic anemia
|
|
|
|
Thrombocytopenia, eczema, frequent infections, who am I?
|
Wiskott-Aldrich, X-linked congenital disorder
|
|
|
|
What factor is deficient in von willebrand disease?
|
Factor Viii and von willebrand
|
|
|
|
Defect in ______ causes Glanzmann thrombasthenia.
|
gpIIb/IIIa receptor
|
|
|
|
Defect in _____ causes Bernard Soulier syndrome.
|
gp Ib- the recptor for vWF
|
|
|
|
Teenager with painless lymphadenopathy, see nodules and fibrotic balls and cells have prominent nucleoli. Dx?
|
Hodgkins Lymphoma - Nodular sclerosing type --> kids/teens
|
|
|
|
see "multiple large, round, malignant appearing cells with high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio in background of large numbers of mixed inflammatory cells" Dx:
|
Hodgkin's disease. CD30, CD15 for mixed cellularity type
|
|
|
|
What are sx of TTP?
|
FAT RN; Fever; Anemia Hemolytic;Thrombocytopenia; Renal abnormalities, Neurolgical abnormalities
|
|
|
|
How are HUS and TTP different?
|
There's no CNS symptoms in HUS, otherwise they're exactly the same!!!
|
|
|
|
Patient get HIT. Then she develops UA/NSTEMI and requires anticoagulation. Which one is indicated?
|
Bivalirudin- a direct thrombin inhibitor.
|
|
|
|
What is the MOA of HIT?
|
Auto IgG antibodies against PF4 and forms a complex with heparin.
|
|
|
|
When do you use protamine sulfate?
|
When patient was on Heparin, and they OD', they have hematuria, start bleeding a lot. Don't use for HIT, that's different!
|
|
|
|
What is left shift?
|
Means there is an increase in neutrophilic cells, from the myeoloid line, indicates a extracellular bacterial infection usually.
|
|
|
|
What happens if you mix Macrolide + Warfarin?
|
Macrolides are CYP3A4 blockers, they'll block warfarin metabolism and potentiate it's effects: see increased INR
|
|
|
|
What is the MOA of macrolides?
|
They bind to the 50 S subunit of ribosomes and block protein synthesis
|
|
|
|
See lines of zahn, alternating layers of fibrin, are these clots pre-mortem or post-mortem?
|
See lines of zahn = pre-mortem, it homogenous, then it's POST-MORTEM! only rbc's, no fibrin
|
|
|
|
AML M3, key words?
|
Auer Rods and DIC!!!
|
|
|
|
AML M6, think of?
|
Erythrocytes, RBC's
|
|
|
|
Buzzwords for t(9;22) ?
|
Philadelphia Chromosome BCR-ABL
CML; Tyrosine Kinase Granulocyte lineage: PMN's!!! |
|
|
|
What's LAP? leukocyte alkaline phosphatase?
|
It's increased by PMN's after inflammation.
|
|
|
|
Is see +blasts in leukemia?
|
It's ACUTE, all or aml ( 50%) chance.
|
|
|
|
+ Small lymphocytes with macrophages surrounded by clear spaces. This is known as? + ovarian mass. Dx?
|
This is Burkitt's lymphoma, the sporadic form
|
|
|
|
When does hematopoiesis occur in the liver?
|
1 mo., @ 3 weeks, it's at the yolk sac
|
|
|
|
What is the marker of immature cells?
|
TdT
|
|
|
|
What are the myeloproliferative disorders?
|
Polycythemia vera; Chronic Myeloid Luekemia, Myeloid Metaplasia w/ Myelofibrosis, Essential Thrombocythemia
|
|
|
|
What's teh MOA of streptokinase?
|
activates plasminogen, to create plasmin ( scissors) to cut fibrin clots
|
|
|
|
Pt. presents with hyperpigmented macules, irregular margins on back. And precocious development of breasts at age 5. What bony problem should be found?
|
Dx. McCune-Albright syndrome, or Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Bone is replaced by fibroblasts, collagen, irregular bony trebeculae. See whorls of connective tissue in bone. See cafe au lait or coast of Maine spots and precocious puberty.[musk]
|
|
|
|
What is responsible for relaxation of muscle right after contraction?
|
Binding of Calcium to calsequestrin
|
|
|
|
What nerve innervates the extensors of the thumb?
|
Radial nn.
|
|
|
|
What is the source of new bone in fractures?
|
Periosteum
|
|
|
|
Small round blue cells were found in biopsy of a long bone in 10 year old. Dx?
|
Ewing's sarcoma
|
|
|
|
What are the findings in rheumatoid arthritis synovial joint?
|
See proliferative synovitis with many lymphocytes, macrophages and plasma cells. Synovial membrane is thickened with lots( pannus).
|
|
|
|
Pt. had surgery in axillary region, and now is unable to perform chin-ups, what nerve was lesioned?
|
Latissmus dorsi mm. inovlve din chin ups, the swimmer's muscle. It's innervated by the thoracodorsal nn. C6,-8 [musk]
|
|
|
|
Patient presents with Klumpke's palsy + anhydrosis, ptosis, miosis. Which trunk of the brachial plexus was damaged?
|
Lower trunk, down to T1. T1 = Horner's Syndrome. Klumpke's Claw hand. Loss of intrinsic mm. ( interosseus mm). [musk]
|
|
|
|
What sites are the most common sources of bone metastasis (both blastic and lytic)?
|
Breast and Prostate CA!!!![musk]
Lung, Kidney, Thryoid CA cause lytic bone lesions. But Blastic and Lytic come from Breast or Prostate. |
|
|
|
In avascular necrosis of the femoral head. What artery is most likely compromised?
|
MEDIAL femoral circumflex artery
|
|
|
|
Illiopsoas inserts onto which part of the femur?
|
LESSER trochanter of the femur
|
|
|
|
Midshaft fracture may damage which artery?
|
Profunda brachii artery, branch off the brachial artery
|
|
|
|
Surgical neck fracture may lesion may lacerate which artery?
|
Posterior circumflex humeral artery
|
|
|
|
Median and Ulnar nerves come from which part of the brachial plexus?
|
The lower trunk
|
|
|
|
What is the course of the suprascapular nerve and what mm. does it innervate?
|
Suprascapular nn. innervates supraspinatus and infraspinatus
|
|
|
|
What's an appropriate treatment for Type I osteoporosis, post-menopausal osteoporosis?
|
Raloxifene: decreases bone resorption. Doesn't cause breast pain, and decreases risk for breast cancer.
|
|
|
|
When the right genioglossus is paralyzed, ( lesion XII), which side would the tongue protrude?
|
The right genioglossus acts to protrude to the other side. So damage to the right genioglossus would make the tongue protrude to the right. Paralysis, results in deviation towards the side of the lesion.
|
|
|
|
What is the MOA of celecoxib?
|
It's an NSAID, but it's selective against COX-2. Can be used for acute management of RA ( symmetric joint pain, with fever, lymphadenopathy, HSM)
|
|
|
|
What's the advantage of a COX-2 inhibitor versus COX-1?
|
COX-2 decrease inflammation as does COX-1, but don't decrease the prostoglandins that protect the GI lining
|
|
|
|
Which nerve supplies sensation to the dorsum of the foot and is involved in dorsiflexing the foot, extending toes, and inverting the foot?
|
Common peroneal or fibular nerve.
|
|
|
|
Patient fell on hand and then lesioned a nerve as a result of anterior dislocation of the lunate carpal bone. Which nerve is this?
|
Median nn.
|
|
|
|
Patient had a fracture of the hamate, which nerve is most likely compromised?
|
Ulnar!
|
|
|
|
Which nerve innervates the adducting muscles of the thigh?
|
obturator nn.
|
|
|
|
What nerve innervates the gluteus maximus ( lateral rotator)?
|
INFERIOR gluteal nn.
|
|
|
|
What is the significance of the lateral medial and posterior cords?
|
They are named for their relation to the axillary artery in the axilla
|
|
|
|
What is treatment for acute gout?
|
NSAIDS or Colchicine, NSAIDS are selective COX inhibitors, Colchicine, blocks Microtubules and prevents leukocyte migration and phagocytosis. BTW, Chediak Higashi- lack of microtubles**
|
|
|
|
What is the treatment for chronic gout?
|
Allopurinol, blocks Xanthine oxidase, prevents the synthesis of uric acid. Used for chemo also (mercaptopurine). Also can use probenicid, blocks uric acid reabsorption, increases its excretion.
|
|
|
|
The nerve that passes anterior to the supracondylar ridge is the?
|
Median Nerve, therefore you'd see ulnar deviation, from unopposed ulnar contraction of via ulnar nerve at flexor digitorum and flexor carpi ulnaris
|
|
|
|
See bone destruction and periosteal elevation, soft tissue swelling, indicates?
|
Osteomyelitis
|
|
|
|
See pathologic fractures in child, to rule out abuse, what finding should you look for?
|
Blue Sclera, indicates osteogenesis imperfecta, due to lack of collagen I, "brittle bone" disease
|
|
|
|
What is the lesion that can be caused by psuedomonas?
|
Ecthyma gangrenosum, seen in septic patients infected with pseudomonas
|
|
|
|
Does clavicle from via membranous or endochondral ossification?
|
clavicle is actually not a long bone, it's membranous like skull and other flat bones, facial bones
|
|
|
|
At what level does the vertebral artery enter the foramina ?
|
C6, compression can cause compromised perfusion to cerebellum, brainstem
|
|
|
|
What antibiotics could exacerbate Myasthenia gravis?
|
Aminoglycosides, gentamicin can act like curare - nicotinic acetylcholine receptor blocker.
|
|
|
|
What facial mm. is involved in opening the mouth?
|
Lateral pterygoid mm. ( not orbicularis oris- this muscle is for pursing the lips)
|
|
|
|
What is genetic cause of DMD?
|
X-linked recessive disorder, due to a FRAMESHIFT mutation in the dystrophin gene.
|
|
|
|
What does Type II collagen make?
|
Cartilage
|
|
|
|
Patient presents with crepitus in joints after having a severe infection. What toxin is most likely found?
|
Dx: Gas Gangrene( hear crepitus in joints-myonecrosis). Bug: Clostridium Perfringens. Makes alpha toxin, a lecithinase that causes massive hemolysis, increased vascular permeability and bleeding.
|
|
|
|
What type of bug is Clostridium perfringens?
|
Gram +, Anaerobic, spore forming rod, + Nagler's reaction for lecithinase, lyses the egg yolk agar.
|
|
|
|
What is histologic finding in RA?
|
LMP's and proliferative synovitis, Lymphocytes, macrophages, and plasma cells.
|
|
|
|
What are SE of TCA's? such as skeletal mm relaxant, cyclobenzaprine?
|
Anti-cholinergic, dry mouth, dry eyes, tachy, mydriasis
|
|
|
|
What are the SE of NSAIDS?
|
decreased Renal blood flow, gastric ulceration.
|
|
|
|
Where is the median nn. located?
|
In the carpal tunnel between the palmaris longus and the flexor carpi radialis
|
|
|
|
Did you know celecoxib, NSAID, has a sulfa component?
|
Well, now you do!
|
|
|
|
Pt. went on deer hunting trip, and developed arthritis. What else would be found on past medical history?
|
Bell's Palsy, Erythema migrans ( bull's eye lesion). Dx: Lyme disease by burgdorelea burgdorferi.
|
|
|
|
Desmin is a feature of?
|
Muscle cells, do desmin stain in rhabdomyosarcoma in head and neck tumors
|
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of bacterial monoarticular joint pain and arthritis?
|
Gonorrhea, he got it while sleeping with a prostitute. Septic arthritis is either gonococcal or non-gonoccal, in which case it'd be staph, but MCC is gonoccocal.
|
|
|
|
What causes increases in maximal velocity of muscle contraction?
|
Maximal velocity of muscle contraction is highest when ATPase activity is high, and when the force is low = 0. The greater the afterload, the slower the velocity of muscle contraction.
|
|
|
|
How can you measure active tension?
|
Active tension = Total tension- Passive tension
|
|
|
|
What are histologic findings in Rheumatoid Nodules ( subcutaneous) ?
|
Fibrionid necrosis $$ surrounded by PALISADING HISTIOCYTES $$
|
|

